- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
The Future of Metaverse & AI
The Future of Metaverse & AI

The Future of Metaverse & AI
Why in News?
In 2022, various innovative technologies have emerged, related to Metaverse and AI (Artificial Intelligence), which may raise concerns and present Opportunities.
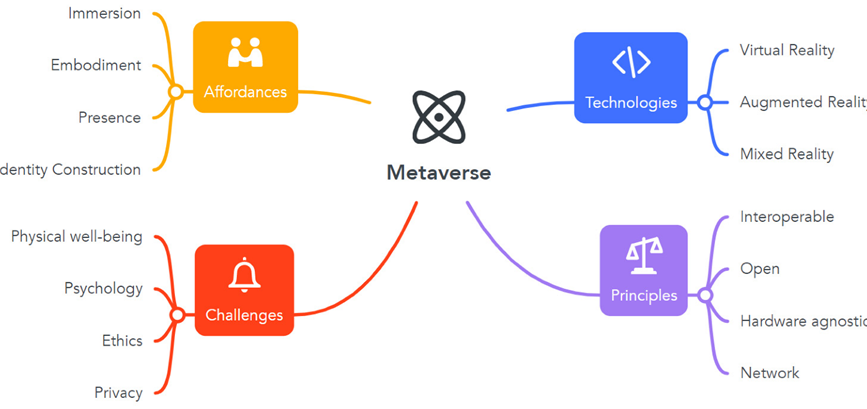
What is Metaverse?
- It is extension of real world into the digital realm.
- It gives a multi-user experience for anyone using it around the globe.
- Accessing this virtual world requires the Internet and digital devices.
- The technology behind this is called Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR).
- The growth of Digital India is accelerated by India’s large young population which is deeply acquainted with digital interactions and recreations.
What will be the Future Challenges and Opportunities of Meta-AI?
While the technical, demographic and policy foundations for the metaverse appear to be present in India, there remains the operational challenge of building the metaverse.
- In 2023, this intelligence will be seen coming into more products that we use every day, for example, Gmail that will not just auto-suggest but also write next mail to the boss.
- The big disruptor could be an affordable device that logs users into the Metaverse easily, maybe it will just be a smartphone. The challenge will be with the hardware that lets people access these virtual worlds without making people bankrupt in the real world.
- The ChatGPT can answer “follow-up questions”, and can also “admit its mistakes, challenge incorrect premises, and reject inappropriate requests.” but most such AI elements are now in standalone products, which is more play than work.
- Twitter and Facebook are struggling to remain relevant amid an increasingly digital native audience. Meta, for instance, knows that it will have to think beyond its present social media platforms as users move to the Metaverse. But that might not be something that will shift soon.
- The Internet spreads is becoming more localized and multilingual, in countries like India. Hence, the tech challenge in more ways than one, as there need to test out new technologies that can convert the content of the internet for these new users without much human intervention.
Significance of Metaverse:
- As hybrid workforces become the norm and with travel still not as easy as earlier, extended reality (XR) could become the answer to collaborate and communicate virtually.
[XR is umbrella term for all the new technologies, including augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR) plus those that are still to be created.]
- All immersive technologies extend the reality we experience by either blending the virtual and “real” worlds or by creating a fully immersive experience.
- A few more commercial versions of the Metaverse are expected to be accessible to regular users during the year.
What are the Ethical Concerns related to AI?
- Yet, the study in Nature also finds that AI can actively hamper 59 or 35% of SDG targets.
- AI requires massive computational capacity, which means more power-hungry data centres and a big carbon footprint.
- AI could multiply digital exclusion.
- Many desk jobs will be framed out by AI, such as accountants, financial traders and middle managers.
- Without clear policies on reskilling workers, the promise of new opportunities will in fact create serious new inequalities.
- Investment is likely to shift to countries where AI-related work is already established widening gaps among and within countries.
- AI also presents serious data privacy concerns.
- We shape the algorithms and it is our data AI operate on.
- In 2016, it took less than a day for Microsoft’s Twitter chatbot, “Tay”, to start emitting racist content, based on the material it encountered.
What are the Principles of a Responsible AI?
- Privacy and Security: Personal data of data subjects must be safe and secure, such that only authorised persons must access personal data for specified and necessary purposes, within a framework of sufficient safeguards to ensure this process.
- Safety and Reliability: AI systems must have built-in safeguards to ensure the safety of stakeholders.
- Equality: AI systems must ensure equality keeping in mind that similar people in similar circumstances are treated equally.
- Inclusivity and Non-Discrimination: AI systems must be developed to be inclusive of all stakeholders, and must not discriminate through bias between stakeholders on religion, race, caste, sex, descent, place of birth or residence in matters of education, etc.
- Principle of Transparency: The design and training of AI systems is key for its functioning. The system must be audited and be capable of external scrutiny to ensure transparency.
- Principle of Accountability: Since there are various actors in the process of developing, deploying and operationalizing an AI system, the accountability structures must be clearly set out in a publicly accessible and understandable manner.
- Protection and Reinforcement of Positive Human Values: It focuses on the possible harmful effects of AI systems through collection of personal data for profiling.