- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 13th FEBRUARY 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 13th FEBRUARY 2025
13-02-2025

Nigeria
Why in news?
- Nigeria's mobile data price hike follows government subsidy cuts and inflation, straining consumers already facing economic hardship.
About Nigeria:
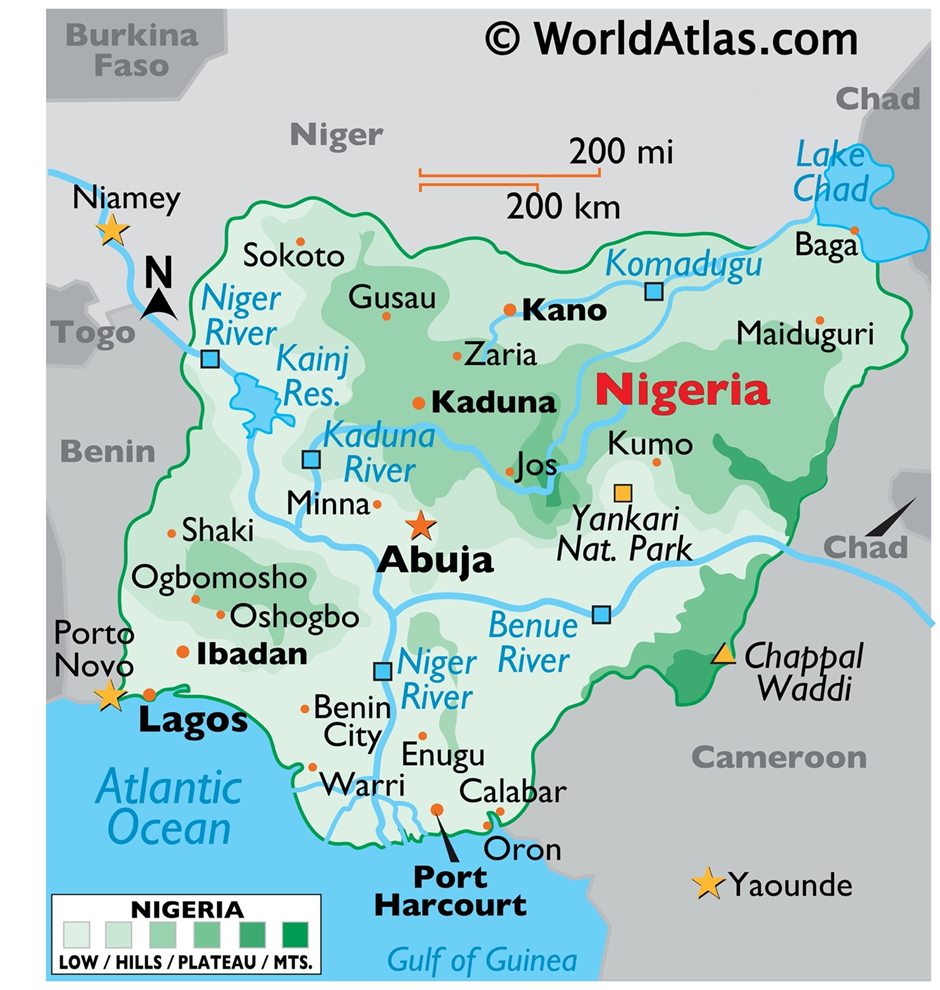
- Location and Geography:
- Nigeria is located in West Africa, bordered by Niger to the north, Chad to the northeast, Cameroon to the east, and Benin to the west. The Atlantic Ocean lies to the south, providing a crucial maritime boundary.
- Topographically, Nigeria has diverse landscapes, including coastal plains, savannas, plateaus, and mountains.
- The Niger River and Benue River are the two major waterways, forming a Y-shaped confluence at Lokoja.
- The climate varies from tropical rainforests in the south to Sahelian conditions in the north. The humid coastal region experiences heavy rainfall, while the northern region experiences semi-arid conditions, which lead to periodic droughts and desertification.
- Potential Natural Resources:
- Natural resources are abundant, making Nigeria an economic powerhouse. It has the second largest oil reserves in Africa after Libya and the largest gas reserves in Africa, primarily in the Niger Delta and offshore fields.
- Other resources include coal, limestone, tin, iron ore, lead, zinc, gold, and uranium.
- The agricultural sector is also significant, with key exports including cocoa, palm oil, rubber, and cassava. However, the sector remains underdeveloped due to inadequate infrastructure and climate challenges.
- Reason behind rise in inflation:
- The removal of fuel subsidies in 2023 significantly increased transportation and production costs, affecting businesses and consumers alike.
- Simultaneously, the depreciation of the naira (Nigerian currency) has made imports more expensive, raising the cost of essential goods and further straining household budgets.
- High energy costs and an erratic power supply have compounded the problem, forcing businesses to rely on costly generators, which escalate operational expenses. Additionally, insecurity in food-producing regions due to insurgent and bandit attacks has disrupted agricultural output, leading to food shortages and rising prices.
- Lastly, government borrowing and fiscal policies have contributed to a growing public debt burden, leading to higher interest rates, and further dampening economic stability and investment.
- The rising cost of living has triggered widespread protests and discontent. Food inflation is particularly severe, with staples like rice, bread, and maize becoming unaffordable for many households.
- The Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) has raised interest rates and implemented currency reforms to curb inflation, but structural economic issues persist, making economic recovery slow.
- Despite economic challenges, Nigeria remains a regional powerhouse with vast potential for industrialisation, technological growth, and agricultural expansion, provided that governance, security, and economic policies improve.
Brahmagiri Wildlife Sanctuary
Why in news?
- The state government's plan to establish a tribal village in Brahmagiri Wildlife Sanctuary's buffer zone raises concerns about their safety and potential wildlife conflicts, sparking debates on human-animal coexistence.
About Brahmagiri Wildlife Sanctuary:
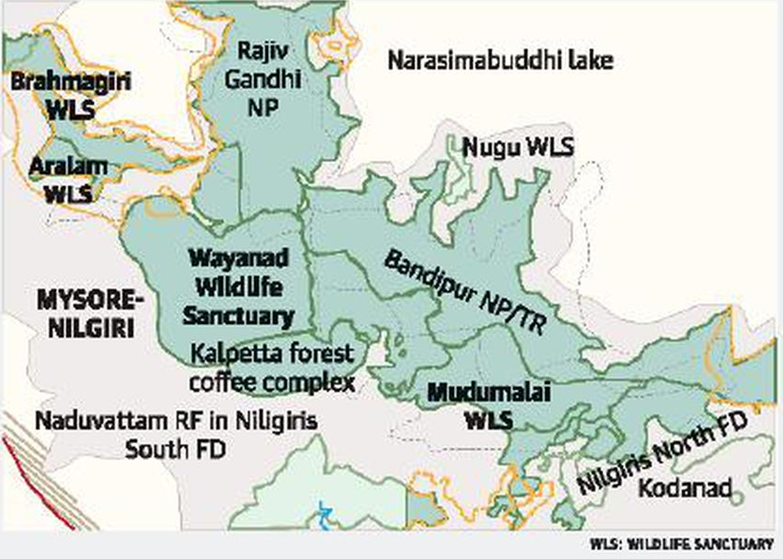
- Location:
- Brahmagiri Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the Kodagu district of Karnataka and is part of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage Site known for its rich biodiversity.
- The sanctuary is named after Brahmagiri Peak, which stands at 1,607 meters.
- The Lakshmana Tirtha River, a tributary of the Cauvery River, originates within the sanctuary, adding to its ecological significance.
- The terrain is characterised by undulating hills, steep valleys, and numerous hillocks, creating a diverse habitat for wildlife.
- Flora and Fauna:
- The sanctuary supports a mix of evergreen and semi-evergreen forests, interspersed with shoal forest patches in grasslands.
- Bamboo groves are also prominent, contributing to the unique ecosystem.
- The surrounding coffee and cardamom plantations create a buffer zone but also lead to human-wildlife interactions.
- Brahmagiri Wildlife Sanctuary is home to a wide range of fauna, including the rare and endangered lion-tailed macaque, which is endemic to Western Ghats.
- Other notable species include tigers, elephants, Indian gaurs, barking deer, and Malabar giant squirrels.
- Arboreal species like the giant flying squirrel and common langur are also frequently spotted.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict:
- The expansion of human settlements, agriculture, and plantations near the sanctuary has led to increased encounters with wildlife.
- Elephants and tigers often venture into human habitation, causing damage to crops and livestock, leading to retaliatory actions by locals.
- The state government's plan to settle tribals in the buffer zone has further raised concerns about their safety and the risk of intensifying conflicts.
- Deforestation and habitat fragmentation have also forced wildlife into human-dominated landscapes, necessitating better conservation measures, such as improved wildlife corridors and conflict mitigation strategies.
Swat Valley
Why in news?
- Pakistan's Swat Valley faces rising Taliban threats, prompting heightened security. Recent attacks on officials and civilians signal a resurgence, raising fears of instability and echoing the region's past militant insurgency.
About Swat Valley:
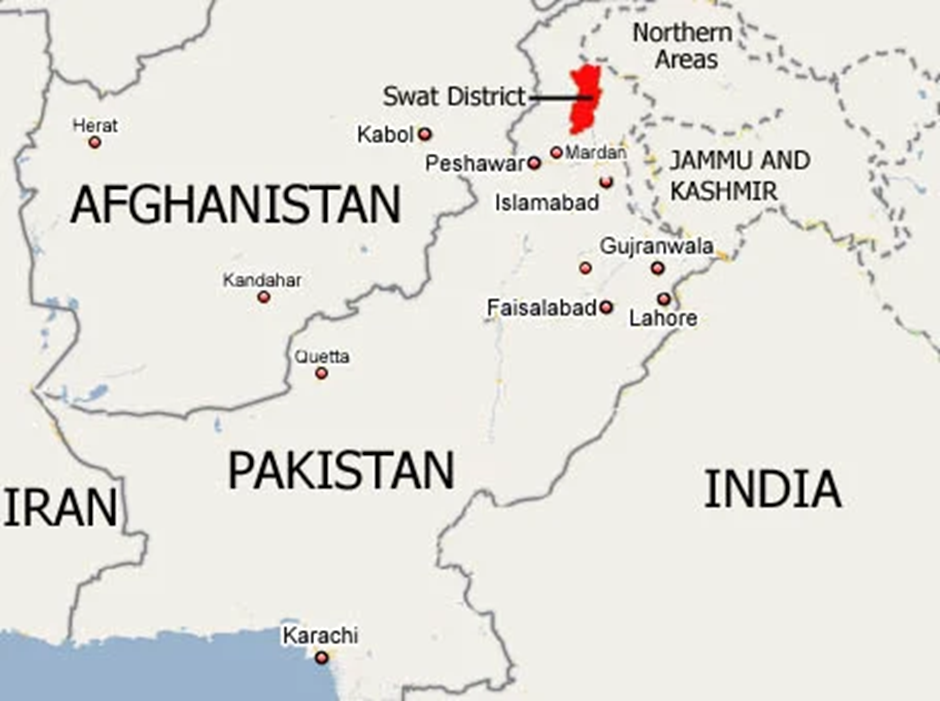
-
-
- Location and Geography:
- Location and Geography:
-
- Swat Valley, located in northern Pakistan’s Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province, is often called the “Switzerland of Pakistan” due to its scenic landscapes, lush green valleys, and snow-capped mountains.
- Nestled within the Hindu Kush mountain range, it is traversed by the Swat River, which sustains agriculture and local livelihoods.
- The valley experiences a temperate climate, with cold winters and mild summers, making it a popular tourist destination.
-
- Regional Security Concerns:
- Regional Security Concerns:
-
- Despite its natural beauty, Swat Valley has faced serious security challenges over the years. In the early 2000s, it became a stronghold for the Tehrik-e-Taliban Pakistan (TTP), which imposed strict militant rule, banning education for girls and enforcing harsh punishments.
- The Pakistani military launched Operation Rah-e-Rast (2009) to reclaim the region, restoring relative peace.
- However, security concerns have resurfaced, with the TTP and other militant groups regaining strength.
- Since early 2025, there have been targeted killings, bombings, and attacks on security forces, prompting heightened military presence.
- With growing instability in neighbouring Afghanistan, Pakistan faces renewed security threats, thereby raising fears of Swat once again becoming a battleground for extremist groups.
Banas River
Why in news?
- Archaeologists unearthed 9th-century idols from an ancient submerged temple in Rajasthan’s Banas River, shedding light on early Hindu architecture and historical riverine settlements.
About Banas River:
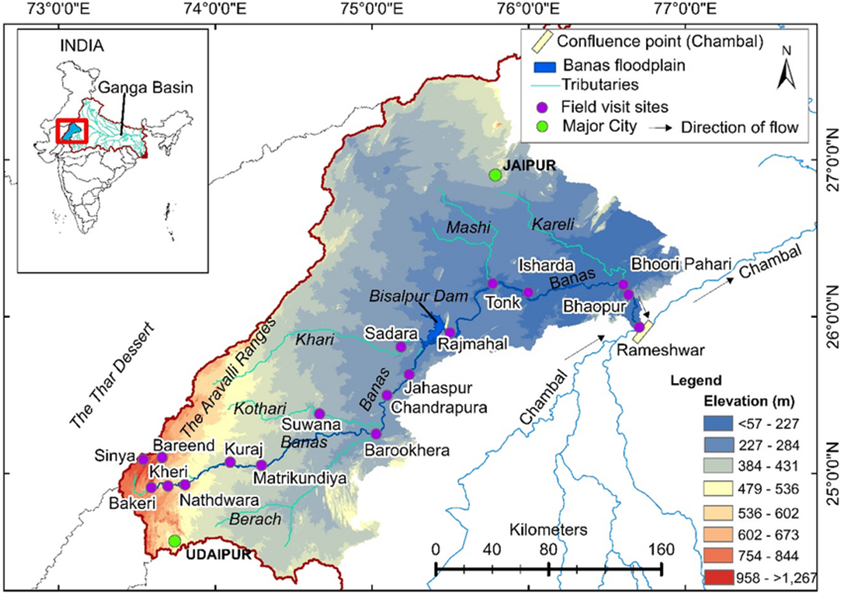
- Location and Origin:
- The Banas River is a major tributary of the Chambal River and flows through Rajasthan. It originates from the Khamnor Hills in the Aravalli Range near Kumbhalgarh in Rajsamand district.
- The river is often referred to as "Van Ki Asha" (Hope of the Forest) due to its crucial role in supporting vegetation and agriculture in the region.
- Although seasonal in nature, the Banas River plays a vital role in irrigation and drinking water supply, with projects like the Bisalpur-Jaipur water scheme ensuring water availability for Jaipur city.
- It traverses multiple districts, including Ajmer, Bhilwara, Bundi, Chittorgarh, Dausa, Jaipur, Pali, Rajsamand, Sawai Madhopur, Tonk, and Udaipur, draining the eastern slopes of the Aravalli Range.
- The river is enriched by several tributaries. Major right-bank tributaries include Berach and Menali, while significant left-bank tributaries are Kothari, Khari, Dai, Dheel, Sohadara, Morel, and Kalisil.
- The Morel River meets the Banas near Hadoli in Sawai Madhopur, and the Kalisil River flows through Sawai Madhopur District, further contributing to the basin.
- Historical and Cultural Significance:
- Apart from its hydrological significance, the Banas River holds historical and cultural importance. Ancient settlements, temples, and artefacts have been discovered along its banks, reflecting Rajasthan's rich heritage. Recent discoveries of 9th-century idols from a submerged temple highlight its archaeological significance.
- The Banas River basin was also a significant centre of Chalcolithic culture (Copper Age), with sites like Gilund and Ahar revealing evidence of early settlements (3000–1500 BCE).
- Excavations indicate copper tools, pottery, and agrarian practices, showcasing advanced metallurgy and trade networks. These findings highlight the region’s early urbanisation and technological advancements.
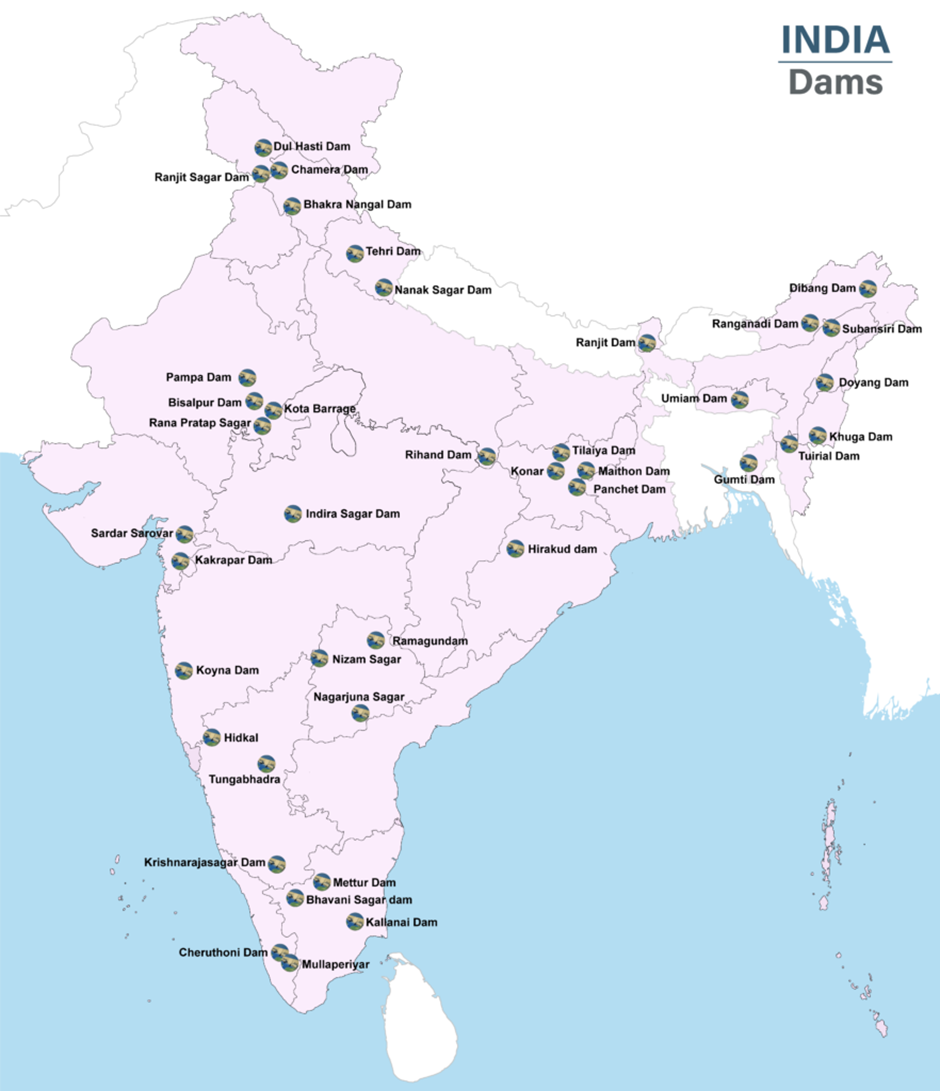
Hirakud Dam
Why in news?
- Union Cabinet approved DRIP-III for Hirakud Dam, Odisha, under the Dam Rehabilitation and Improvement Project, focusing on safety upgrades, climate resilience, and sustainable water management to enhance structural integrity and efficiency.
About Hirakud Dam:
-
-
- Location:
- Location:
-
- Hirakud Dam, built on the Mahanadi River, is India’s longest dam and the world’s longest earthen dam. It is located 15 km upstream of Sambalpur town in Odisha.
- It was constructed using earth, concrete, and masonry and created the Hirakud Reservoir, which is Asia’s largest artificial lake.
- It was inaugurated in 1957 and became India’s first major multipurpose river valley project post-independence, playing a crucial role in irrigation, power generation, and flood control.
- Within the reservoir, Cattle Island, which is home to a herd of wild cattle, is believed to be descendants of livestock left behind by villagers displaced during dam construction.
-
- Economic significance:
- Economic significance:
- The dam supports Kharif irrigation over 155,635 hectares and Rabi irrigation over 108,385 hectares, ensuring water availability for agriculture in Odisha’s Mahanadi delta. Additionally, 436,000 hectares receive indirect irrigation benefits from released water.
- Power generation capacity stands at 359.8 MW, contributing significantly to the region’s electricity needs.
- The dam provides flood protection to 9,500 sq. km of fertile delta land, mitigating disasters caused by the Mahanadi’s seasonal flooding.
|
UPSC CSE PYQs Q1. Consider the following pairs :
Answer: Option A
Q2. In which of the following states is lion-tailed macaque found in its natural habitats?
Answer: option A
|
|
Also Read |
|
UPSC Foundation Course |
|
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | CSAT Foundation Course |



