- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
RBI's New Guidelines on Settlement of Dues by ARCs
RBI's New Guidelines on Settlement of Dues by ARCs

- On January 20, 2025, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) updated its rules for how Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) should handle the settlement of loans and debts.
- The new guidelines say that ARCs must first explore all possible ways to recover the debt before agreeing to settle.
- This change aims to make sure settlements happen only when they are the best option left for recovering money.
- The updated rules are part of the 'Master Direction – Reserve Bank of India (Asset Reconstruction Companies) Directions, 2024.'
Key Changes in the New Guidelines:
-
Board-Approved Policy for Settling Dues:
- ARCs are now required to create a policy, approved by their board, for how they will handle debt settlements. This policy should include:
- A cut-off date to decide which borrowers can qualify for a one-time settlement.
- How much discount can be given for different types of debts when calculating the settlement amount.
- The method used to calculate the value of any security (collateral) linked to the debt.
- ARCs are now required to create a policy, approved by their board, for how they will handle debt settlements. This policy should include:
-
Settlement Only After Trying Other Recovery Methods:
- The key change is that settlements should only happen after ARCs have explored all other ways of recovering the money from the borrower.
- Settlement should only be considered if all other options have failed and it is seen as the best possible option.
-
Net Present Value (NPV) of the Settlement:
- The NPV of the settlement (Value of future payments in today’s money) should be at least equal to the value that can be recovered from the collateral.
- This ensures that the settlement amount is fair and doesn’t fall below what the assets are worth.
-
Lump-Sum Payment Preferred:
- The settlement amount should ideally be paid in one lump sum.
- If that’s not possible, the borrower must submit a business plan and explain how they will earn money and manage cash flows in the future to support paying the debt in installments.
-
Special Procedure for Large Borrowers (Over ₹1 Crore):
- For borrowers who owe more than ₹1 crore, the settlement plan must be reviewed by an Independent Advisory Committee (IAC).
- The final decision will be made by the Board of Directors, including at least two independent directors.
-
Procedure for Smaller Borrowers (₹1 Crore or Below):
- For borrowers with debts below ₹1 crore, the ARC must ensure that no one who was involved in acquiring the debt is part of the team approving the settlement.
- Additionally, a quarterly report on the settlement progress must be submitted to the board.
-
Fraud and Wilful Defaulters:
- For borrowers who are labeled as frauds or wilful defaulters, the same rules apply as for those with debts above ₹1 crore, regardless of the amount owed.
- This ensures that fraud cases are not treated more leniently.
What Are Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs)?
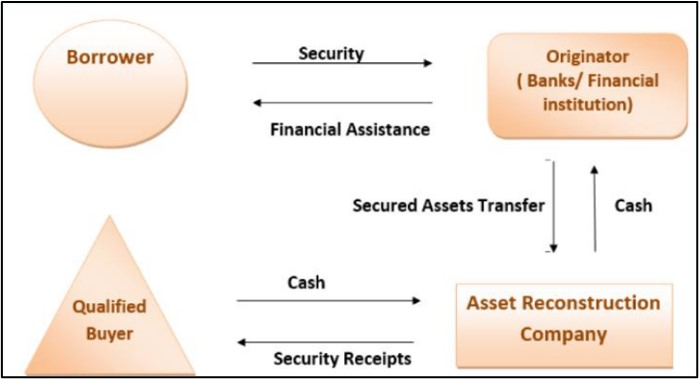
ARCs are special financial companies that buy bad loans (or Non-Performing Assets, NPAs) from banks and other lenders. These are loans that borrowers have stopped paying, and ARCs help banks clean up their balance sheets by taking over these debts.
What are Non-Performing Assets (NPA) ?A loan is Known as a Non-Performing Asset (NPA) when the borrower has failed to make payments for 90 days or more. For agricultural loans, it's classified as an NPA if payments are overdue for two cropping seasons. Categories of NPAs:
|
- Role of ARCs: When a bank has bad loans that it can’t recover, it sells these loans to ARCs at a discounted price. The ARC then tries to recover the loans or sell the assets linked to them.
- Regulation: ARCs are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India and follow the rules set out in the Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Securities Interest Act, 2002 (SARFAESI Act).
Key Terms in the Context of ARCs
- Asset Reconstruction: The process of buying a loan or asset from a bank to recover or realize the value of the debt.
- Securitisation: The process of turning loans or debts into securities (investments) and selling them to qualified buyers.
- Qualified Buyers: These are financial institutions, banks, insurance companies, and other companies that are allowed to buy debts from ARCs to help raise funds.
Benefits of ARCs
- Improved bank health: ARCs help banks reduce their NPA burden, freeing up capital and improving their financial health.
- Enhanced credit flow: Clean balance sheets allow banks to lend more freely.
- Specialized expertise: ARCs have expertise in resolving complex NPAs, leading to better recovery outcomes.
- Market development: ARCs contribute to the development of a market for distressed assets.
- A distressed asset is an asset that is sold at less than its value because the owner or business needs immediate cash.
What is Securitization and how is it different from Asset Reconstruction ?
- Securitization is the process of pooling together liquid financial assets (such as debt) and converting them into marketable securities (backed by those assets). These securities are then sold to investors.
Key Differences
|
Feature |
Asset Reconstruction |
Securitization |
|
Focus |
Managing and resolving bad loans (NPAs) |
Creating liquid, tradable assets from illiquid loans. Illiquid is the state of a security or other asset that cannot quickly and easily be sold |
|
Players |
Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) |
Banks, Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) |
|
Goal |
Maximizing recovery of debt from defaulted borrowers |
Raising funds for banks, improving liquidity |
|
Methods |
Debt restructuring, asset sale, legal action |
Pooling assets, issuing securities backed by those assets |
|
Risk Transfer |
ARC takes on the risk of the NPA |
Investors who buy the securities bear the risk |
Conclusion
The RBI's new guidelines aim to make the settlement process between ARCs and borrowers more fair and thorough. By requiring ARCs to first explore all ways of recovering the debt, and ensuring that settlements are made only after careful consideration, these rules provide a better framework for managing bad loans.
|
Also Read |
|
Public Administration Optional |
UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
UPSC Monthly Mgazine |
Question Answer Practice For UPSC |
Free MCQs for UPSC Prelims |
UPSC Test Series |
ENSURE IAS NOTES |
Our Booklist |




