- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- NCERT Medieval History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Philippine President Signed 2 New Laws to Demarcate South China Sea Territories
Philippine President Signed 2 New Laws to Demarcate South China Sea Territories
11-11-2024
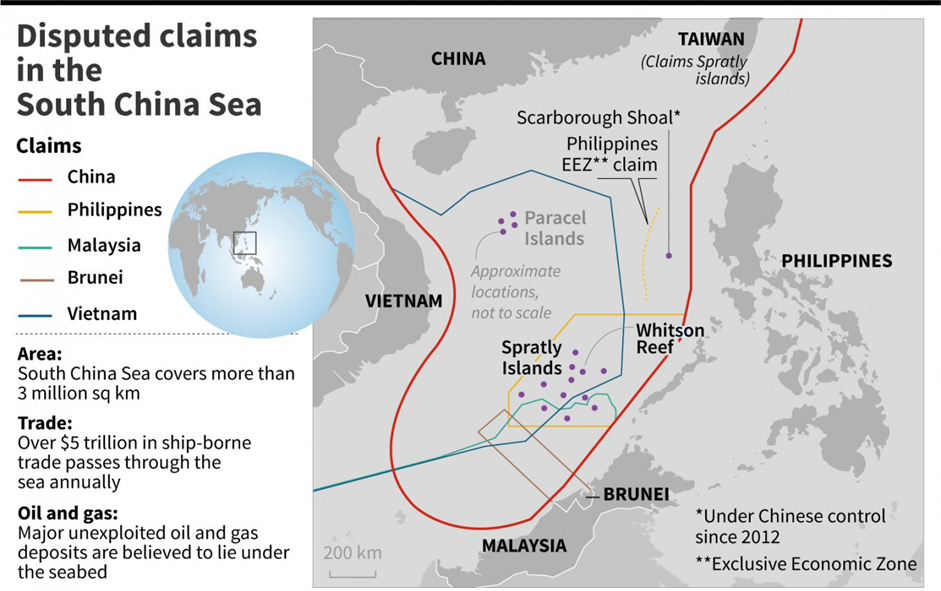
- On 8 November 2024, Philippine President Ferdinand Marcos Jr. signed two laws that strengthen the country's claim over its waters, especially in the disputed South China Sea.
- These new laws are causing tensions with China, which claims most of the South China Sea.
The New Philippine Laws:
-
Philippine Maritime Zones Act:
- This law clearly marks the areas where the Philippines has full rights to the seas, including the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), and other waters outside its mainland.
- Key Points:
- Defines the Philippine EEZ as a 200-nautical-mile area around the country where it has exclusive rights to use the resources (like fish, oil, and gas).
- EEZ stands for Exclusive Economic Zone, which is a maritime area that extends up to 200 nautical miles from a coastal state's baselines.
- In this zone, the coastal state has the right to explore and exploit resources, as well as the responsibility to manage and conserve them.
- This says that the Philippines has full control over the resources in this area, and no other country can exploit them.
- This follows the rules of the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), which sets international laws on ocean boundaries.
- Defines the Philippine EEZ as a 200-nautical-mile area around the country where it has exclusive rights to use the resources (like fish, oil, and gas).
-
Philippine Archipelagic Sea Lanes Act:
- This law allows the Philippines to set specific routes for foreign ships and aircraft that pass through the country’s archipelago.
- Key Points:
- Foreign vessels can pass through, but they must follow Philippine laws.
- The Philippines regulates which sea lanes and air routes can be used by ships and planes, while still respecting international law.
China’s Reaction:
- China has expressed strong opposition to these new laws.
- The Chinese Foreign Ministry summoned the Philippine Ambassador to protest, saying the laws violate China’s sovereignty over the area.
- China insists it has historical rights over the entire South China Sea, based on the “nine-dash line”, which the international community does not accept.
The South China Sea Dispute:
- The South China Sea is one of the most important and resource-rich parts of the world.
- This makes it a point of conflict because many countries, including China, Vietnam, Malaysia, and the Philippines, claim parts of it.
- 2016 Ruling: An international court in The Hague ruled in 2016 that China’s claims are not valid.
- This ruling supports the Philippines’ rights to its Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) in the region, but China refuses to accept this decision and continues to claim most of the area.
Philippines’ Legal Position
- UNCLOS Compliance: Both laws are based on UNCLOS, which sets the rules for the use of seas worldwide.
- Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ): The Philippines is entitled to resources in this 200-mile zone under international law, and it has the right to control activities like fishing and oil exploration.
- The laws also back up the 2016 arbitration ruling that rejected China’s territorial claims.
- Strengthening Maritime Rights: The new laws:
- Make clear where the Philippines has sovereign rights and control over its waters.
- Reaffirm the Philippines' ownership of artificial islands built in its EEZ.
Impact on International Relations
-
Tensions with China:
- These laws directly challenge China’s claim over the South China Sea.
- China views this as an attack on its territorial rights.
- China has used military force to enforce its claims, including building islands and using ships and planes to intimidate other countries in the area.
-
U.S. Involvement:
- The United States is a treaty ally of the Philippines and has stated it will defend the Philippines if it faces an attack in the South China Sea.
- This increases the risk of a military conflict involving China, the Philippines, and the U.S.
-
Global Impact:
- If China continues to reject international law, this could affect other countries’ rights to navigate or use resources in the South China Sea.
- ASEAN countries, such as Vietnam and Malaysia, also have claims in the area and could be impacted by these developments.
Enforcement and Challenges
- Enforcing the Laws: While the Philippines has passed these laws, enforcing them may be difficult due to China’s military presence in the area.
- China’s Aggression: China has been increasingly aggressive, using its coast guard and navy to intimidate the Philippines and other countries.
What Should the Philippines Do?
-
Diplomatic Efforts:
- The Philippines should continue to engage with China and other countries to protect its rights.
- It should also work with regional allies like the U.S., Japan, and Australia to build support for its position.
- Strengthen Defense: The Philippines should focus on improving its defense capabilities, including its navy and coast guard, to better protect its maritime territory.
- International Support: The Philippines can push for global support in international organizations like the United Nations to uphold the 2016 court ruling and ensure that China respects international law.
- Regional Cooperation: The Philippines should try to work with other Southeast Asian countries to ensure peace and stability in the South China Sea and to protect shared resources.
What is United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)?
Is UNCLOS Customary International Law?
Who Has Ratified UNCLOS?
How Many Countries Are in UNCLOS?
Did the U.S. Sign UNCLOS?
Who Did Not Sign or Ratify UNCLOS?Countries that have not signed or ratified UNCLOS:
|




