- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
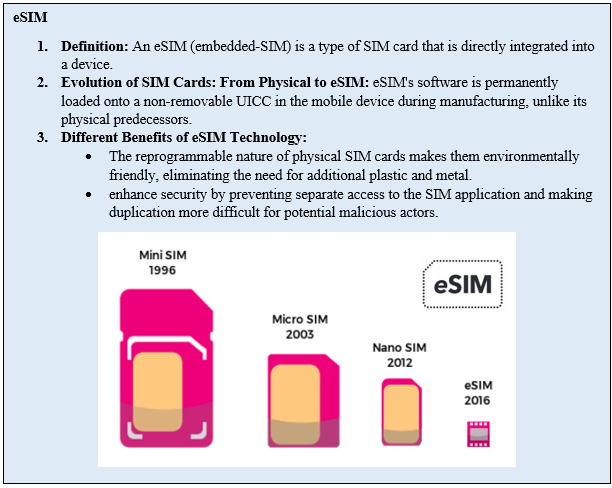
SIM Cards
SIM Cards
25-10-2023

Why in News?
In contemporary times, Smartphone usage has significantly outpaced other electronic devices, necessitating a proper description of Subscriber Identification Module (SIM) Cards, an essential component of smartphones.
About SIM Card
- Definition: A SIM card is a microchip that identifies subscribers on a cellular network, serving as an individual's ID card within the network's vast city.
- International mobile subscriber identity (IMSI): The ID card contains an IMSI, a unique number used to confirm the identity of the subscriber when others attempt to contact them on the network.
- Role in Network Access: A SIM card is required to connect a mobile phone to a GSM-based cellular network. The connection is secured using a unique authentication key (SAK), which functions as both a digital lock and key mechanism.
- SIM cards store SAK, which is inaccessible through phones. When a phone communicates with the network, it signs signals using this key, verifying connection legitimacy.
- Duplicating a SIM card is possible by accessing and copying the authentication key onto multiple cards.
- Information Storage:
- A SIM card is not only used for network access but also functions as a storage unit for various types of data. The device stores not only the IMSI but also the integrated circuit card identifier, the subscriber's location area identity, and a list of preferred roaming networks.
- SIM cards can store emergency contact numbers, contacts, and SMS messages, provided they have sufficient space.
- This compact chip is crucial for the functionality and security of mobile communication on GSM-based networks.
How Does a SIM Card Work?
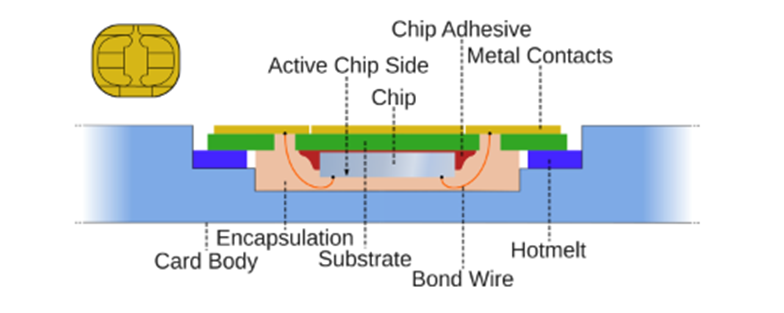
- Standard of SIM Card: SIM cards are compliant with the ISO/IEC 7816 international standard, which is managed by the International Organization for Standardization and the International Electrotechnical Commission.
- Pin Functions and Standards: The ISO/IEC 7816-2 standard defines the roles of pins on a SIM card, which are segmented into metal contacts for specific purposes.
- The SIM card has 15 pins, each indicating different functions.
- SIM Card's Network Role: The phone sends data through the network when a subscriber calls a recipient's number, authenticated by the SIM card key.
- The data is sent to a telephone exchange, where the recipient's identity is confirmed and a call is directed to them.
How have SIM cards changed?
- Evolution of Smart Cards: Smart cards, including SIM cards, have been in existence since the late 1960s, evolving significantly due to Moore's law-driven technological advancements.
- Moore's law states that the number of transistors in an integrated circuit (IC) doubles every two years, resulting in faster and cheaper computers over time.
- SIM Card Standards and Development: The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) played a crucial role in developing the GSM Technical Specification for SIM cards.
- The study analyzed various physical features such as operating temperature and contact pressure, as well as authentication and data access characteristics.
- Transition and Compatibility: The term 'SIM card' initially encompassed both hardware and software until 2G networks, but with the advent of the Universal Mobile Telecommunications System and 3G networks, it changed.
- The term 'SIM' was used to refer to the software, while the hardware was referred to as the Universal Integrated Circuit Card (UICC).