- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM)
Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM)
04-07-2024
South Korea has recently reported the first case of Naegleria fowleri, a rare and deadly brain-eating amoeba.
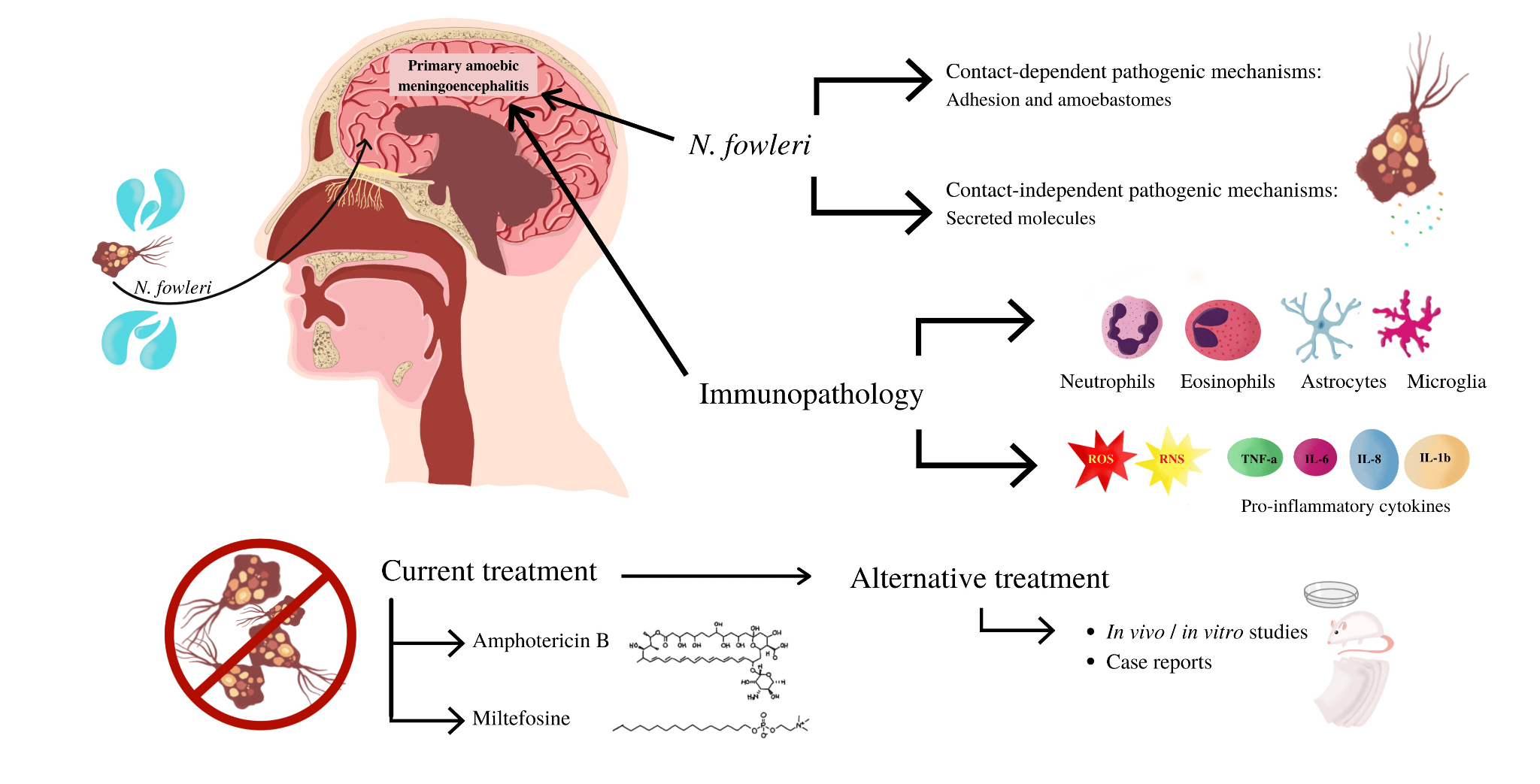
What are Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM):
- What is PAM?
- A rare and typically fatal infection of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord).
- Cause:
- Caused by Naegleria fowleri, a free-living amoeba found in shallow surface waters, improperly maintained swimming pools, hot tubs, and spas, especially in warm climates.
- The amoeba enters the brain through the nose when individuals swim in contaminated warm, fresh water.
- Symptoms:
- Symptoms appear within five days of infection and progress rapidly.
- Early symptoms include fever, headache, vomiting, and sensitivity to light.
- Later stages may involve a stiff neck, seizures, hallucinations, and even coma.
- Treatment:
- No standard treatments exist for PAM.
- Combination therapy using anti-parasitic medications offers the most promise.
- Distinction from Granulomatous Amebic Encephalitis:
- PAM differs from granulomatous amebic encephalitis, another rare and usually fatal infection of the central nervous system caused by different free-living amoebas, such as Acanthamoeba species or Balamuthia mandrillaris.
Amoeba: A General Term
- Amoeba refers to single-celled organisms belonging to the biological kingdom Protista.
- Amoebas are eukaryotic microorganisms characterized by shape-shifting abilities and movement using pseudopods.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi