- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- NCERT Medieval History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PSLV-C61 Mission and the EOS-09 Satellite
PSLV-C61 Mission and the EOS-09 Satellite
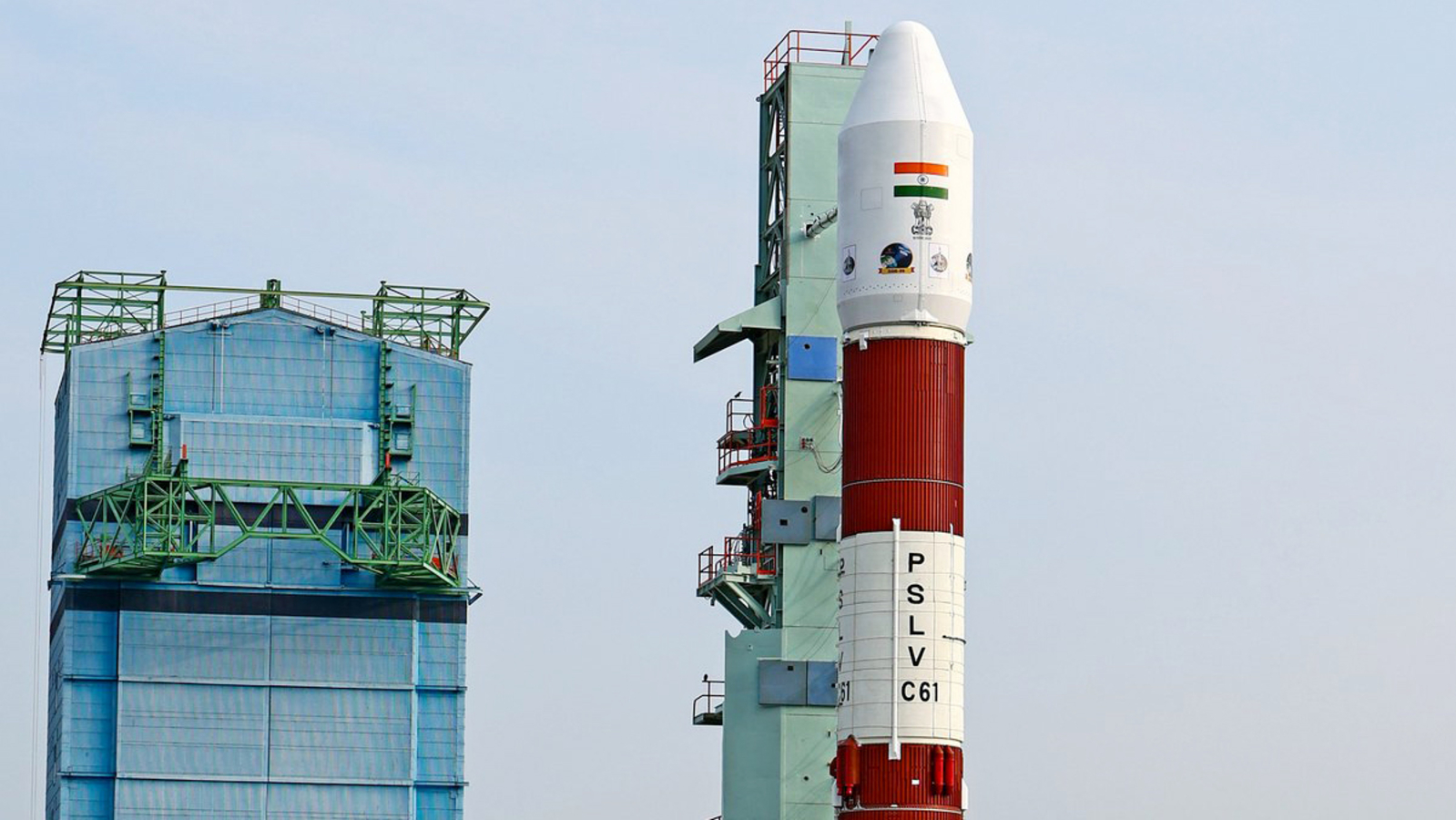

- ISRO launched the PSLV-C61 mission on May 18, 2025, aiming to place the EOS-09 satellite into a Sun-Synchronous Polar Orbit.
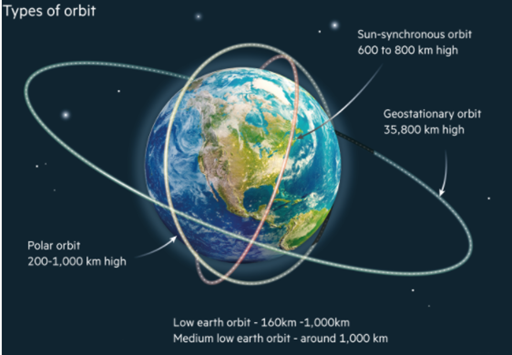
- A Sun-Synchronous Polar Orbit (SSO) is a specific type of polar orbit where a satellite maintains a consistent relationship with the Sun.
- This means the satellite always passes over a given point on Earth's surface at the same local time. SSOs are also known as helio-synchronous orbits.
- The mission failed due to a malfunction in the 3rd stage of the rocket.
- ISRO Chairman V. Narayanan confirmed that the failure was caused by a sudden drop in chamber pressure in the 3rd -stage solid motor casing.
What is PSLV?
- PSLV stands for Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle.
- It is an indigenously developed four-stage expendable rocket system by ISRO.
- The PSLV is referred to as the "Workhorse of ISRO" due to its high success rate and operational reliability.
Legacy of PSLV
- The PSLV achieved its first successful launch in October 1994.
- It is known for launching multiple satellites in a single mission, often serving both domestic and foreign clients.
- It Launches remote sensing, meteorological, navigation, communication, and scientific research satellites.
- Notable missions:
- Chandrayaan-1 (Moon, 2008)
- Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan) (2013)
- Aditya-L1 (Sun, 2023)
- Astrosat (India’s first space observatory)
Key Technical Specifications of PSLV-XL
|
Feature |
Details |
|
Stages |
4 (Solid-Liquid-Solid-Liquid) |
|
Lift-off Mass (XL variant) |
Up to 320 tonnes |
|
Payload to SSPO (600 km) |
~1,750 kg |
|
Payload to Sub-GTO |
~1,425 kg |
|
Total Height |
~44 meters |
|
Launch Site |
Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota |
Stage-wise Description of PSLV
- Stage 1 (PS1) uses solid HTPB propellant and provides the initial thrust. It includes 6 strap-on boosters in the XL configuration.
- Stage 2 (PS2) uses a liquid Vikas engine, powered by UDMH and N2O4, and operates after atmospheric exit.
- Stage 3 (PS3) is a solid propellant stage using HTPB, designed to provide high thrust. This was the stage that failed in the C61 mission.
- Stage 4 (PS4) is a liquid stage powered by two engines using MMH and MON. It is restartable and responsible for final satellite insertion.
What is EOS-09 Satellite
- The EOS-09 is an Earth Observation Satellite designed for high-resolution remote sensing.
- It supports various civilian applications including agriculture, water resource monitoring, urban planning, and disaster response.
- It was intended to be deployed in a 600 km Sun-Synchronous Polar Orbit to ensure consistent lighting conditions.
PSLV Variants and Configurations
|
Variant |
Description |
Strap-on Boosters |
Payload to SSPO |
|
PSLV-CA (Core Alone) |
No strap-ons; used for lighter payloads |
None |
~1,019 kg |
|
PSLV-G |
Standard with 6 boosters |
6 |
~1,600+ kg |
|
PSLV-XL |
Extended; high capacity |
6 (XL type) |
~1,750 kg |
|
PSLV-DL |
Dual booster config |
2 |
~1,200–1,300 kg |
|
PSLV-QL |
Quick launch, 4 boosters |
4 |
~1,523 kg |
Comparison: PSLV (Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle) and GSLV (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle)
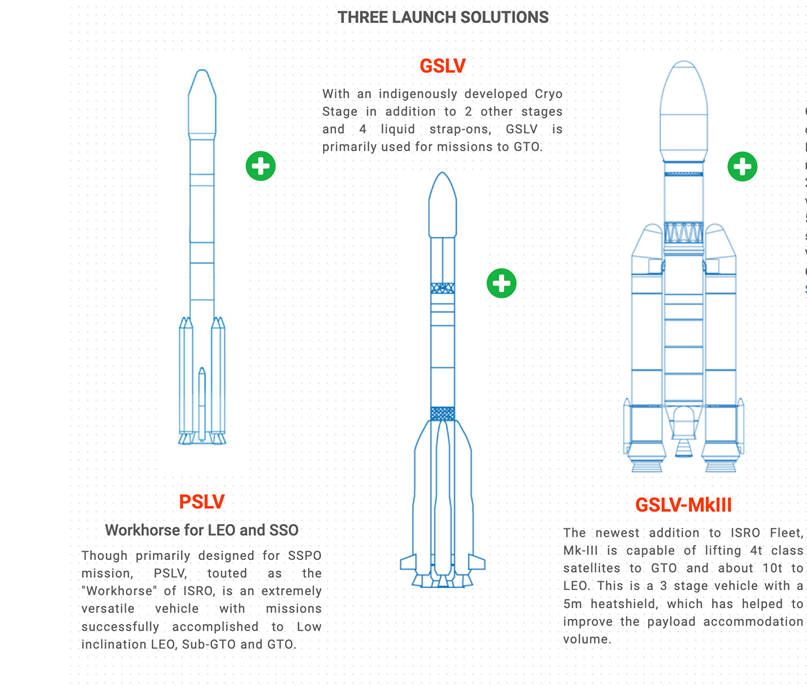
- The PSLV and GSLV are both used by India to launch satellites, but they have different capabilities and purposes.
- PSLV is primarily used for launching Earth observation and remote sensing satellites into lower orbits, while GSLV is designed for launching heavy communication satellites into Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO).
- GSLV also utilizes a cryogenic stage, which PSLV does not, for more powerful launches.
|
Feature |
PSLV |
GSLV |
|
Number of Stages |
4 |
3 |
|
Propulsion Type |
Solid and Liquid |
Liquid and Cryogenic |
|
Lift-off Mass |
Approximately 320 tonnes |
Approximately 420 tonnes |
|
Primary Orbit Type |
SSPO and Low Earth Orbit |
GTO and High Earth Orbit |
|
Maximum Payload |
~1.75 tonnes (SSPO) |
~2.25 tonnes (GTO) |
|
Key Missions |
Earth Observation and Scientific |
Communication and Heavy Payloads |
|
Notable Variants |
CA, G, XL, DL, QL |
Mk I, Mk II, Mk III |
Implications of PSLV-C61 Failure
- The PSLV-C61 failure is a rare setback in PSLV’s largely successful record.
- It highlights the technical complexity of multi-stage launches, especially with solid propulsion systems.
- ISRO’s quick diagnosis and public communication indicate transparency and institutional resilience.
- The relaunch of EOS-09 will be crucial for maintaining confidence in the PSLV’s reliability.
Strategic Importance of PSLV
- The PSLV has played a critical role in India’s space diplomacy, launching satellites for over 30 countries.
- It has enabled India to become a low-cost, reliable launch partner in the global space market.
- Despite occasional failures, the PSLV continues to be central to ISRO’s scientific and strategic missions.
Conclusion
The PSLV remains a cornerstone of India’s space program, known for its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and proven performance. The PSLV-C61 failure underscores the importance of continuous innovation and rigorous quality control. ISRO’s response demonstrates its maturity as a scientific organization, and the upcoming reattempt of EOS-09 will be an opportunity to reaffirm PSLV's legacy.




