- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Kosi-Mechi River Linking
Kosi-Mechi River Linking
27-07-2024
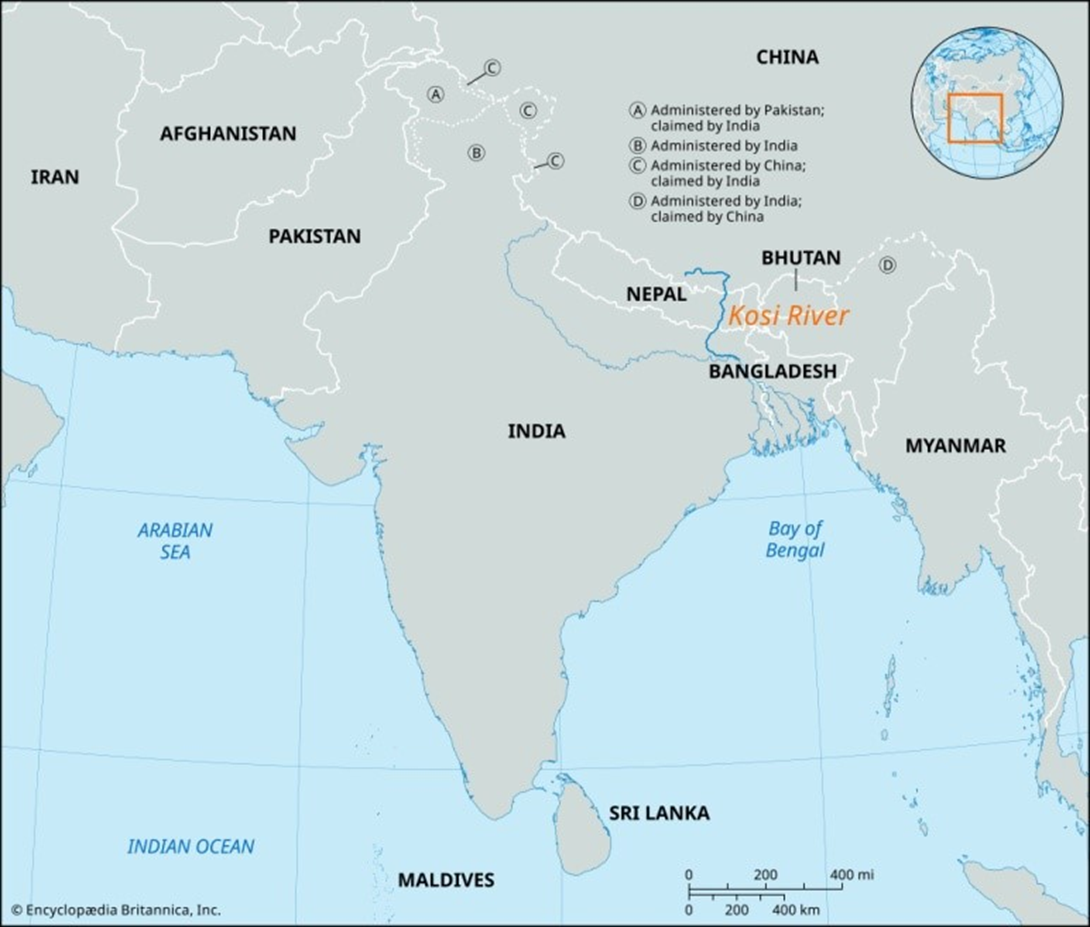
The long-awaited Kosi-Mechi river interlinking project in Bihar is closer to becoming a reality, with the Union Budget 2024-25 allocating a substantial Rs 11,500 crore.
The Project
- This project is a green project.
- Its environmental approval note states the project involves no displacement of population and there is no acquisition of any forest land.
- This project will provide a diversion to the surplus water of Kosi River through existing Hanuman Nagar barrage to Mechi River of Mahananda basin by a 2 km long canal.
- Purpose of the project: Flood control and irrigation for over 14 lakh hectares.
- There are no national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, or eco-sensitive zones within 10 km radius of the project.
Project Benefits and Significance
- The Kosi-Mechi interlinking project aims to address the recurring flood issues in Bihar by diverting excess water from the Kosi River to the Mechi River.
- The project is expected to significantly enhance irrigation capabilities, benefiting agricultural activities in the region.
- The environmental clearance for the project underscores its sustainability, ensuring minimal ecological impact.
- The allocation of Rs 11,500 crore in the Union Budget highlights the government's commitment to addressing flood management and agricultural development in Bihar.
About Kosi River:
- Origin: Confluence of three streams: The Sun Kosi, The Arun Kosi, and The Tamur Kosi.
-
Also known as: Saptakoshi for its seven upper tributaries.
- Flow: Trans-boundary river which flows through China, Nepal, and India.
-
Tributary of: Left bank: Ganges, near Kursela in Katihar district.
- Length: 729 km.
-
River basin borders: Tsangpo River basin in the north, Mahananda River basin in the east, Ganges Basin in the south, and the Gandaki River basin in the west.
-
Drainage: 74,500 sq.km, only 11,070 sq.km lie within Indian Territory.
-
Tributaries: Sun Koshi, Tama Koshi or Tamba Koshi, Dudh Koshi, Indravati, Likhu, Arun, and Tamore or Tamar.
-
Peaks located in the basin: Mount Everest, Kangchenjunga, Lhotse, Makalu, Cho Oyu, and Shishapangma.
- Projects: Kosi Barrage or Bhimnagar Barrage, Kosi-Mechi Interlink, Sapta Koshi High Dam Multipurpose Project, Sun Koshi Storage-cum-Diversion Scheme.
About Mechi River:
- Origin: Mahabharat Range in Nepal.
- Flow: Trans-boundary river flowing through Nepal and India.
-
Tributary of: Right Bank: Mahananda River, join at Kishanganj district of Bihar.
- Part of: Mahananda River basin.
- Drainage: Part of Mahananda River drainage which is 11,530 square kilometers.
Kosi-Mechi Interlink:
- Vulnerability: Kosi is known as the "sorrow of Bihar," as it has caused widespread human suffering in the past due to flooding and very frequent changes in course. (During the last 200 years, the river has shifted westwards for a distance of about 112 km).
Bihar Flood:
- Bihar is the state most affected by floods, accounting for close to 17.2 per cent of the total flood-prone areas in the country.
- Of the total 9.41 million ha, 6.88 million ha — 76 per cent of north Bihar and 73 per cent of south Bihar — is flood-prone.
- Currently, 28 of 38 districts in the state are flood-prone.
Conclusion and Forward-Looking Approach:
- The Kosi-Mechi river interlinking project represents a significant step forward in managing the recurring flood issues in Bihar and enhancing agricultural productivity.
- With its environmentally friendly approach and substantial government investment, the project is poised to bring about transformative changes in the region.
- Looking ahead, the successful implementation of this project could serve as a model for similar initiatives across the country, demonstrating the potential of innovative water management solutions to address complex environmental and agricultural challenges.
- As the project progresses, continuous monitoring and evaluation will be crucial to ensure its long-term sustainability and effectiveness, paving the way for a more resilient and prosperous future for the people of Bihar.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus




