- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Revolutionising Drug Development: RoseTTAFold
Revolutionising Drug Development: RoseTTAFold
RoseTTAFold, an AI-based prediction tool, has marked a significant scientific advancement in computational drug development during the last four years.
What is RoseTTAFold ?
-
Developers: Researchers at the University of Washington, U.S.
-
Methodology: RoseTTAFold employs "generative diffusion-based architectures," a type of AI model, to predict structural complexes.
-
Data Processing: The tool's neural networks utilize extensive input data to generate the desired output 3-dimensional structures of proteins.
-
Deep Learning for Protein Structure Prediction: RoseTTAFold leverages deep learning to swiftly and accurately predict protein structures based on limited information. Traditionally, determining the structure of just one protein could take years of laboratory work.
-
Three-Track Neural Network: RoseTTAFold is a "three-track" neural network that concurrently analyzes patterns in protein sequences, interactions between amino acids, and possible 3-dimensional structures of proteins.
RoseTTAFold's capabilities extend beyond predicting static structures of proteins and protein-protein interactions. It can predict structures and interactions for any combination of proteins, DNA, and RNA.
What are Peptides?
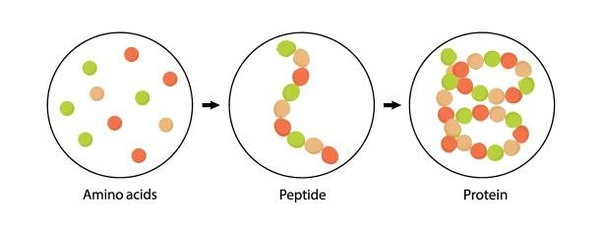
Peptides are short chains of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. They are essentially smaller versions of proteins, typically containing 2 to 50 amino acids.
Key points about peptides:
-
Natural occurrence: Peptides are found in all living organisms and play crucial roles in various biological functions.
-
Diverse functions: Peptides can act as hormones, neurotransmitters, and signalling molecules, influencing processes like growth, metabolism, and immune response.
-
Potential benefits: Peptide supplements are being studied for their potential benefits in areas such as anti-aging, muscle growth, and fat loss.
-
Sources: Peptides can be found in various foods like meat, fish, dairy, and legumes, as well as in some dietary supplements.
Peptides vs. Proteins
While both peptides and proteins are made up of amino acids, peptides are smaller and contain fewer amino acids compared to proteins. This smaller size allows peptides to be more easily absorbed by the body and penetrate tissues like the skin and intestines.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi



