- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Olympus Mons, Mars' Massive Volcano
Olympus Mons, Mars' Massive Volcano
20-06-2024
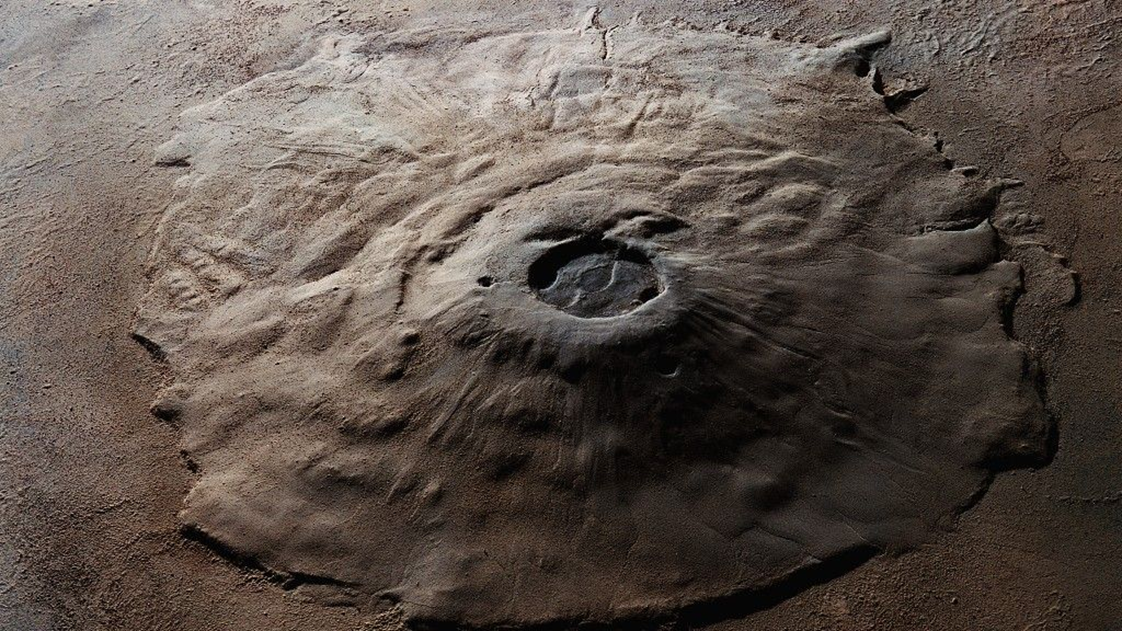
Scientists have recently uncovered the presence of frost on Olympus Mons, the tallest volcano on Mars, which suggests an active water cycle on the Red Planet.
About Olympus Mons:
- Location: Olympus Mons is a shield volcano situated in the western hemisphere of Mars.
-
Size and Scale:
- It holds the title of the highest point on Mars and the largest known volcano in our solar system.
- 16 miles (24 kilometres) high, the mountain is three times higher than Mount Everest.
- Its colossal width of 340 miles (550 kilometers) exceeds the entire chain of Hawaiian Islands.
- In comparison, Earth's largest volcano, Hawaii's Mauna Loa, measures 120 kilometers in diameter and 9 kilometers in height.
- Age: Olympus Mons is an ancient formation, estimated to be about 3.5 billion years old, indicating its early formation in Martian history.
- Profile: It is a remarkably flat mountain, with slopes as gentle as 2 to 5 degrees.
-
Summit Features:
- The summit is marked by a caldera, a vast depression resulting from volcanic activity, measuring 50 miles (80 kilometers) across.
- Unique to Olympus Mons, the summit caldera consists of several overlapping pits formed during various eruptive phases.
Key Facts about Shield Volcanoes:
-
Largest Volcanoes on Earth: Shield volcanoes hold the distinction of being the largest volcanoes on our planet.
-
Gentle Slopes: Unlike composite volcanoes, shield volcanoes do not form towering mountains with conical peaks. Instead, they are characterized by broad, gently sloping structures.
-
Lava Composition: Shield volcanoes are almost exclusively composed of basalt, a type of lava known for its high fluidity when erupted.
- Due to basalt's low viscosity, it can spread more effectively on the surface. Consequently, eruptions from shield volcanoes result in extensive lava flows covering great distances.
-
Formation Process: Shield volcanoes are built through successive eruptions that occur intermittently over vast periods of time.
-
Eruption Characteristics:
- Eruptions at shield volcanoes are typically non-explosive unless water somehow enters the vent.
- They are characterized by low-explosivity fountaining that forms cinder cones and spatter cones near the vent.
Examples: The Hawaiian shield volcanoes are iconic examples of this type of formation.



