- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Melting of West Antarctica's Ice Sheet
Melting of West Antarctica's Ice Sheet
03-11-2023
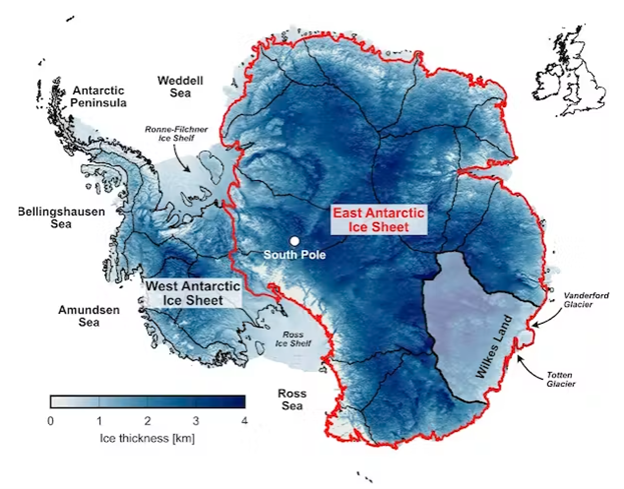
Why in News?
Recently, A study has made concerning predictions about the inevitable melting of the West Antarctic ice sheet due to warming ocean waters.
What do Ice Sheets Represent?
- About:
- An ice sheet is a massive glacial ice mass that covers over 50,000 square kilometers of land.
- The West Antarctic ice sheet, spanning vast land areas, is home to a significant amount of freshwater.
- Greenland and Antarctica, the world's two major ice sheets, collectively hold approximately two-thirds of the Earth's freshwater.
- Ice sheets' mass changes, either increasing or decreasing, can lead to a decrease or an increase in global mean sea levels.
- Processes Driving West Antarctic Ice Sheet Melting:
- Ice shelves stabilize land-based glaciers, melting through warm ocean waters eroding their edges, which are the edges of an ice sheet floating on the ocean.
- Ice shelves shrink or disintegrate, accelerating glaciers behind them, releasing more ice into the ocean and causing sea level rise.
How Do They Affect Sea Levels?
- Current Trends and Findings:
- Recent findings reveal widespread warming of the Amundsen Sea and increasing ice shelf melting in all scenarios considered.
- The projected melting will undoubtedly lead to a significant increase in sea level, significantly affecting coastal communities worldwide.
- Implications for India and Vulnerable Coastal Regions:
- India's vast coastline and dense population make it highly susceptible to sea level rise.
- Rising seas could lead to displacement or climate refugees for coastal communities, underscoring the need for adaptive strategies like protective infrastructure construction.

Actions has India Taken Related to Antarctica
- India entered the Antarctic Treaty in 1983 and gained consultative status on September 12th, 1983.
- The National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research, also known as the National Centre for Antarctic and Ocean Research, is India's leading R&D institution focused on Polar and Southern Ocean research.
- The Indian Antarctic Act of 2022 governs Antarctica's activities, focusing on mineral protection, native plant conservation, and prohibiting non-native bird introductions.
- India currently operates two research stations in Antarctica, Maitri and Bharati.
- Dakshin Gangotri, the first station built before 1985, is no longer operational.
Way Forward
- The Antarctic Treaty and its associated agreements are strictly adhered to for the preservation of the continent's unique environment and ecosystems.
- More efficient materials and infrastructure for research stations and vessels operating in harsh polar conditions, minimizing environmental impact needs to be developed.
- Researchers are exploring solar radiation management as a potential solution to slow ice melting, potentially using moderated emissions to combat ice sheet degradation.



