- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Quantum Computing and National Security
Quantum Computing and National Security

- In an era marked by rapid technological transformations, quantum computing stands at the forefront of innovations that could fundamentally alter national security landscapes.
- Recognizing this, NITI Aayog’s Frontier Tech Hub (NITI-FTH), in collaboration with the Data Security Council of India, has released a strategic paper titled "Quantum Computing: National Security Implications & Strategic Preparedness".
- The document underlines the urgent need for India to adapt, invest, and prepare for a quantum future where security, intelligence, and power dynamics will be increasingly shaped by advancements in quantum technology.
What is Quantum Technology
- Quantum technology, is an advanced field, draws its power from principles of quantum mechanics—a field of physics that governs the behavior of subatomic particles.
- Unlike classical computing that processes bits as 0s or 1s, quantum computing uses qubits which can exist in multiple states simultaneously, thanks to phenomena such as:
- Superposition – A particle can exist in several states at once until measured.
- Quantum Entanglement – Two particles, once linked, can influence each other’s behavior regardless of distance.
- Interference – Quantum states can amplify or cancel each other out, affecting the final outcome of computations.
These properties enable quantum computers to solve problems at a speed and scale far beyond the reach of today’s most powerful supercomputers.
How Quantum computing is reshaping the National Security Paradigm?
NITI Aayog’s paper highlights five strategic domains where quantum computing is poised to reshape national security priorities:
1. Cryptography and Cybersecurity: One of the most immediate threats of quantum computing lies in its ability to break traditional encryption algorithms—especially those based on RSA and ECC, which secure banking systems, military communications, and classified data.
- Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) is emerging as a safeguard—these are cryptographic methods designed to resist quantum attacks.
- Example: The USA's National Quantum Initiative Act (2018) emphasizes the urgency of adopting PQC to counter future cyber threats.
- India’s Concern: A transition plan to PQC is crucial, especially in critical sectors like finance, defense, and infrastructure.
2. Enhanced Intelligence Gathering: Quantum computing’s superior processing power enables rapid analysis of vast, complex datasets, making it ideal for deciphering encrypted communication, identifying security threats, and predicting enemy movements.
- Example: NATO's 2024 strategy includes quantum-ready defense applications like sensing, imaging, and secure communications through quantum cryptography.
3. Secure Communications through Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)
QKD uses the principles of quantum mechanics to generate and distribute encryption keys that are secure against any kind of interception or tampering.
- Example: China’s 2,000 km long QKD network between Beijing and Shanghai is a global benchmark in secure quantum communication.
4. Military Hardware and Quantum-enabled Warfare: Quantum technology will revolutionize military capabilities—from materials science breakthroughs to quantum-enhanced AI systems for autonomous drones, missile guidance, and surveillance systems.
- Example: Quantum-powered AI systems are being developed to enable autonomous decision-making in complex battlefield environments.
5. Economic and Geopolitical Warfare: Quantum threats are not just physical—they could destabilize financial systems by breaking encryption used in digital transactions, potentially triggering large-scale economic disruptions.
- Example: The U.S. National Quantum Initiative also views quantum innovation as vital for economic security.
Moreover, nations that secure early quantum breakthroughs will possess a technological edge difficult for others to match. This could lead to a new geopolitical order driven by quantum supremacy.
- Example: China's Micius Satellite (2016) demonstrated the world’s first quantum-encrypted satellite communication, highlighting its global leadership in the domain.
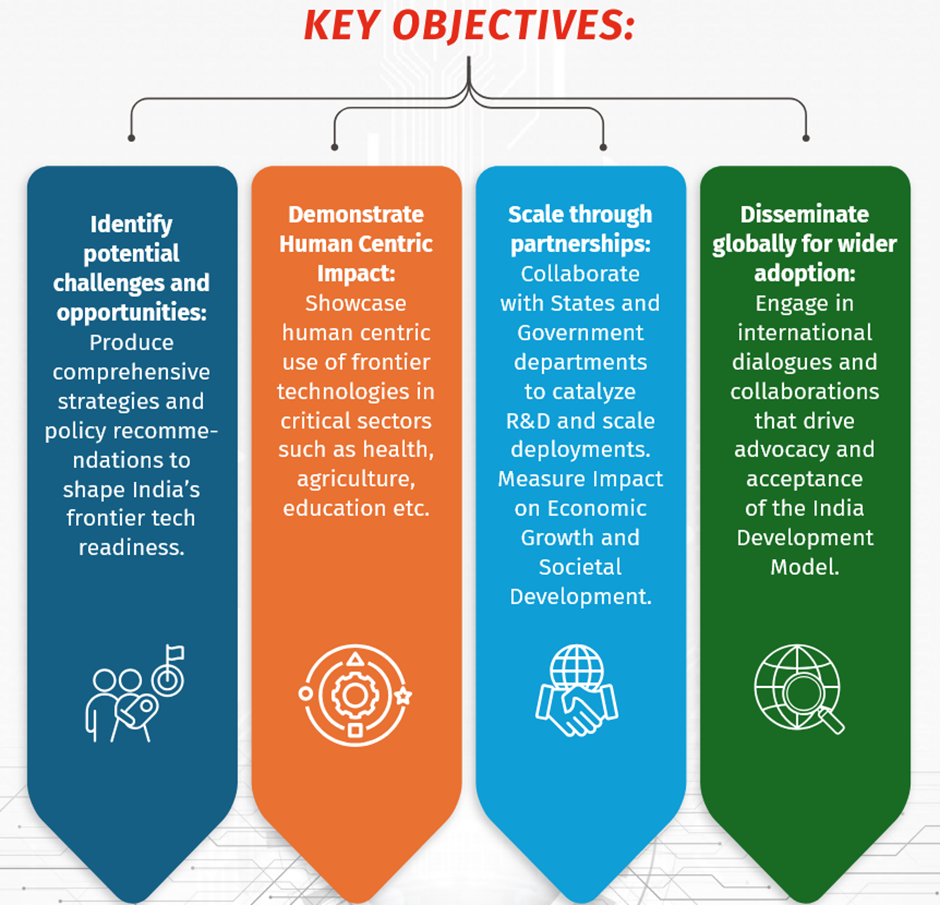
NITI-FTH Key Objectives
Strategic Recommendations for Quantum Preparedness
NITI-FTH outlines a comprehensive roadmap for India’s transition into a Frontier Tech Nation, with a special focus on quantum readiness:
1. Continuous Monitoring: Establish a dedicated national quantum task force to track global advancements and adversarial capabilities.
2. Cryptographic Intelligence and PQC Transition
- Conduct regular audits to identify vulnerabilities.
- Adopt a risk-prioritized PQC roadmap with POCs, certifications, and cross-sectoral information sharing.
- Example: Google Chrome's trial run of post-quantum algorithms like Kyber in real-world browser environments.
3. Strengthen the Quantum Workforce
- Introduce Quantum Information Science (QIS) in higher education.
- Provide re-skilling and training for existing talent.
- Reform immigration policies to attract global quantum expertise.
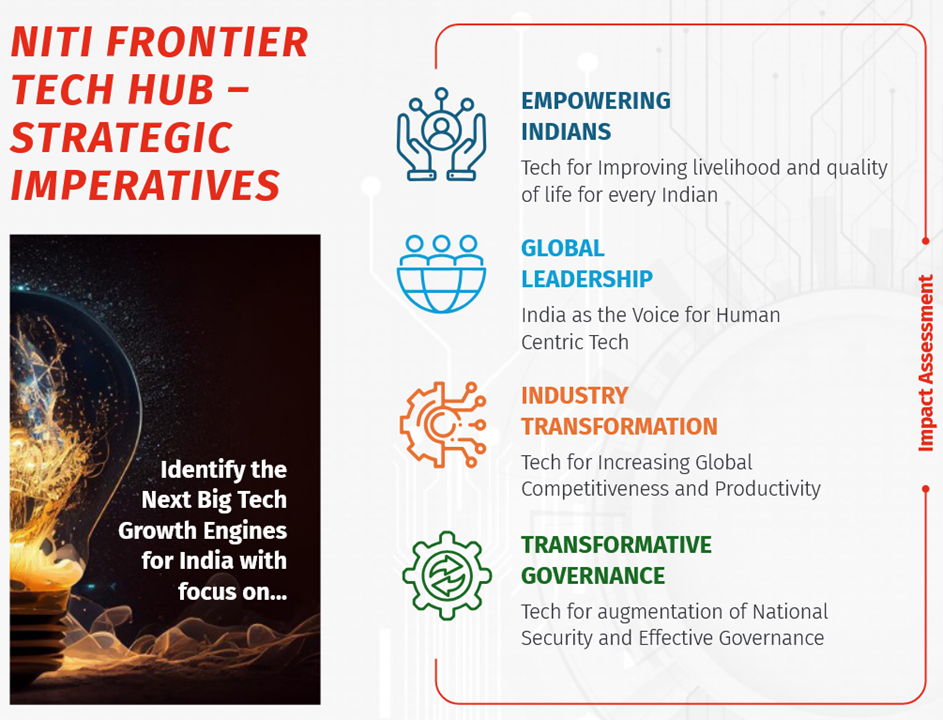
NITI-FTH: Operating Principles: Trust, Collaboration, Responsibility and Inclusivity
4. Build a Robust Quantum Ecosystem: Take inspiration from global models:
-
- Quantum Economic Development Consortium (QED-C) – USA
- Quantum Strategic Industry Alliance for Revolution – Japan
5. Foster International Collaboration
- Collaborate with like-minded nations on quantum tech development.
- Example: India-EU signed an Intent of Cooperation on HPC, Quantum Technologies, and Climate Modeling in 2022.
6. Other Strategic Measures
- Set up an Early Warning System for scientific breakthroughs.
- Implement a Crypto Agility Framework to quickly switch to quantum-safe algorithms.
- Ensure flexible R&D funding responsive to quantum progress.
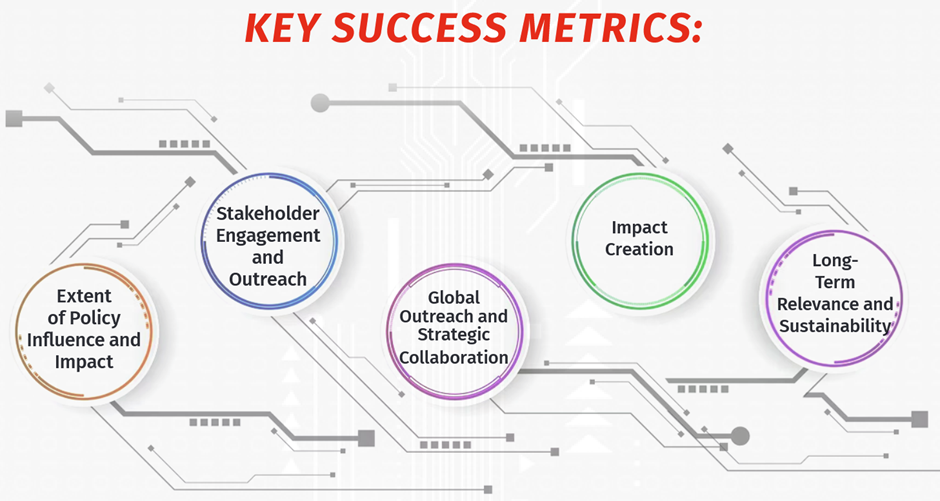
NITI-FTH Key Success Metrics
|
Key Challenges in Harnessing Quantum for National Security Despite the momentum, several formidable challenges must be overcome:
This strategic gap puts India at a disadvantage in the global quantum race.
Example: IBM’s 433-qubit Osprey processor faces limitations in scalability and error rates.
|
Steps Taken by India to Strengthen Quantum Capabilities
India has recognized the transformative and strategic potential of quantum technologies and has begun laying the foundation for long-term development.
- National Quantum Mission (2023): Launched to seed, nurture, and scale up R&D and build a vibrant ecosystem in Quantum Technologies (QT). It aims to position India as a global quantum hub by 2030.
- Quantum-Enabled Science and Technology (QuEST) Program (2018): An initiative by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) to support national quantum labs and provide infrastructure for sustained R&D.
- Academic and Research Hubs
- IISc Bangalore: Hosts a center focused on quantum algorithms and error correction.
- IIT Madras: Established the Centre for Quantum Information, Communication and Computing (CQuICC).
- National Mission for Quantum Frontier: Trains students and researchers with essential quantum skills.
- Private Sector and Startups: QNu Labs: Selected under the NQM, it's developing the world's first end-to-end quantum-safe heterogeneous network.
- C-DOT Delhi: Developed an indigenous QKD solution and operates a Quantum Communication Lab.
Conclusion: Quantum as the Key to Strategic Resilience
Quantum computing is not just another technological innovation—it is a force multiplier in defense, intelligence, economic security, and global diplomacy. As India sets its vision for Viksit Bharat @2047, quantum readiness will be a cornerstone of its strategic resilience and technological sovereignty.
|
Microsoft’s Majorana 1: Its 1st Quantum Computing Chip
Refer Current Affairs Total (CAT) Magazine February 2025, Page 88-90 for Comprehensive Coverage of Microsoft’s Majorana 1. |
|
Also Read |
|
UPSC Foundation Course |
|
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | CSAT Foundation Course |




