- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- NCERT Medieval History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 7th JULY 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 7th JULY 2025

Texas
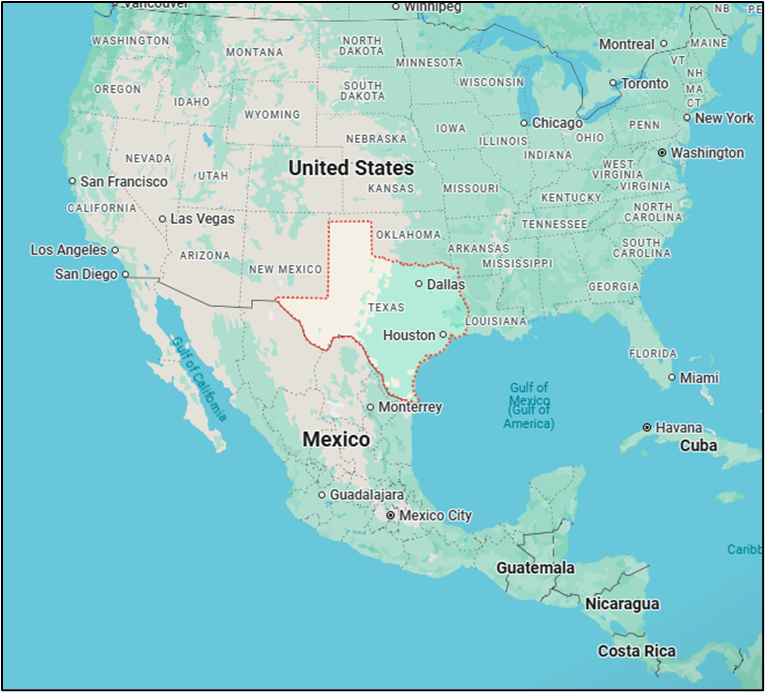
Why in the News?
- A very serious flood happened in Central Texas, especially in areas like Kerr County and San Antonio.
- It rained heavily, and the Guadalupe River rose very fast, making the water levels dangerous.
What are the Key Highlights?
- Country: United States of America (USA)
- Region: South-Central part of the United States
- Latitude & Longitude: Between 25°50′ N to 36°30′ N and 93°30′ W to 106°38′ W
- Borders:
- North: Oklahoma
- East: Arkansas and Louisiana
- South: Mexico and the Gulf of Mexico
- West: New Mexico
- Area and Size:
- Second largest state in the USA (after Alaska)
- Total area: Around 695,600 square kilometers
- Bigger than many countries like France or Afghanistan
- Climate:
- East Texas: Humid and subtropical (more rainfall, forests)
- West Texas: Dry and desert-like (arid and semi-arid)
- Central Texas: Known for unpredictable weather and prone to flash floods (e.g., recent flood in Hill Country)
- North Texas: Experiences cold winters and hot summers
- South Texas: Hot and humid (close to the Gulf of Mexico)
- Major Rivers and Water Bodies:
- Rio Grande: Forms the natural border with Mexico
- Red River: Forms the northern border with Oklahoma
- Sabine River: Eastern border with Louisiana
- Trinity, Brazos, Colorado (of Texas): Important rivers in central and eastern Texas
- Gulf of Mexico: Southern border, key for ports, trade, and hurricanes.
- Landforms:
- East: Pine forests and lowlands
- Central (Hill Country): Plateau and hilly terrain (prone to flash floods)
- West; Desert and mountain ranges (e.g., Guadalupe Mountains)
- Panhandle region (Northwest Texas): Flat high plains
- Coastal Plains: Along the Gulf Coast, important for oil and gas industry
- Major Cities:
- Austin: Capital of Texas
- Houston: Largest city, major oil and space research center (NASA)
- Dallas: Financial and tech hub
- San Antonio: Historic city with Spanish influence
- El Paso: Near the Mexico border, major trade link
- Natural Resources:
- Oil and Natural Gas: Texas is the leading oil producer in the USA
- Wind and Solar Energy: Huge renewable energy production
- Agriculture: Cotton, cattle, and wheat
- Minerals: Limestone, salt, gypsum
- Natural Disasters:
- Hurricanes (from the Gulf of Mexico)
- Tornadoes (especially in North Texas – part of "Tornado Alley")
- Flash floods (Hill Country and Central Texas)
- Droughts and wildfires (West Texas)
- Strategic Importance
- Borders Mexico: Key for immigration, trade, and border security
- Access to Gulf of Mexico: Boosts shipping and oil exports
- Hosts major military bases, NASA, and technology hubs
Helgoland
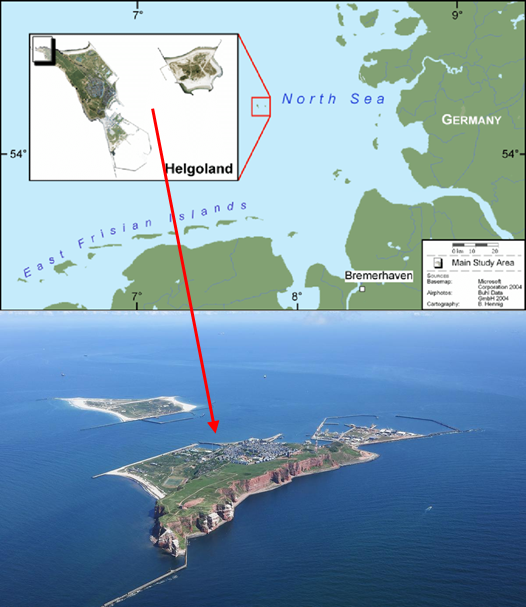
Why in the News?
- Helgoland, a small island in the North Sea near Germany, is in the news because it is being remembered as the place where quantum mechanics was born.
- This year marks 100 years since Werner Heisenberg had a major scientific breakthrough on this island in June 1925.
- His ideas changed the way we understand atoms and helped start a new field of science called quantum physics.
What are the Key Highlights?
|
Feature |
Description |
|
Country |
Germany |
|
Sea |
North Sea |
|
Coordinates |
Approximately 54°11′N 7°53′E |
|
Distance from Mainland |
About 46–50 km off the German coast |
|
State/Region |
Belongs to the state of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany |
|
Nearest Port |
Cuxhaven (on the German mainland) |
|
Island Group |
Comprises two main islands: Helgoland (main) and Düne (a smaller islet) |
|
Total Area |
About 1 square kilometre |
|
Geology |
Made up mainly of red sandstone cliffs, unique in the North Sea region |
|
Climate |
Mild maritime climate; windy, with clean air (important for health tourism) |
Strategic Importance (Historical):
- Once a naval fortress of the German Empire.
- Played roles during both World Wars due to its strategic North Sea location.
- Was heavily bombed during WWII; British forces even used it as a bombing practice site.
- Returned to West Germany in 1952 after being under British control post-WWII.
Ecological Importance:
- The surrounding waters are rich in marine biodiversity.
- The island is a bird-watching hotspot, especially during migratory seasons.
- Dune Island is known for seal colonies and protected natural habitats.
Tourism and Culture:
- Helgoland is a popular holiday destination, especially for its clean air and calm atmosphere.
- It is a duty-free zone in Germany, attracting shoppers.
No cars are allowed on the island, making it a quiet, pedestrian-friendly area.




