- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- NCERT Medieval History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PRIMARY AGRICULTURAL CREDIT SOCIETIES (PACS)
PRIMARY AGRICULTURAL CREDIT SOCIETIES (PACS)

Latest Context
The Government has made five new measures to improve the revenue of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS), as well as expand the job prospects in rural regions, in order to realise the Prime Minister's vision of "Sahkar Se Samridhi".
- The government's "Sahkar Se Samriddhi" motto aspires to bring about national prosperity as a whole. Transparency, modernisation, and increased competition were advocated as ways to enhance cooperatives.
New Five Decisions
- On the basis of viability, PACS that are not currently acting as sellers of fertiliser will be identified and gradually encouraged to do so.
- PACS that do not already operate as Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samridhi Kendras (PMKSK) would be included in PMKSK's purview.
- In 2022, the Minister of Chemicals & Fertilisers officially opened 600 PMKSK.
- The PMKSK will provide agri-inputs, soil, seed, and fertiliser testing facilities to meet the diverse demands of the farmers.
- The selling of organic fertilisers, particularly fermented organic manure (FoM), liquid fermented organic manure (LFOM), and phosphate-enriched organic manure (PROM), will be associated with PACS.
- In this supply and marketing chain for bio-organic fertilisers, fertiliser corporations will function as an aggregator for small bio-organic producers to market the finished product under the Market Development Assistance (MDA) plan of the Department of Fertilisers. PACS will be counted among the wholesalers and retailers.
- PACS may also be used by drone business owners to spray pesticides and fertiliser. Property surveys may also be done with drones.
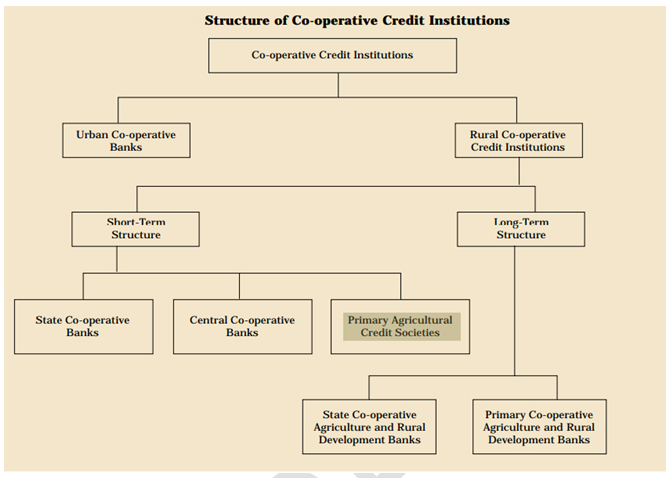
Facts about Primary Agricultural Credit Societies
- The State Cooperative Banks (SCB) at the state level constitute the first tier of a three-tier cooperative credit framework, with PACS acting as the last link.
- The District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs), which function at the district level, get credit from the SCBs. PACS, which works with farmers directly, collaborates with the DCCBs.
- PACSs provide farmers short- and medium-term agricultural loans for a range of farming and agricultural endeavours.
- In 1904, the first PACS was established.
Status:
- The Reserve Bank of India reported that there were 1.02 lakh PACS as of December 27, 2022. Only 47,297 of them were in the black as of the end of March 2021.
Relevance:
-
Access to Credit:
- Small farmers are given access to loans, which they may use to buy seeds, fertiliser, and other farm supplies. They are able to enhance their output and money thanks to this.
-
Financial Inclusion:
- PACS provide to a greater level of financial inclusion in rural areas where access to regulated financial services is constrained. Farmers who might not have access to formal financial services are given basic banking services including savings and loan accounts.
-
Convenient Services:
- Farmers can easily obtain PACS services because of their frequent placement in rural locations. PACS has the ability to grant credit quickly and with little documentation.
-
Promoting Savings Culture:
- PACS encourages farmers to save money so they may invest in their fields and enhance their quality of life.
-
Enhancing Credit Discipline:
- PACS encourage farmers to manage their credit by making them return their loans on time. This aids in lowering the risk of default, which poses a significant problem for the rural finance sector.
Challenges with the PACS
Insufficient Coverage:
- Geographically active PACS do, however, cover almost 90% of the 5.8 villages in some areas of the nation, particularly in the north-east.
- Furthermore, only 50% of all rural homes are covered by the rural population as members.
Insufficient Resources:
- In comparison to the rural economy's short- and medium-term credit demands, the PACS's resources are far too little.
- Even with these insufficient finances, the majority comes from higher financing agencies rather than from money that societies hold or deposits that they have mobilised.
Overdue and NPAs:
- Large overdue have grown to be a significant issue for the PACS.
- PACS reported loan totalling Rs. 1,43,044 crore and NPAs of Rs. 72,550 crores in accordance with the RBI report from 2022. Of the 20,897 PACS in Maharashtra, 11,326 are in losses.
- They limit the flow of loanable money, weaken societies' capacity for both borrowing and lending, and give them the impression that societies of defaulting debtors are acting maliciously.
Way Forward
- PACS are crucial organisations in India's rural finance sector and may make a substantial contribution to the goals of the Vocal for Local movement and Atmanirbhar Bharat (an independent India). These 100-year-old institutions can act as the cornerstone of a local economy that is self-sufficient.
- PACS need to be made more effective, financially viable, and available to farmers in order to reach their full potential. They must enhance their management and operations to do this.
- Additionally, in order to ensure efficient administration and the capacity to address the requirements of farmers, the regulatory framework controlling PACS needs to be reinforced.

Prelims
Q1. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- In terms of short-term credit delivery to the agriculture sector, District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs) deliver more credit in comparison to Scheduled Commercial Banks and Regional Rural Banks.
- One of the most important functions of DCCBs is to provide funds to the Primary Agricultural Credit Societies.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Q2. With reference to ‘Urban Cooperative Banks’ in India, consider the following statements: (2021)
- They are supervised and regulated by local boards set up by the State Governments.
- They can issue equity shares and preference shares.
- They were brought under the purview of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 through an Amendment in 1966.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q.“In the villages itself no form of credit organization will be suitable except the cooperative society.” – All India Rural Credit Survey. Discuss this statement in the background of agricultural fi nance in India. What constraints and challenges do financial institutions supplying agricultural fi nance face? How can technology be used to better reach and serve rural clients? (2014)



