- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 25th MARCH 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 25th MARCH 2025
25-03-2025

Strait of Hormuz
Why in news?
- Amid tensions with the US, Iran showcased its military strength on Saturday by deploying missile systems on the disputed Greater Tunb, Lesser Tunb, and Abu Musa islands near the strategic Strait of Hormuz.
About Strait of Hormuz:
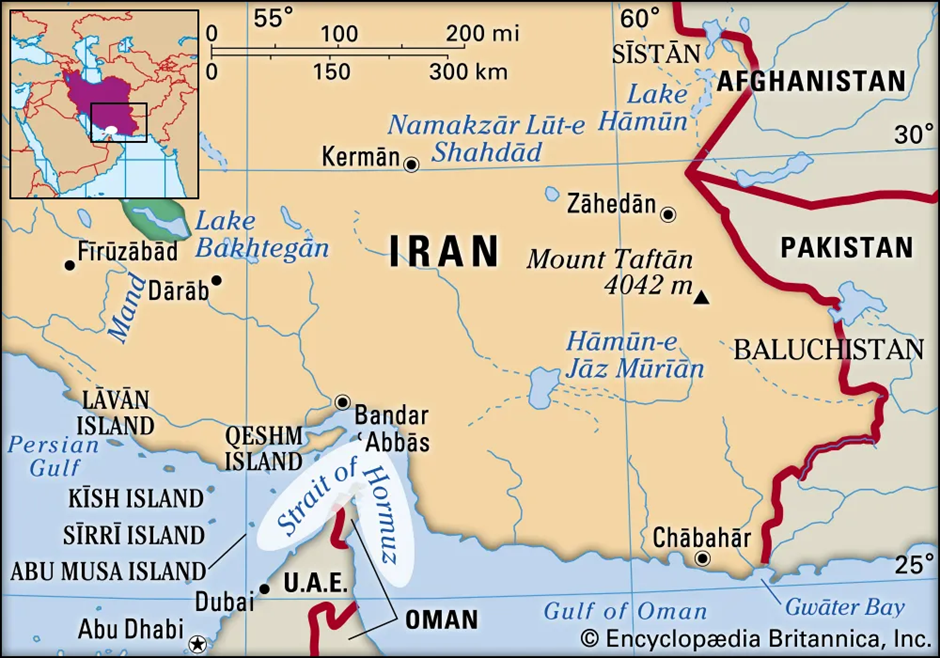
- Location and Geography:
- The Strait of Hormuz is a narrow waterway situated between Iran to the north and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Musandam (Oman) to the south.
- It connects the Persian Gulf to the Gulf of Oman, serving as a crucial maritime passage.
- The strait is approximately 167 kilometres long, with its width ranging from 39 kilometres to 95 kilometres.
- The Gulf of Oman lies to the east of the strait, while the Persian Gulf is to its west.
- Some notable islands in the strait include Hengam, Hormuz, and Qishm.
- Geostrategic Importance:
- The Strait of Hormuz is one of the world’s most critical choke points for global energy trade.
- Around 30% of the world’s liquefied natural gas (LNG) and 25% of global oil shipments pass through this narrow waterway.
- It is vital for major oil-exporting countries, including Saudi Arabia, the UAE, Kuwait, Iraq, and Iran, making it a hotspot for geopolitical tensions.
- The strait plays a significant role in India’s energy security, as a large portion of its oil and LNG imports pass through this route.
- Disputed Islands:
- Greater Tunb, Lesser Tunb, and Abu Musa are three disputed islands located near the Strait of Hormuz.
- These islands are strategically important, as they provide control over the maritime traffic passing through the strait.
- They are currently administered by Iran, but the United Arab Emirates (UAE) claims sovereignty over them.
- The dispute has been a source of regional tension, with periodic escalations between Iran and the UAE, often involving military posturing.
Sukhna Wildlife Sanctuary
Why in news?
- The Punjab government informed the Supreme Court in its affidavit that the Eco Sensitive Zone around Sukhna Wildlife Sanctuary for Nayagaon municipal committee will remain 100 meters instead of 1 to 3 km.
About Sukhna Wildlife Sanctuary:
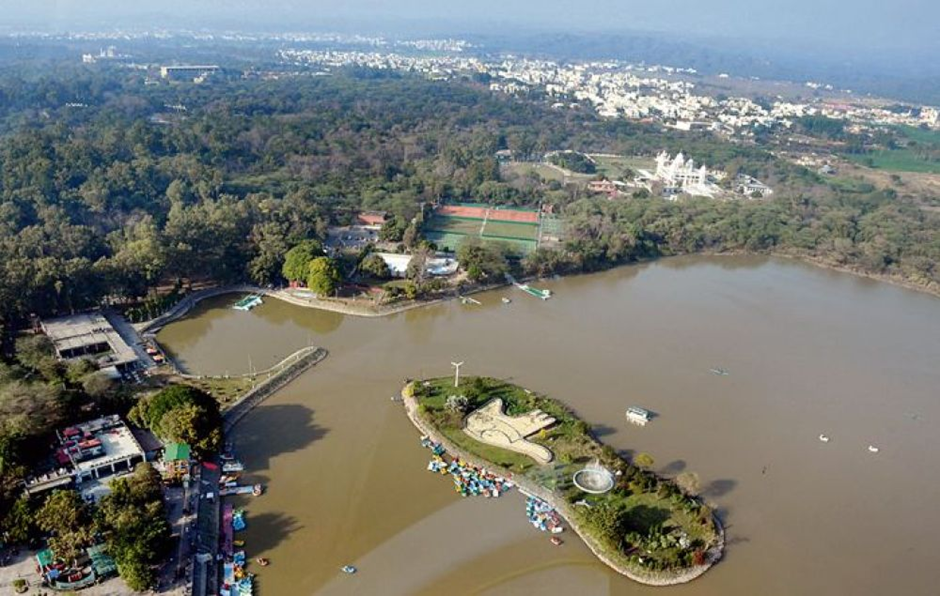

- Location and Geography:
- Sukhna Wildlife Sanctuary is a protected area in Chandigarh, situated near Sukhna Lake at the foothills of the Shivalik range.
- The Sukhna Lake was created in 1958 by Le Corbusier by diverting the Sukhna Choe, a seasonal stream from the Shivalik hills.
- The sanctuary was established in 1998, covering an area of 2,600 hectares for soil conservation and afforestation.
- Soil and Vegetation:
- The region is geologically unstable, prone to soil erosion during rains due to sandy soil with clay pockets.
- The sanctuary consists of forests, grasslands, and wetlands, with around 150 water bodies forming its catchment area.
- Flora and Fauna:
- Flora: Includes Khair, Phulai, Kikar, Shisham, Amaltas, Amla, Jhingan, and Vasaka.
- Fauna: Mammals such as squirrels, common mongoose, Indian hare, porcupine, jungle cat, jackal, and wild boar.
- Avifauna: Common birds include peacocks, hill mynas, jungle crows, black drongos, parrots, and doves, along with migratory birds.
About Eco-Sensitive Zones (ESZs):
- Eco-Sensitive Zones (ESZs) act as buffer zones around Protected Areas, restricting activities that may harm the environment and biodiversity.
- They are regulated under the Environment Protection Act, 1986, with guidelines issued by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- ESZs generally extend from 100 meters to 10 km around national parks and wildlife sanctuaries, varying by location.
- Activities like commercial mining, industries, and deforestation are prohibited, while regulated activities include eco-tourism and sustainable agriculture.
Greenland
Why in news?
- Greenland criticizes the planned visits of Second Lady Usha Vance and a Trump adviser, expressing disapproval of their scheduled trips to the region.
About Greenland:
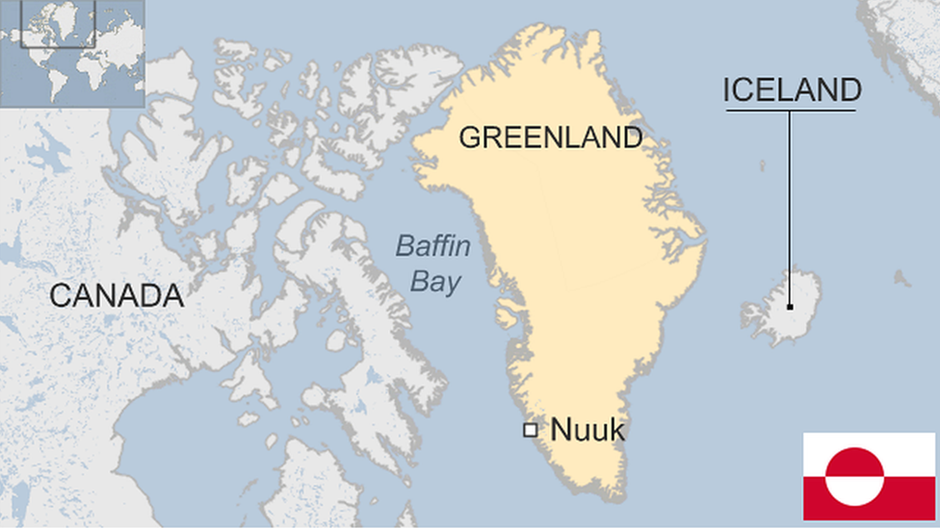
- Location and Geography:
- Greenland is the world’s largest island, situated between the Arctic and Atlantic Oceans.
- It is geographically closer to North America but politically associated with Denmark, located nearly 3,000 km (1,860 miles) away.
- The island has significant strategic and economic importance, given its natural resources and Arctic location.
- Political Status:
- Greenland is an autonomous territory under Danish control, with self-governance in domestic affairs.
- However, decisions regarding foreign policy and defence are managed by Copenhagen (capital of Denmark).
- The U.S. has maintained a military presence on the island since World War II, emphasising its security interests in the Arctic.
- Greenland has an active independence movement, with nearly 80% of its population favouring separation from Denmark.
- Trump’s Interest in Greenland:
- U.S. President Donald Trump expressed interest in acquiring Greenland due to its strategic military location and natural resources.
- The U.S. sees Greenland as crucial for Arctic security, especially against growing Russian and Chinese influence.
- The island is rich in rare earth minerals, which are vital for modern technology and defence industries.
- Trump’s administration even considered leveraging NATO’s influence to facilitate the acquisition, provoking strong opposition from Greenland’s political leaders.
- Although Greenland's government firmly rejected the proposal, Trump’s interest underscored the island’s growing geopolitical significance in global affairs.
Mula River
Why in news?
- The Mula River faces severe ecological threats due to persistent water hyacinth overgrowth, harming biodiversity.
About Mula River:
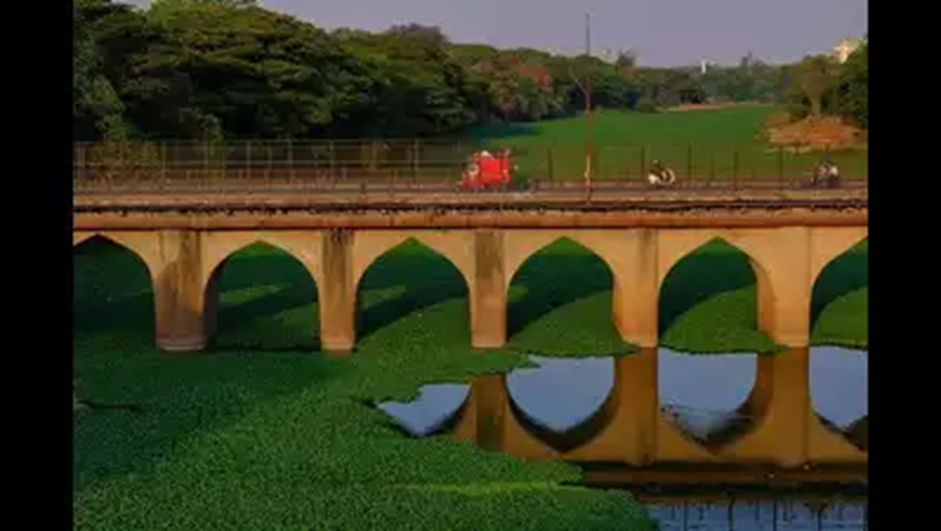

- Origin and Course:
- The Mula River originates near the Western Ghats in Maharashtra and is dammed at Mulshi Dam, forming Mulshi Lake.
- It flows through Pune city, where it merges with the Pawana River (left bank) and Mutha River (right bank), forming the Mula-Mutha River, which later joins the Bhima River, a tributary of the Krishna River.
- The river serves as a natural boundary between the Pimpri-Chinchwad Municipal Corporation and the Pune Municipal Corporation.
- Several bridges span the river, including the Rajiv Gandhi Bridge and Harris Bridge.
- Reasons Behind Water Hyacinth Growth:
- High Pollution Levels: The Mula River receives around 125 MLD (Million Litres per Day) of untreated sewage from Pune city, providing nutrient-rich water that supports hyacinth growth.
- Industrial and Domestic Waste: Effluents from factories, chemicals, and solid waste dumping increase organic matter, accelerating the plant's spread.
- Slow Flow of Water: The river’s stagnant sections, due to urban encroachments and damming, provide ideal conditions for the rapid multiplication of water hyacinth.
- Lack of Regular Maintenance: Absence of mechanical removal and sustainable waste management worsens the spread of this invasive species.
Key Facts About Water Hyacinth:
- It is a free-floating aquatic plant native to South America, introduced to India during British rule as an ornamental species.
- The plant has beautiful purple flowers but rapidly forms dense mats, choking water bodies.
- Environmental Impact:
- It blocks waterways, making them unsuitable for fishing, transport, and recreation.
- It depletes oxygen levels, leading to fish mortality and disruption of aquatic ecosystems.
- It traps pollutants, worsening water quality in already polluted rivers like Mula.
- Significance & Uses:
- Used in bio-fertilisers and organic agriculture.
- The plant’s fibrous stems are used to make handicrafts like bags, baskets, and mats.
Nandi Hills
Why in news?
-
- Authorities plan to ban vehicular entry to Nandi Hills on weekdays to control traffic congestion and preserve the eco-sensitive zone.
- Authorities plan to ban vehicular entry to Nandi Hills on weekdays to control traffic congestion and preserve the eco-sensitive zone.
About Nandi Hills:
- Location and Geography:
- Nandi Hills, also known as Nandidurg, is an ancient hill station in the Chikkaballapur district of Karnataka, about 60 km from Bengaluru and 10 km from Chikkaballapur town.
- It is a popular tourist destination known for scenic landscapes and historical significance.
- The hills are the source of major rivers, including the Arkavathy, Ponnaiyar, Palar, Papagni, and Penna rivers.
- The terrain consists of rugged hills with steep cliffs at an elevation of 4,850 feet above sea level.
- The region is home to historical forts, including one built by Tipu Sultan, and is famous for spectacular sunrises and a cool climate.
- Climate and Vegetation:
- Nandi Hills has a moderate and pleasant climate throughout the year due to its high altitude.
- Summers are mild (23-29°C), while winters are cooler (around 10°C). The monsoon season (June to September) brings moderate to heavy rainfall.
- The vegetation is a mix of native species and introduced plantations like eucalyptus and coffee.
- The region was once a botanical research site under British officials. The dense forests promote cloud condensation, making the area lush and green.
- Ecological Significance:
- Nandi Hills is an ecological hotspot, providing habitat for rare and endemic species like the Nilgiri woodpigeon, Malabar whistling thrush, and shaheen falcon.
- The forested hills help regulate climate, act as a water catchment area, and support carbon sequestration.
- Economic and Cultural Significance:
- Nandi Hills is a major tourist attraction for hiking, trekking, paragliding, and nature walks.
- The Karnataka tourism department has developed it with a botanical garden, a food court, and a proposed gondola lift system.
- Historically, it was a summer retreat for Tipu Sultan and later British officials. Culturally, it is home to the Yoga Nandeeshwara Temple, an ancient temple dedicated to Lord Shiva.
- Tipu Sultan’s Summer Palace and Tipu Drop are key historical landmarks. Annual cultural and music festivals add to its significance.
- Due to rising tourism, proposals to restrict vehicular entry on weekdays aim to preserve the environment and reduce congestion.
- Conservation efforts are crucial to maintaining the ecological balance of this historically and ecologically significant region.
|
Also Read |
|
| FREE NIOS Books | |




