- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Kerogen: The Source of Hydrocarbons
Kerogen: The Source of Hydrocarbons
17-04-2024

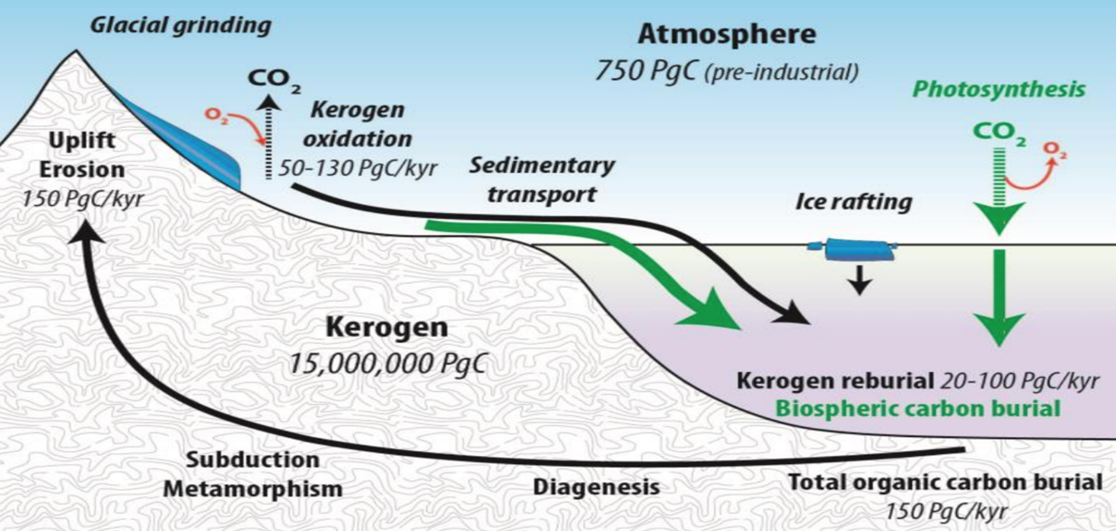
Kerogen is a solid, organic matter found in sedimentary rocks that is the main source of hydrocarbons in underground rocks.
- Kerogen is made up of dead plants, algae, and microorganisms that have been compressed and heated by geological processes.
About Kerogen:
- Composition: Kerogen is the portion of organic matter that cannot be removed using organic solvents, making it insoluble.
- Abundance: Kerogen represents approximately 90% of the organic carbon present in sediments.
- Location and Potential: Kerogen is found in sedimentary rocks and is the source material for almost all petroleum reserves.
- Origin: Kerogen typically consists of algae and woody plant material.
- Components: Kerogen contains both light and heavy hydrocarbons, which act as precursors to oil and natural gas.
- Molecular Weight: Kerogen has a higher molecular weight than bitumen, or soluble organic matter, which is formed from kerogen during petroleum production.
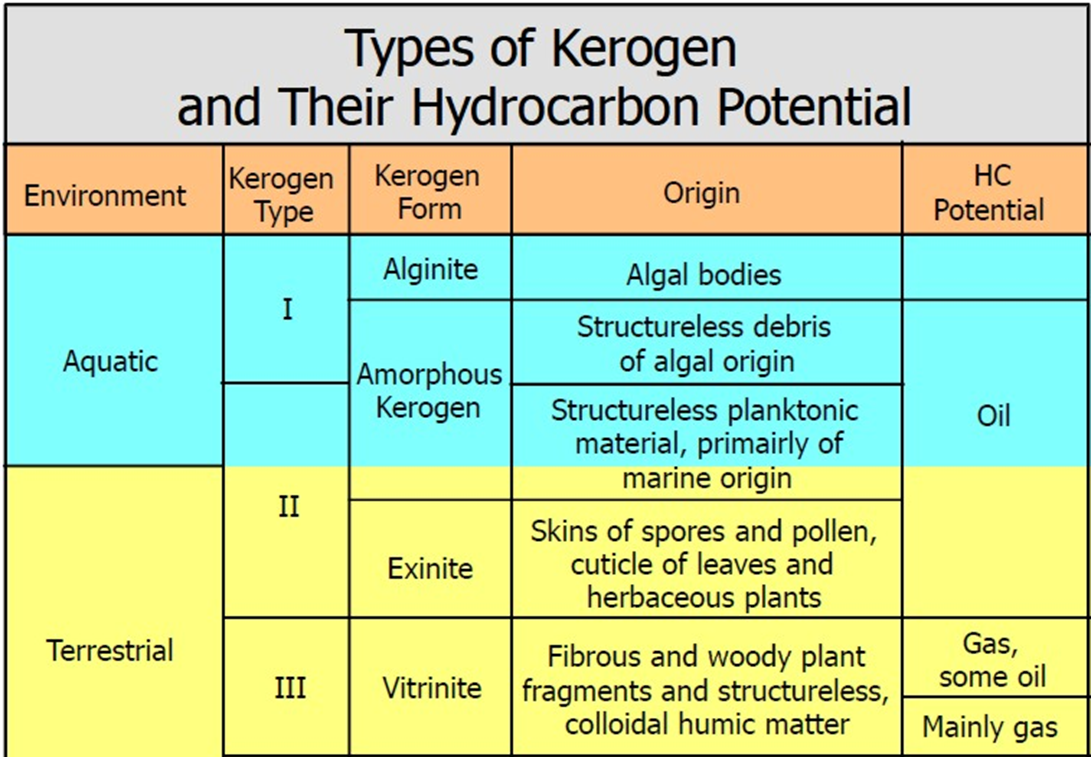
- Classification: Kerogens are classified into three types:
- Type I: Consists primarily of algal and amorphous (likely algal) kerogen, prone to generating oil.
- Type II: A mix of terrestrial and marine source material, capable of generating waxy oil.
- Type III: Woody terrestrial source material, typically generating gas.
- Hydrocarbon Control: The type of kerogen present in a rock largely determines the type of hydrocarbons produced within that rock.
FAQs:
Q: What are Hydrocarbons?
- Hydrocarbons are organic compounds that are made up of hydrogen and carbon atoms.
- They are colorless, hydrophobic, and have a faint odor, similar to gasoline or lighter fluid.
- Hydrocarbons can exist in a variety of phases and molecular structures, including gases, liquids, low melting solids, and polymers.
- Hydrocarbons are naturally occurring and are the basis of coal, natural gas, crude oil, and other important energy sources.
- They are highly combustible and produce carbon dioxide, water, and heat when burned, making them an effective fuel source.
- Examples of hydrocarbons include: Coal, Petroleum, Natural gas, Tar, and Propane.
- Hydrocarbons are important because they store energy in fossil fuels and biofuels. Petroleum is the main raw-material source for organic commodity chemicals such as polymers and solvents.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi



