- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Prime Minister Narendra Modi's Visit to Guyana and 2nd India-CARICOM Summit
Prime Minister Narendra Modi's Visit to Guyana and 2nd India-CARICOM Summit
22-11-2024
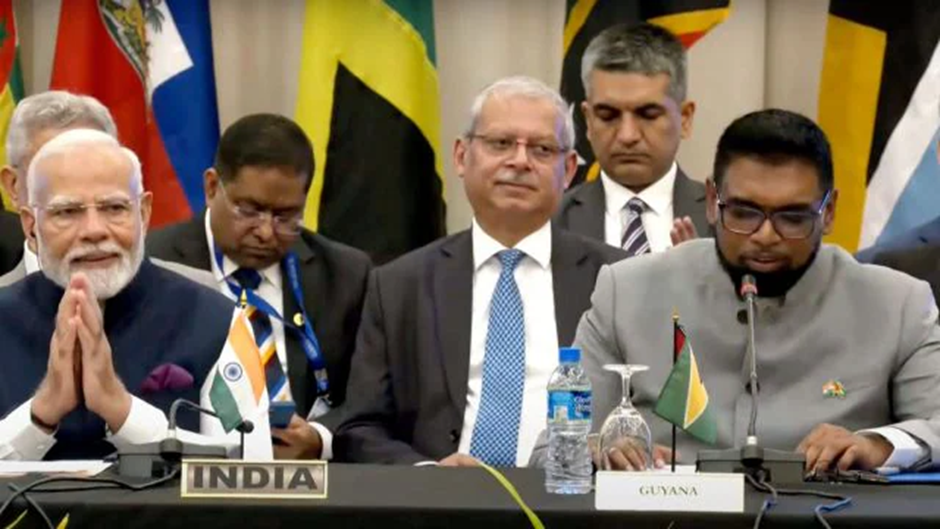

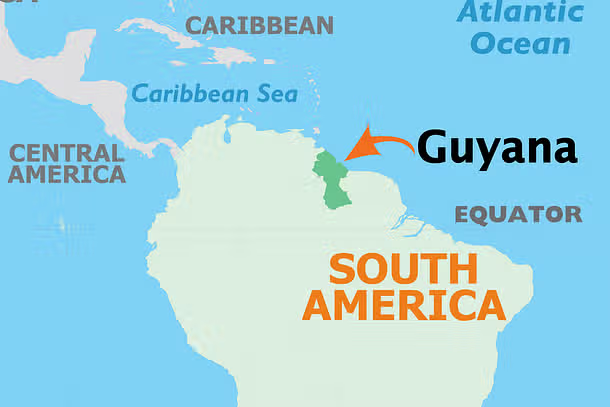
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi visited Guyana on November 20, 2024, becoming the first Indian Prime Minister to visit the country in 56 years. The last Indian PM to visit Guyana was Indira Gandhi in 1968.
- Bilateral Talks and Agreements: PM Modi held discussions with President Mohamed Irfaan Ali of Guyana. As a result, 10 agreements were signed between the 2 countries, focusing on various sectors:
- Energy Security: PM Modi emphasized that Guyana will play an important role in India's energy security. A blueprint for long-term energy cooperation will be developed between the 2 nations.
- Digital Payments: One key agreement is the deployment of India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI) in Guyana, which will facilitate digital financial transactions between the two countries.
- Defense Cooperation: India will continue to support Guyana’s military through training, scholarships, and equipment. As part of this, India has already supplied two Dornier aircraft to Guyana this year.
- Agriculture and Food Security: India provided millet seeds to Guyana in 2023, contributing to improving the country’s food security. Additionally, India agreed to further expand cooperation in the agricultural sector.
- Healthcare: India will establish a Jan Ausadhi Kendra in Guyana to provide affordable medicines.
Guyana, Dominica confer top awards on PM Modi:
-
Guyana:
- Award: The Order of Excellence
- Conferred by: President Irfaan Ali
- Reason: Recognition for contributions during the COVID-19 pandemic, global service, and strengthening bilateral ties.
- PM Modi is the 4th foreign leader to receive The Order of Excellence from Guyana.
- The award honors his exceptional statesmanship and efforts in deepening India-Guyana ties.
-
Dominica:
- Award: Dominica Award of Honour
- Conferred by: President Sylvanie Burton
- Reason: Recognized for India’s support during the COVID-19 crisis (e.g., supplying 70,000 AstraZeneca vaccines).
Future Recognition:
-
Barbados:
- Announced plans to confer its top national award on PM Modi, bringing his total number of international honours to 19.
Guyana-India Bilateral Relations:Establishment of Diplomatic Missions
Cultural Diplomacy
Infrastructure SupportIndia has provided support for several key infrastructure projects in Guyana, including:
Geographical Context of Guyana:
|
India-CARICOM Summit in Guyana
- On November 20, 2024, PM Modi attended the 2nd India-CARICOM Summit in Guyana, where he joined leaders from the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) to discuss areas of mutual interest. This summit was aimed at strengthening ties between India and the Caribbean region.
7 Pillars of India-CARICOM Relations (Acronym: C-A-R-I-C-O-M):
C - Capacity Building
- IT Scholarships: India announced 1,000 information technology scholarships for CARICOM nations.
- Proposed expanding the technology centre India is establishing in Belize to benefit all CARICOM members.
A - Agriculture and Food Security
- Agricultural Technology: India can share advancements in agricultural technology, including the use of drones.
- Promotion of Millet Cultivation: India aims to enhance nutrition in CARICOM countries by promoting the cultivation of millet.
R - Renewable Energy and Climate Change
- International Solar Alliance: Invited CARICOM nations to join the initiative for solar energy development.
- Other Initiatives: Encouraged participation in the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure, Mission Life for Sustainable Lifestyles, and the Global Biofuel Alliance to combat climate change.
- Renewable Energy: Reaffirmation of the previous agreements on renewable energy cooperation and the USD 150 million credit line provided by India to CARICOM countries.
I - Innovation and Technology
- Technological Advancements: India can extend its innovative solutions, including the "Stack" infrastructure and Universal Payment Interface (UPI) for digital payments, to CARICOM nations.
C - Cricket and Culture
- Women's Empowerment through Cricket: Proposed offering 11 scholarships to each CARICOM country for women’s cricket coaching as a tool for empowerment.
O - Ocean Economy
- Marine Resources: India can assist CARICOM nations in developing untapped marine resources, enhancing regional connectivity, and supporting maritime security initiatives.
M - Medicine and Healthcare
- Affordable Healthcare: India offers affordable healthcare solutions through its Janaushadi scheme, which provides low-cost medicines to CARICOM countries.
- India’s contribution during the COVID-19 pandemic was highlighted, including the delivery of vaccines to CARICOM countries. India will continue to assist CARICOM nations in the pharmaceutical sector.
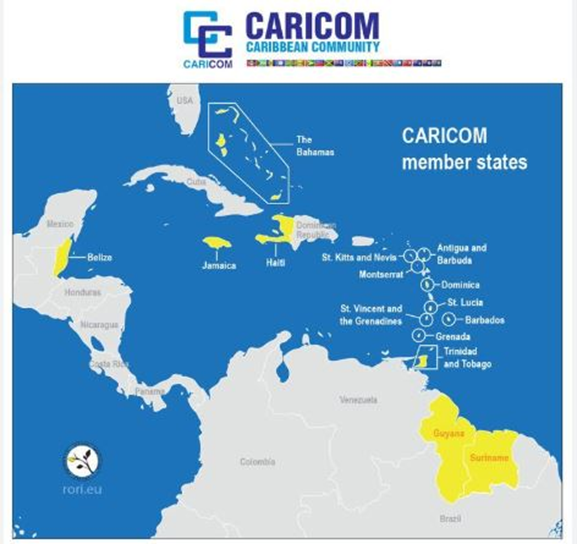
What is CARICOM?
Objectives of CARICOM:CARICOM's objectives are rooted in four main pillars:
CARICOM's Historical Background:
CARICOM Summits and India-CARICOM Relations:
Why is CARICOM Important to India’s Global South Strategy?1. Enhancing Ties with Developing Nations:
2. Additional Global Platform for India:
3. Shared Concerns on Climate Change:
Global South and India’s Role
|