- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
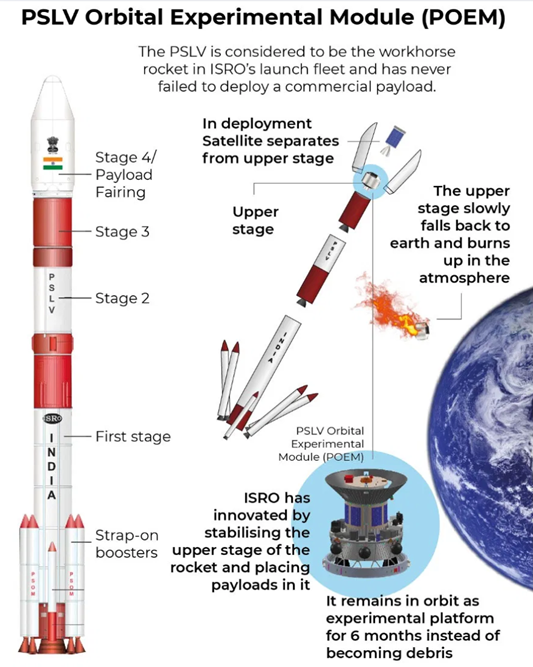
PSLV Orbital Experimental Module (POEM-4) Atmospheric Re-entry by ISRO
PSLV Orbital Experimental Module (POEM-4) Atmospheric Re-entry by ISRO
09-04-2025
- On April 4, 2025, PSLV Orbital Experimental Module (POEM-4) aboard the PSLV-C60 mission successfully re-entered Earth's atmosphere and fell into the Indian Ocean.
- This marked the completion of its mission, which had successfully tested critical space technologies and conducted valuable experiments.
Key Details :
- Mission Name: SpaDeX (Space Docking Experiment)
- Launch Date: it was launched on December 30, 2024, using the PSLV-C60 rocket from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota.
- Orbit: The satellites were positioned in a 475 km circular orbit around Earth.
- On January 16, 2025, ISRO concluded its SpaDeX mission, a historic achievement that made India the 4th country globally to perform space docking.
- United States (1966): NASA’s Gemini VIII became the 1st to dock with the Agena target vehicle.
- Soviet Union (1967): The USSR achieved the 1st automated docking with the Kosmos 186 and Kosmos 188 spacecraft.
- China (2011): China conducted its 1st uncrewed docking with the Shenzhou 8 spacecraft and Tiangong 1 space laboratory.
What is Space Docking?
- Space docking refers to the process by which two spacecraft physically connect in orbit, allowing them to cooperate in space. It is essential for:
- Space stations: For assembling large space structures, like modules that form a space station.
- Interplanetary missions: For transporting equipment, fuel, and crew for extended missions beyond Earth.
- Satellite servicing: For refueling, repairing, or upgrading satellites already in orbit.
- Satellites Involved:
- SDX01 (Chaser Satellite): This satellite actively moved towards the target satellite during the docking process.
- SDX02 (Target Satellite): A stationary satellite, which allowed the chaser satellite to dock with it.
- Both satellites weighed 220 kg.
- Docking Distance: The satellites were brought within 3 meters of each other before the docking procedure began.
Why Space Docking is Essential for India’s Future Missions:
- Space docking will play a crucial role in ISRO's upcoming projects, such as:
- Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS): India’s first space station, requiring docking technology to assemble multiple orbital modules. The 1st module is scheduled for launch in 2028.
- Chandrayaan-4 Mission: India’s planned lunar mission that will require docking between 2 modules—one for sample transfer and the other for re-entry.
- Heavy Payload Missions: Docking technology will be critical for transporting large payloads that cannot be launched in a single mission.
- Interplanetary missions will also require multiple spacecraft to dock in orbit to combine resources for extended operations.
Innovative Technologies Tested in SpaDeX:
The SpaDeX mission tested various advanced technologies, including:
- POEM-4's Payloads :14 contributed by various ISRO centres and 10 by academia and private industry. Some key payloads include:
- Relocatable Robotic Manipulator (Walking Robotic Arm): Developed by ISRO’s Inertial Systems Unit, this arm demonstrated an inchworm-like technique for reaching targets.
- Debris Capture Robotic Manipulator: Designed to capture tethered space debris.
- Compact Research Module for Orbital Plant Studies: Investigated the growth of cowpea seeds in space.
- Amity Plant Experimental Module (APEMS): Analyzed how spinach plant cells react to microgravity compared to Earth gravity.
- RVSat-1 Payload: Studied the growth of gut bacteria to understand astronaut health.
- BGS Amateur Radio Payload for Information Transmission: Used VHF frequency modulation to transmit audio, text, and images.
- RUDRA 1.0 HPGP: Tested a green propulsion system with 1 newton of thrust.
- VYOM 2U: Developed a safer monopropellant as an alternative to hydrazine.
Conclusion: The successful re-entry of POEM-4 marks a monumental achievement in India’s space exploration journey. It demonstrates India’s growing technological prowess and strategic vision for future space missions. The lessons learned and technologies tested will help India advance its ambitions in human space exploration, lunar missions, and space station construction.



