- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Present Relevance of Global South
Present Relevance of Global South
11-07-2023
Latest Context:
Presently, many countries in Africa, Asia and Latin America are reluctant to support NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) in the ongoing Ukraine conflict and this has again brought the term "Global South" into focus.
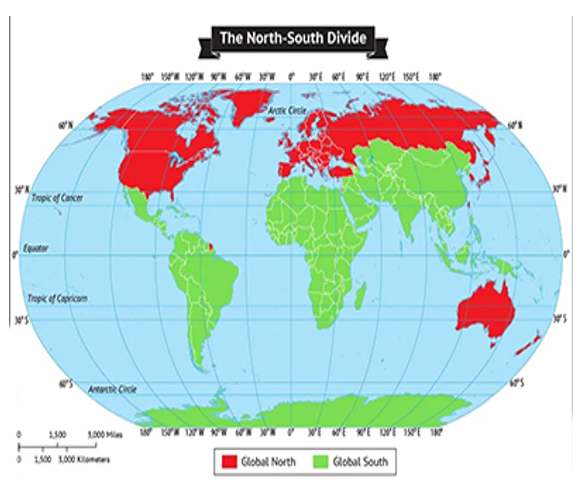
What is Global South?
- Basically, the term Global South was first coined by political activist Carl Oglesby in the year 1969.
- This term gained momentum after the dissolution of the USSR in 1991, which led to the end of the "Second World."
- Before 1991, developing nations were mostly referred to as the "Third World”.
- The term "Global South" refers to a concept that emerged as a way to categorize and describe countries or regions with lower levels of economic development and political power compared to the more economically advanced and politically influential countries of the "Global North."
- The Global South encompasses a diverse group of countries primarily located in Africa, Asia, Latin America, and the Caribbean.
- The Global South is characterized by various common challenges, such as poverty, underdevelopment, limited access to healthcare and education, political instability, and a history of colonization and exploitation. These countries often face similar issues related to economic inequality, social justice, human rights, and sustainable development.
- The division between the Global North and Global South is not strictly geographical but rather a socio-economic and geopolitical categorization. Some countries in the Global South, such as Brazil, China, India, and South Africa, have experienced significant economic growth and development in recent decades, blurring the traditional boundaries of the North-South divide.
- Generally, the term Global South is often used in academic, political, and policy discussions to highlight the shared challenges and interests of these countries and to promote global solidarity, cooperation, and equitable development. It serves as a reminder of the historical and ongoing disparities in wealth, power, and influence between different regions of the world.
Significance of Global South in today’s world:
- Economic Potential: Many countries in the Global South, such as China, India, Brazil, and South Africa, have experienced remarkable economic growth and have become major players in the global economy. These countries contribute to global trade, investment, and production, and their economic success has the potential to reshape the global economic landscape.
- Demographic Power: The Global South is home to a large portion of the world's population, with growing youth populations and a rising middle class. This demographic advantage presents opportunities for economic growth, innovation, and market expansion. It also poses challenges related to providing adequate healthcare, education, employment, and infrastructure to support the needs of a rapidly growing population.
- Resource Richness: The Global South possesses abundant natural resources, including oil, gas, minerals, and agricultural land. These resources play a crucial role in the global economy, as they are often in high demand by countries in the Global North. Managing and harnessing these resources sustainably and equitably is a significant challenge and opportunity for the Global South.
- Global Governance and Diplomacy: The Global South has been increasingly active in global governance and diplomacy, seeking a more equitable and inclusive international order. Countries from the Global South have formed alliances, such as the G77 and the Non-Aligned Movement, to raise their voices and advocate for their interests on various global issues, including trade, climate change, human rights, and development.
- Development and Sustainable Goals: The Global South faces pressing development challenges, including poverty, inequality, climate change, and access to essential services. Addressing these challenges is crucial not only for the well-being of people in the Global South but also for achieving global sustainable development goals. Efforts to reduce poverty, improve education, healthcare, infrastructure, and to promote sustainable practices in the Global South have the potential to create a more equitable and sustainable world for all.
- Cultural and Intellectual Contributions: The Global South is a rich source of diverse cultures, languages, traditions, and knowledge systems. The contributions of Global South countries in areas such as literature, arts, music, philosophy, and science are vital for global cultural diversity and the enrichment of human understanding.
What are the Challenges in front of Global South?
- High Poverty and Inequality: Many countries in the Global South struggle with high levels of poverty and income inequality. Limited access to basic needs such as food, clean water, healthcare, and education disproportionately affects marginalized populations, widening social and economic disparities.
- Development Gap: There is a substantial development gap between countries in the Global South and the more economically advanced countries of the Global North. Insufficient infrastructure, inadequate healthcare systems, low levels of education, and limited access to technology hinder progress in various sectors.
- Political Instability and Conflict: Political instability, corruption, weak governance, and frequent conflicts are prevalent in some regions of the Global South. These issues undermine economic growth and sustainable development, leading to a cycle of poverty and underdevelopment.
- Climate Change and Environmental Vulnerability: The Global South is particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including extreme weather events, rising sea levels and ecosystem degradation. These environmental challenges can lead to displacement, food insecurity, and loss of livelihoods, further increasing poverty and inequality.
- Health and Disease Burdens: The Global South faces significant health challenges, including limited access to healthcare services, infectious diseases (such as malaria, HIV/AIDS, and tuberculosis), and inadequate healthcare infrastructure. These factors contribute to high morbidity and mortality rates and hinder overall development.
- Debt Burden and Financial Challenges: Many countries in the Global South struggle with high levels of external debt, which limits their ability to invest in essential infrastructure, social programs, and sustainable development initiatives. Financial volatility, lack of access to affordable credit, and unequal terms of trade also pose challenges to economic stability and growth.
- Digital Divide: The digital divide refers to the gap in access to and use of information and communication technologies between countries and populations. Limited access to technology, internet connectivity, and digital skills in the Global South hinder economic growth, education, and participation in the global digital economy.
- Brain Drain: The Global South often experiences a "brain drain" phenomenon, where skilled professionals, including doctors, engineers, and academics, migrate to wealthier countries in search of better opportunities. This talent drain deprives the Global South of human capital and increase the challenges faced in various sectors.
Conclusion
In recent years, the rise of the Global South as an economic and political force has challenged traditional power calculations and brought attention to the changing global order. So, recognizing the significance of the Global South is essential for fostering global cooperation, reducing global inequalities, and promoting a more inclusive and balanced world order.
Must Check: IAS Coaching Centre In Delhi