- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Launch Vehicle Mark
Launch Vehicle Mark
10-07-2023
Latest Context:
ISRO (Indian Space Research Organization) will launch Chandrayaan-3 with the LVM (Launch Vehicle Mark) 3.
About the Launch Vehicles of ISRO
- Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV): PSLV is one of the most reliable and versatile launch vehicles developed by ISRO. It is capable of launching a wide range of satellites into various orbits, including sun-synchronous orbit (SSO) and geostationary transfer orbit (GTO). PSLV has been used for numerous successful missions, including the Chandrayaan-1 and Mars Orbiter Mission.
- Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV): GSLV is a launch vehicle designed for placing satellites into geostationary orbits. It uses both solid and liquid propellant stages. GSLV has variants such as GSLV Mk II and GSLV Mk III, with Mk III being the more powerful version capable of launching heavier payloads.
- Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV): SSLV is a smaller launch vehicle being developed by ISRO specifically for launching small satellites. It is designed to provide an affordable and dedicated launch option for smaller payloads.
- Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV): ISRO has been working on the development of a reusable launch vehicle technology. The RLV is intended to enable the launch of satellites into space and return to Earth for reuse, potentially reducing the cost of space access.
About the LVM (Launch Vehicle Mark) 3
- The Launch Vehicle Mark 3 (LVM3), also known as GSLV Mk III (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III), is a launch vehicle developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- It is designed to carry heavier payloads into space, including large communication satellites and potential future manned missions.
Some key features and specifications of the GSLV Mk III are:
- Payload Capacity: The GSLV Mk III has a capability to launch payloads of up to 4,000 kilograms to Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) and 10,000 kilograms to Low Earth Orbit (LEO). It significantly increases India's capability to launch heavier satellites.
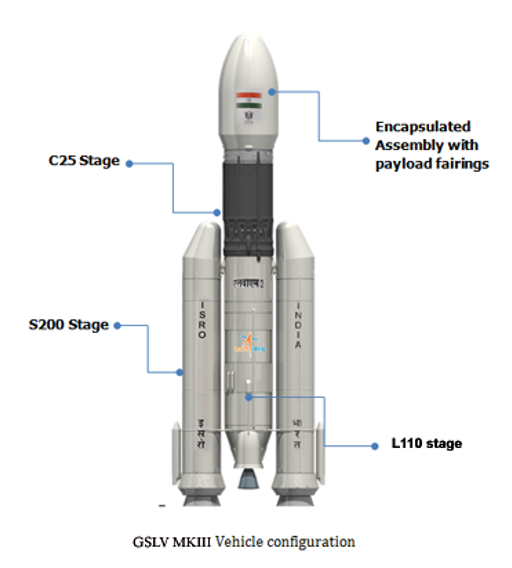
- Stages: The GSLV Mk III is a three-stage launch vehicle. The first stage, known as S200, consists of two solid propellant boosters that provide the initial thrust. The second stage, called L110, uses a liquid propellant engine. The third stage is a cryogenic upper stage named C25, which uses liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen as propellants.
- Height and Diameter: The GSLV Mk III stands about 43 meters tall with a diameter of 4 meters. The core stage, which includes the liquid propellant engine, is about 21 meters long.
- Applications: The GSLV Mk III is primarily intended for launching large communication satellites, both for national and international customers. It also has the potential to support future manned space missions undertaken by ISRO.
- Missions: The GSLV Mk III has been used for various successful missions. Notable among them is the Chandrayaan-2 mission in 2019, which aimed to land a rover on the lunar surface. While the lander module encountered some issues during the descent and landing phase, the overall mission was a significant achievement for ISRO.
Conclusion:
The development of the GSLV Mk III/LVM3 strengthens India's launch capabilities and reduces its dependence on foreign launch services. It represents a significant step forward in India's space program and provides the country with the capability to undertake more ambitious space missions in the future.
Must Check: IAS Coaching Centre In Delhi



