- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 13th MARCH 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 13th MARCH 2025

Gulf of Oman
Why in news?
- Iran, Russia, and China have launched joint naval exercises in the Gulf of Oman, continuing their annual military cooperation for the fifth consecutive year.
About Gulf of Oman:
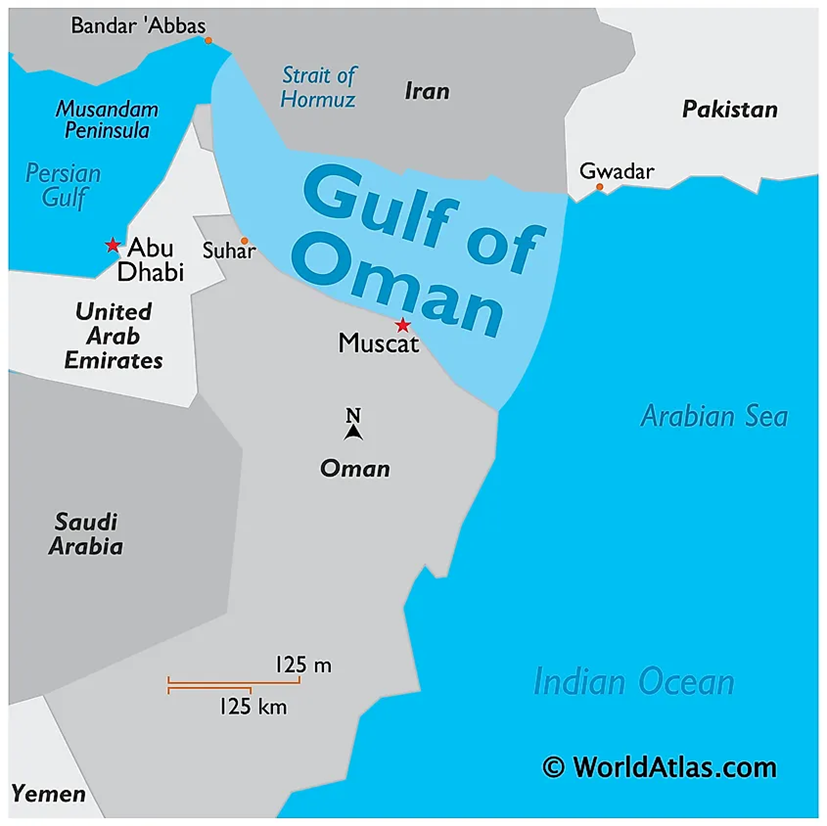
- Location and Geography:
- The Gulf of Oman, also known as the Gulf of Makran, is the western extension of the Arabian Sea in the Middle East, forming the only entrance from the Indian Ocean to the Persian Gulf.
- It connects the Arabian Sea to the Strait of Hormuz, a strategic chokepoint that leads into the Persian Gulf.
- The Gulf is bordered by Iran and Pakistan in the north, Oman in the south, and the UAE in the west.
- Important ports along its coast include Ṣuḥār, Muscat, and Ṣūr in Oman, and Jāsk and Chāh Bahār in Iran.
- The Gulf hosts several islands, such as Sheytan Island, Al Fahal Island, and Dimaniyat Islands, contributing to regional maritime activities.
- Geo-political and Geo-economic Importance for India
- The Gulf of Oman plays a crucial role in India's energy security, as nearly one-third of the world’s oil trade passes through the Strait of Hormuz, making the stability of this maritime route essential for India's economic interests.
- It serves as a critical trade route, facilitating India’s exports and imports with West Asian nations.
- The development of Chabahar Port in Iran, with Indian assistance, provides an alternative trade route to Afghanistan and Central Asia, reducing dependence on Pakistan’s Gwadar Port.
- Additionally, Indian investments in Oman’s Duqm Port enhance trade connectivity and energy cooperation.
- India has strengthened its naval presence in the region through strategic partnerships with Oman and Iran, using Chabahar as a key foothold.
- However, the involvement of China, Russia, and Iran in joint naval exercises, such as Marine Security Belt 2025, poses strategic concerns, impacting India’s Indian Ocean Region (IOR) strategy.
- The region is also a hotspot for maritime piracy and regional conflicts, necessitating India’s engagement in maritime security operations and ensuring freedom of navigation.
- Apart from energy and trade, the Gulf’s fishing and marine economy holds significance for India’s seafood exports to Gulf nations, contributing to economic ties.
Volcán de Fuego
Why in news?
- Guatemala's Volcán de Fuego erupted violently, unleashing explosions, incandescent material, and pyroclastic flows, endangering nearby communities with intense shockwaves.
About Volcán de Fuego:
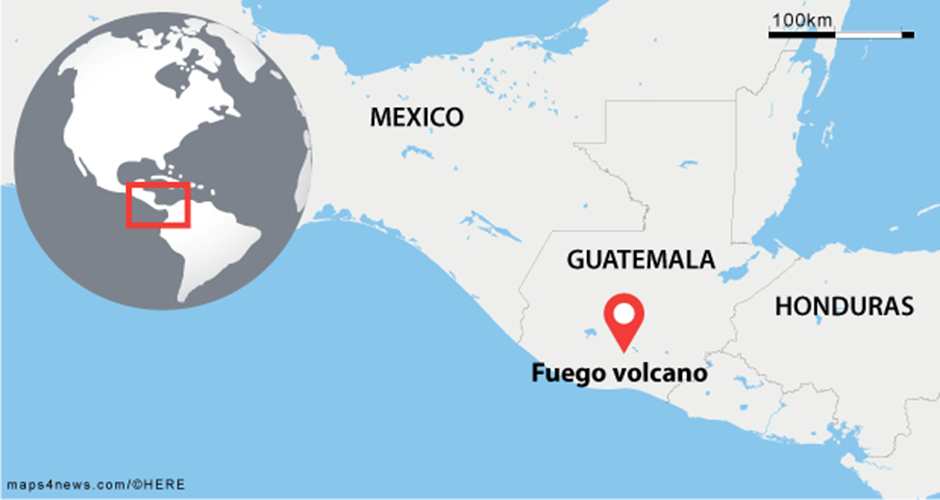
- Location:
- Volcán de Fuego, meaning "Volcano of Fire" in Spanish, is a stratovolcano located in Guatemala, near the former capital Antigua.
- It is one of three major stratovolcanoes overlooking the region and is considered one of Central America's most active volcanoes.
- Guatemala lies within the Pacific Ring of Fire, a highly seismic and volcanically active zone, leading to frequent eruptions and earthquakes.
- Reason Behind Volcanic Eruption:
- Volcán de Fuego's eruptions are characterised by explosive activity, lava flows, and pyroclastic flows, which pose severe risks to nearby communities.
- As a stratovolcano, it has a steep, cone-shaped structure with alternating layers of lava and pyroclastic material. The viscous andesite and dacite lava contribute to high gas pressures, resulting in violent eruptions.
- The volcano sits above a subduction zone, where the Cocos Plate is being forced under the Caribbean Plate, generating magma and leading to frequent eruptions.
- It has a long history of violent eruptions, with records dating back to the 16th century. A deadly eruption in 2018 claimed 194 lives, with 234 people reported missing.
Ghana
Why in news?
- Ghana has eliminated several IMF-mandated "nuisance" taxes to boost economic growth, ease business operations, and reduce the financial burden on citizens, aiming to enhance domestic revenue without excessive taxation.
About Ghana:
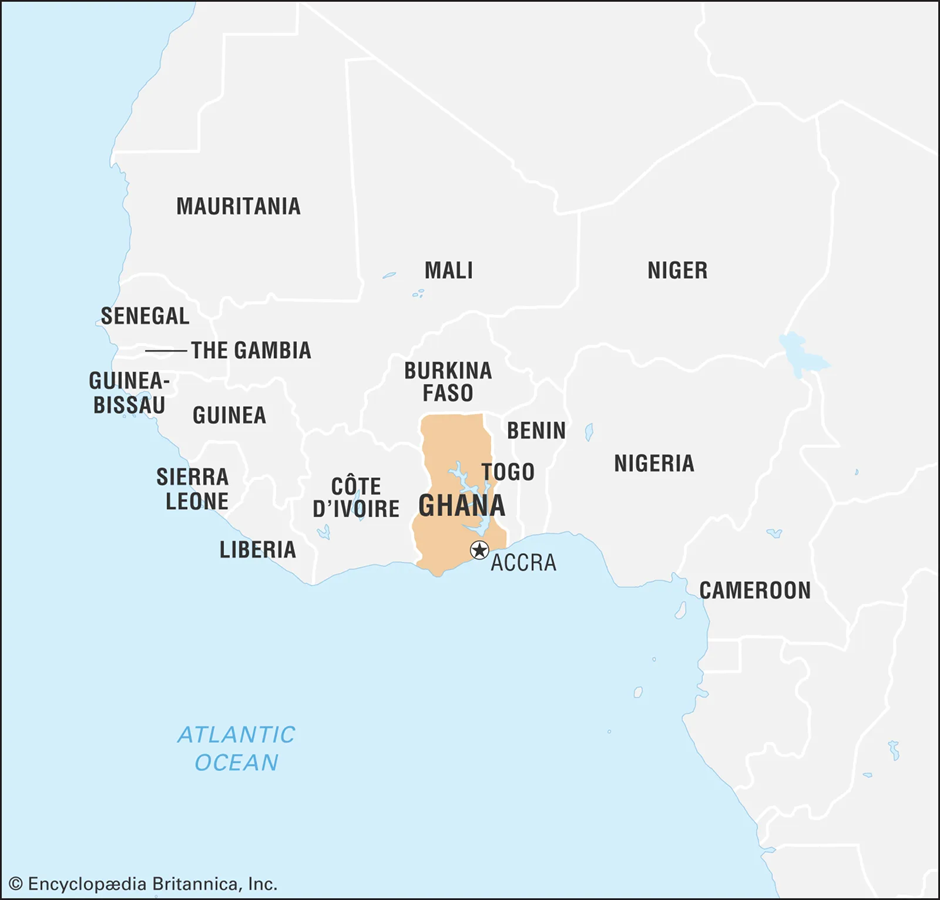
- Location and Geography:
- Ghana is a West African nation bordered by Côte d'Ivoire to the west, Burkina Faso to the north, Togo to the east, and the Gulf of Guinea to the south.
- The country has a diverse landscape, including coastal plains, savannahs, and rainforests, which support agriculture and natural resource extraction.
- Accra, the capital city, serves as the political and economic hub.
- Potential Natural Resources:
- Ghana is one of the leading gold producers in Africa, with significant deposits of bauxite, manganese, and diamonds.
- Additionally, oil and gas reserves discovered offshore in recent years have contributed to economic growth.
- Cocoa production is another key sector, making Ghana the second-largest cocoa exporter globally.
- However, illegal mining (galamsey) has led to environmental damage, prompting the government to regulate the sector through the newly proposed Ghana Gold Board.
- Economic Crisis and IMF Bailout:
- Ghana's economy has faced severe financial distress, driven by high debt levels, inflation, currency depreciation, and fiscal mismanagement.
- The economic challenges led the previous government to seek a $3 billion bailout from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) in 2023.
- To meet IMF conditions, the government introduced several Covid-era taxes aimed at boosting revenue.
- However, these taxes placed an additional financial burden on businesses and citizens, exacerbating the economic downturn.
- IMF-Mandated Taxes and Their Removal:
- To meet the IMF’s conditions, the previous government imposed several "nuisance levies," which included:
- 1% levy on mobile money transfers
- Value-added tax (VAT) on motor vehicle insurance
- 10% tax on lottery winnings
- Emission levy on industries and vehicles
- 1.5% tax on unprocessed gold from small-scale miners
- These taxes were introduced to increase government revenue but were met with public dissatisfaction due to their impact on disposable income and business operations.
- Reason Behind Scrapping the Taxes:
- The newly elected government under President John Mahama announced the removal of these taxes to reduce the financial burden on citizens and businesses.
- The finance minister stated that eliminating these levies would increase disposable income, stimulate business growth, and support economic recovery.
- To compensate for the revenue shortfall, the government plans to:
- Enhance tax revenue collection through amendments in the Revenue Administration Act.
- Improve road toll collection as part of an infrastructure initiative called the "Big Push."
- Strengthen the Ghana Gold Board to regulate the gold sector and boost foreign exchange reserves.
South Sudan
Why in news?
- Uganda has sent troops to South Sudan amid rising concerns of a civil war, aiming to stabilize the region and prevent escalating conflict between rival factions.
About South Sudan:
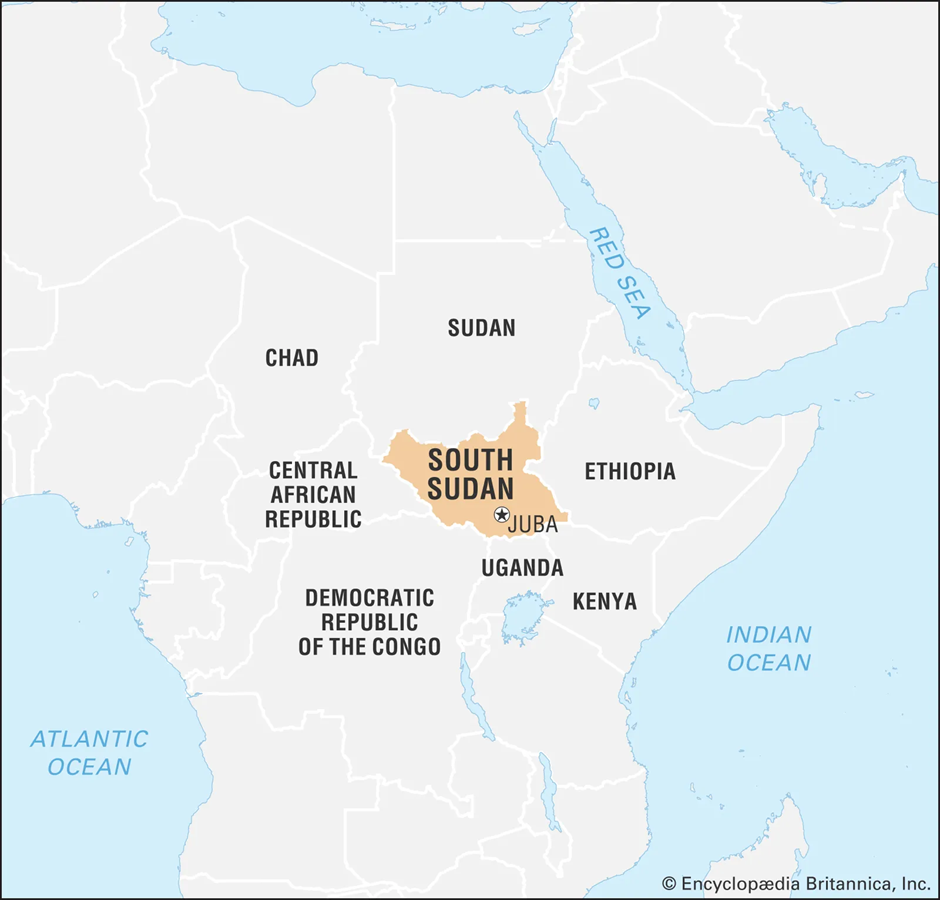
- Location and Formation:
- South Sudan, the world's youngest nation, is a landlocked country in East-Central Africa.
- It shares borders with Sudan to the north, Ethiopia to the east, Kenya and Uganda to the south, the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the southwest, and the Central African Republic to the west.
- The country gained independence from Sudan on July 9, 2011, following a referendum where the majority voted in favour of secession.
- Juba serves as its capital and largest city. The region has endured decades of conflict, first during Sudan’s civil wars and later due to internal struggles among its leaders.
- Rising Tensions and Risk of Civil War:
- South Sudan is once again on the brink of civil war as tensions between President Salva Kiir and First Vice President Riek Machar escalate.
- The power-sharing agreement signed in 2018, which ended a five-year civil war, is now unravelling amid political disputes and factional violence.
- Key factors behind the rising tensions include:
- Political Rivalry: Kiir’s government has arrested ministers and military officials linked to Machar, intensifying hostilities.
- Ethnic Militias: Clashes have erupted between the South Sudanese army and the White Army militia, an ethnic Nuer force historically aligned with Machar.
- Sporadic Violence: Deadly conflicts have been reported in Nasir, a town in the Upper Nile region, where dozens of soldiers and a general were killed.
- External Military Involvement: Uganda has deployed special forces to Juba, mirroring previous interventions in 2013 and 2016 when civil war erupted.
- Key Regions Associated with the Conflict:
- Juba: The capital city and the political centre, where Ugandan troops have been deployed to secure Kiir’s administration.
- Upper Nile Region: A conflict-prone area where Nasir town has witnessed recent clashes.
- Jonglei State: Historically affected by ethnic violence and home to armed militias.
- Unity State: A major oil-producing region, often targeted during conflicts.
- Equatoria Region: Previously a stronghold for opposition forces and subject to continued instability.
Brahmani River
Why in news?
- Eight years after construction began, the bridge over the Brahmani River in Jajpur, Odisha, remains incomplete, causing severe connectivity issues and hardships for locals relying on alternative routes.
About Brahmani River:
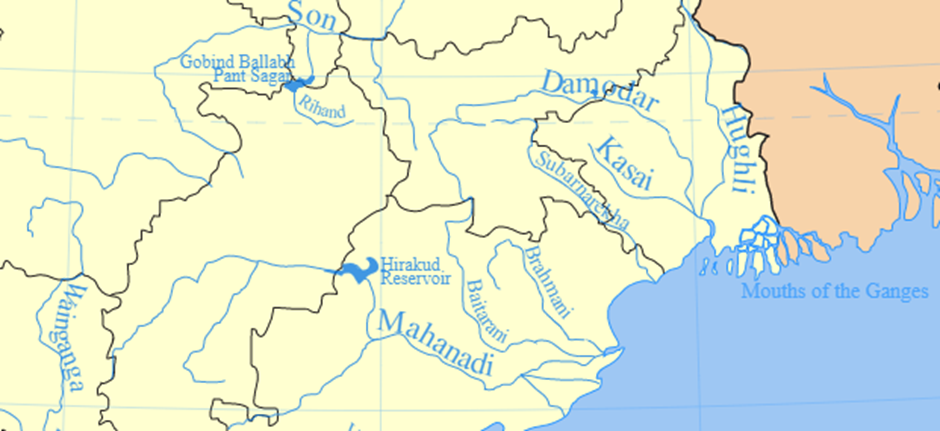
- The Brahmani River is one of the major rivers of Odisha, formed by the confluence of the Sankh and South Koel rivers near Rourkela.
- The Sankh River originates near the Jharkhand-Chhattisgarh border, while the South Koel River arises in Lohardaga, Jharkhand, on the Chota Nagpur Plateau.
- Flowing through Sundargarh, Deogarh, Angul, Dhenkanal, Cuttack, Jajpur, and Kendrapara districts, the Brahmani eventually merges with the Baitarani River, forming a delta before emptying into the Bay of Bengal at Dhamra.
- It is the second-longest river in Odisha after the Mahanadi.
- Several tributaries, including Tikira, Singadajore, Nigra, and Kharsuan, join the Brahmani along its course.
- Near its mouth, the river is part of the Bhitarkanika Wildlife Sanctuary, known for its estuarine crocodiles.
- The Rengali Dam, Samal Barrage, Jokadia Anicut, and Jenapur Anicut are important irrigation projects on the river.
|
UPSC CSE PYQs
Q1. Which of the following countries are well known as the two largest cocoa producers in the world? (2024)
Answer: Option C Q2. Consider the following rivers:
Which of the above rise from the Eastern Ghats?
Answer: Option B Q3. What is the importance of developing Chabahar Port by India? (2017)
Answer: Option C
Q4. Two important rivers- one with its source in Jharkhand (and known by a different name in Odisha), and another, with its source in Odisha merge at a place only a short distance from the coast of bay of Bengal before flowing into the sea. This is an important site of wildlife and biodiversity and a protected area. Which one of the following could be this? (2011)
Answer: Option A |
|
Also Read |
|
| FREE NIOS Books | |