- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
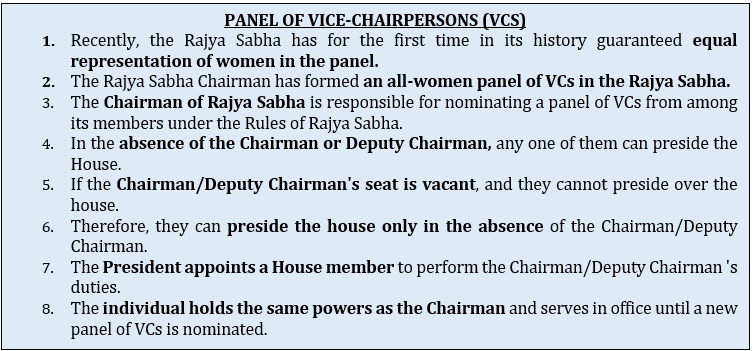
NARI SHAKTI VANDAN [CONSTITUTION (106TH AMENDMENT)] ACT, 2023
NARI SHAKTI VANDAN [CONSTITUTION (106TH AMENDMENT)] ACT, 2023
![img-NARI SHAKTI VANDAN [CONSTITUTION (106TH AMENDMENT)] ACT, 2023](https://i.filecdn.in/755esias/th-1-1697885409944.jpg)
Context
- In September 2023, the Constitution (106th Amendment) Act, 2023, was passed by Parliament to grant one-third reservation to women in the Lok Sabha, State Assemblies, and the NCT of Delhi.
Historical Background of Women’s Reservation
|
Pre-Independence Period |
Post-Independence Period |
|
|
Background of the bill
- The Constitution has been amended several times to allocate seats for women in Parliament and state legislative assemblies.
|
Bill |
Key Provisions |
Reason for lapse |
|
81st Amendment Bill, 1996 |
to allocate at least 1/3 of the total number of seats in the House of the People and State Legislative Assemblies for women. |
Dissolution of 11th Lok Sabha |
|
84th Amendment Bill, 1998 |
The proposed enactment aims to grant 15-year reservation for women in Lok Sabha, SLAs, and the National Capital Territory of Delhi. |
Dissolution of 12th Lok Sabha |
|
85th Amendment Bill, 1999 |
to ensure women's reservation in legislative bodies. |
Lack of consensus amongst the political parties |
|
108th Amendment Bill 2008 |
to allocate 1/3rd of all seats in Lok Sabha and SLAs to women, with the allocation of these seats to be determined by Parliament's prescribed authority. |
Dissolution of 15th Lok Sabha. |
|
128th Amendment Bill, 2023 |
a 33% reservation for women in the Lok Sabha, SLAs, and the Legislative Assembly of the National Capital Territory of Delhi. |
Both Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha passed the bill |
Key changes between 2008 and 2023 Bills
|
2008 bill |
2023 bill |
|
|
Reservation in Lok Sabha |
One-third of Lok Sabha seats in each state/UT to be reserved for women |
One-third of Lok Sabha seats for women across all Lok Sabha seats |
|
Rotation of Seats |
Reserved seats to be rotated after every general election to Parliament/legislative assembly |
Reserved seats to be rotated after every delimitation exercise |
Key Features of the 2023 Act
-
 Reservation for Women in Lower House (Lok Sabha):
Reservation for Women in Lower House (Lok Sabha): - The Bill introduced Article 330A to the constitution, incorporating provisions from Article 330, which grants seats to SCs/STs in the Lok Sabha.
- The Bill allows for the rotation of reserved seats for women to different states or Union Territories.
- The Bill aims to allocate one-third of the seats reserved for SCs/STs to women on a rotational basis.
- Reservation for Women in State Legislative Assemblies:
- The Bill introduces Article 332A, which mandates the reservation of seats for women in every state Legislative Assembly.
- One-third of the seats reserved for SCs and STs should be allocated to women.
- One-third of the seats allocated to women in direct elections to the Legislative Assemblies will also be reserved for them.
- Reservation for Women in NCT of Delhi (New clause in 239AA):
- The bill added a new clause Article 239AA(2)(b) that stipulates Reservation of 1/3rd seats for women in the Legislative Assembly of the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi.
- Article 239AA of the constitution grants special status to the Union Territory of Delhi as the national capital in terms of administrative and legislative functioning.
- Commencement of Reservation (New article - 334A):
- The Bill incorporated Article 334 of the constitution, which mandates parliament to review reservation provisions after 70 years of laws' existence.
- The provisions of this act will take effect after delimitation and the first census taken after the commencement of this act.
- The bill introduced a 15-year sunset clause for the review of reservation provisions for women by parliament.
- Parliament can legally extend the reservation for women.
- Rotation of Seats:
- The Parliament may by law determine the periodic rotation of seats reserved for women after each subsequent delimitation.
- This act's provisions will not impact the representation in legislative assemblies and the Lok Sabha until their dissolution.
Arguments in favor
|
Argument |
Significance |
|
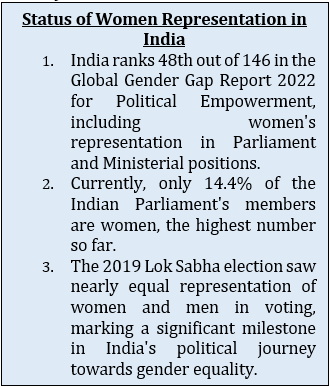
Increase in political representation of women |
India ranks low in global women's political representation, trailing behind 140 other countries, according to the Inter-Parliamentary Union 2021 Report. |
|
The ability of women’s leadership to bring change |
The study provides empirical evidence indicating that women leaders prioritize public goods that address women's concerns. |
|
Women legislators have been linked to enhanced economic outcomes and improved infrastructure development. |
|
|
A step towards decriminalization of politics |
Reserved seats can potentially decrease the presence of politicians with severe criminal cases. |
|
The Lok Sabha currently has 159 MPs facing serious criminal charges such as rape, murder, attempted murder, kidnapping, and crimes against women. |
|
|
More women vote share |
The political representation of women is consistently increasing, ensuring that their voting patterns are aligned with their overall voting patterns. |
|
Breaking patriarchy |
The policy advocates for gender equality in political leadership and decision-making. |
|
Gender-sensitization |
The text challenges conventional gender roles and perceptions of women's roles. |
|
Performance at local level |
Oxfam India's assessments show that local reservation for women has significantly increased crime reporting and improved access to basic amenities like drinking water and schools. |
|
Promoting Women-led development |
The implementation of this strategy can facilitate increased women's involvement in national and state-level policymaking. |
Arguments against the act
|
Argument |
Explanation |
|
Not a Homogeneous Group |
Women are not a homogenous community like caste groups, making comparisons with caste-based reservations inappropriate. |
|
Violation of the Equality Principle |
Critics argue that reserving seats for women contradicts the Constitution's equality guarantee, as it may be seen as a lack of merit-based competition. |
|
No Separate OBC Reservation |
The Bill does not offer separate reservations for OBC women, despite their significant proportion in the female population. |
|
Exclusion from Rajya Sabha and Legislative Councils |
The Bill does not provide reservation for women in the Rajya Sabha and legislative councils. The Geeta Mukherjee Committee (1996) recommended the inclusion of women in Rajya Sabha and Legislative Councils. |
|
Dependency on Census and Delimitation |
The implementation of women's reservation relies on the census and delimitation processes, which can be delayed or politically sensitive. |
|
Fear of Proxy Representation |
There are concerns that women may be used as proxies by male family members, similar to the situation in local governments. |
|
Restriction on Voters’ Choice |
Some argue that reserving seats for women restricts voters' choices, suggesting alternatives like women's reservation within political parties. |
|
Less impact on political empowerment of women |
Larger electoral reform issues, such as criminalization of politics and internal democracy in political parties, may hinder the political empowerment of women. |
Way forward
- Timely implementation: The act's implementation
 should be ensured through timely conduct and publication of census data and delimitation exercise.
should be ensured through timely conduct and publication of census data and delimitation exercise. - Capacity building: This involves involving civil society and other institutions in the local training and mentorship of women leaders to ensure their effective mobilization at state and national levels.
- Raise Awareness and Education: To raise awareness about women's rights and the significance of political participation.
- Combat Gender-Based Violence: Implement policies and legal measures to combat gender-based violence and harassment, thereby fostering a safer political environment for women.
- Electoral Reforms: The proposed reforms include the implementation of electoral reforms such as proportional representation and preferential voting to increase the representation of women in the political process.
- Intra-Party Democracy: To institutionalize intra-party democracy and promote more women candidates.
- Strengthen Women’s Self-Help Groups: To encourage women's involvement at the grassroots level to prepare them for higher office positions.
- Support Women’s Agencies: To enhance organizations that promote gender equality and women's empowerment.
- Engage Young Women: To promote girls' involvement in student politics and political debates at colleges and universities.
Conclusion
- The reservation is expected to significantly enhance the nation's development, particularly for women, by tackling the underlying socioeconomic and political disparities.