- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 23rd June 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 23rd June 2025
23-06-2025

1. Strait of Hormuz
Why in the News?
- In June 2025, Iran’s Parliament approved a motion to close the Strait of Hormuz, a key oil transit route.
- This comes after U.S. airstrikes on Iranian nuclear facilities, heightening geopolitical tensions in the Middle East.
- The move could disrupt global energy markets as about 1/5th of the world's oil passes through this strait, affecting oil prices and oil-importing countries like India.
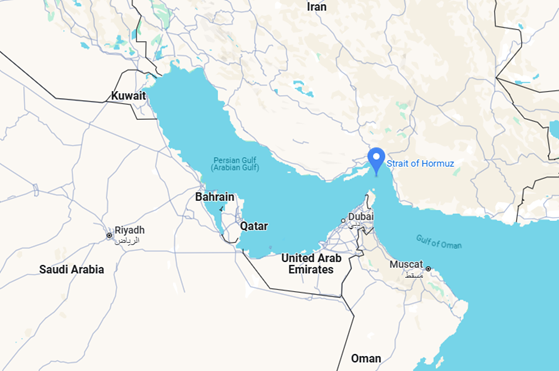
About Strait of Hormuz:
- Location: The Strait of Hormuz is a narrow waterway situated between Iran (to the north) and the Arabian Peninsula — mainly the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Musandam (Oman) to the south.
- Connectivity: It connects the Persian Gulf (on the west) to the Gulf of Oman (on the east), making it a vital maritime route for oil and gas transport.
- Geographical Position: Iran lies on the northern coast, while the UAE and Oman lie on the southern coast of the strait.
- Length and Width: The Strait of Hormuz is approximately 167 km long, with its width ranging from 39 km to 95 km. Despite narrowing in the north, it still allows passage of large vessels.
- Islands in the Region: Important islands within the strait include Hengam, Hormuz, and Qishm, which have strategic and historical relevance.
- Strategic Importance: It is considered one of the world’s most economically and geopolitically important choke points, critical for global energy security.
- Global Oil and Gas Flow: Around 25% of the world’s oil exports and nearly 30% of global liquefied natural gas (LNG) shipments pass through the Strait of Hormuz, making it crucial for global energy markets.
2. Keezhadi
Why in News?
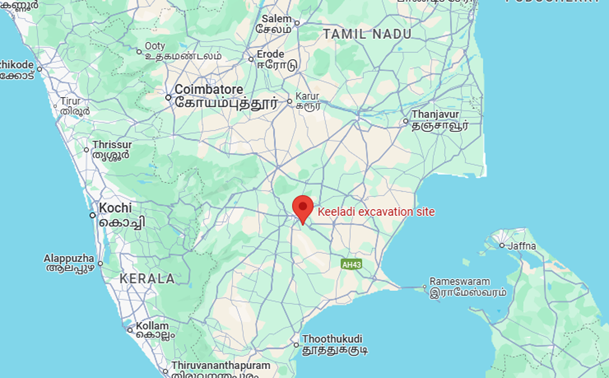
- Keezhadi (or Keeladi), an archaeological site near the Vaigai River in Tamil Nadu, is gaining attention as one of the most significant recent discoveries in India.
- Recent findings — including urban settlement remains, Tamil-Brahmi inscriptions, and evidence of trade and literacy — suggest a flourishing civilization dating back to the 6th–5th century BCE.
- The discovery is seen as challenging long-held historical narratives, especially about the timing and geography of early Indian civilizations.
- However, the excavation has been mired in political controversy, with debates around “Dravidian pride”, accusations of interference, and concerns over the Centre allegedly undermining the findings.
About Keezhadi Excavation:
- It is believed to be a major urban settlement from the Sangam Age.
- This is one of the most important archaeological discoveries in Tamil Nadu since Adichanallur.
- Findings show signs of an urban, literate, and craft-based society, suggesting that urbanisation in South India may have developed independently of northern influences.
About the Sangam Period
- The term ‘Sangam’ comes from the Sanskrit word ‘Sangha’, meaning assembly, referring to the Tamil literary gatherings under the Pandya rulers.
- Sangam literature provides rich information about ancient Tamil society, including governance, trade, agriculture, war, and daily life.
- Important Sangam Texts Include:
- Tolkappiyam – The oldest Tamil grammar text
- Pattupattu – The Ten Idylls
- Ettutogai – The Eight Anthologies
- Padinenkilkanakku – The Eighteen Minor Works
- Three Great Epics – Silappadikaram, Manimekalai, and Civaka Cintamani




