- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Issue of Adverse Possession
Issue of Adverse Possession
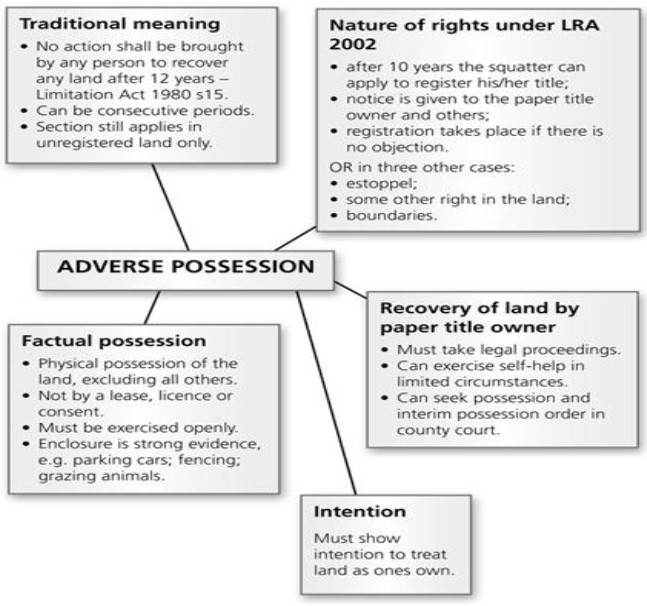
Latest Context:
Recently, the 22nd Law Commission has done a thorough examination of adverse possession and its implications in property law and recommended that no changes are necessary in the existing provisions under the Limitation Act of 1963.
So, What is Adverse Possession?
- Basically, the concept of adverse possession comes from the idea that land must not be left vacant but instead, be put to use.
- Adverse possession refers to the acquisition of property through hostile, continuous, uninterrupted, and peaceful possession.
- The concept aims to prevent long-standing doubts over land ownership and to benefit society by allowing someone to make use of idle land left by the owner.
- It also provides protection to individuals who have regarded the occupant as the rightful owner of the property.
Highlights of the Law Commission report are:
- The Law Commission stated in its 280th report that there is no justification to extend the statute of limitations.
- The report has argued that adverse possession is not a mode of acquiring title by force or fraud, but rather a recognition of the factual situation of possession and the legal consequences that flow from it.
- The report has highlighted the historical and constitutional aspects of adverse possession, and how it is in consonance with the principles of justice, equity and good conscience.
- The report has further stated that adverse possession is not a violation of the right to property under Article 300A of the Constitution, as it does not amount to deprivation or expropriation by the state, but rather a transfer of title by operation of law.
- The report has pointed out that adverse possession is not contrary to the human rights obligations of India under various international treaties and conventions.
- The report has concluded that there is no justification for introducing any change in the law relating to adverse possession, as it would create chaos and confusion in the land records and lead to litigation and disputes.
- The report has suggested that instead of changing the law, the government should focus on improving the administration and management of land records and ensuring that the rights and interests of all parties are duly protected.
Background
- History: The concept of "title by adverse possession" dates back to almost 2000 BC.
- Development: Its development continued through the ‘statutes of limitation’ in England, with the ‘Property Limitation Act of 1874’ being a significant milestone.
- Introduction to India: The law of limitation was introduced in India through the "Act XIV of 1859" and underwent significant changes with the enactment of the Limitation Act in 1963.
Some Major Provisions of the Limitation Act, 1963 are:
- Proof of Adverse Possession: The 1963 Act shifted the burden of proof of adverse possession on the claimant, thereby strengthening the position of the true owner.
- Fixed Time Period: Under the Limitation Act, 1963, any person in possession of private land for over 12 years or government land for over 30 years can become the owner of that property. To claim adverse possession, the possession must be open, continuous, and adverse to the rights of the true owner for the required statutory period.
- The Supreme Court, in the 2004 case of Karnataka Board of Wakf v Government of India, outlined the essential elements for proving adverse possession.
a) The claimants must establish the date of possession, the nature of possession, awareness of possession by the true owner, the continuity of possession, and that the possession was open and undisturbed.
b) In the 1981 ruling in Kshitish Chandra Bose vs. Commissioner of Ranchi, the top court delineated the requirements of openness and continuity.
SC’s Criticism of the Current Law:
- SC in the 2008 case of Hemaji Waghaji Jat v. Bhikhabhai Khengarbhai Harijan and Others, the Supreme Court criticised adverse possession as being unduly harsh on the true owner and benefiting dishonest trespassers. The court urged the government to reconsider and amend the law, recognizing the necessity for a fresh perspective on adverse possession.
- In response to the court's recommendation, the Ministry of Law and Justice referred the matter to the Law Commission in 2008 for examination and a subsequent report.
Some Arguments Against the Adverse Possession are:
- Give Promotion to False Claims: Adverse possession promotes false claims and burdens the judicial system with avoidable litigations.
- No Consent Required: Adverse possession allows someone to acquire property without the consent or knowledge of the true owner. This is considered unfair and unethical, as it disregards the owner's rights and denies them the opportunity to make decisions about their own property.
- Inequitable Outcome: Adverse possession can lead to unjust outcomes, especially when the true owner is unaware of the adverse possessor's occupation. The true owner may suddenly discover that their property has been taken away by someone who had no rightful claim to it, resulting in a loss of property and often emotional distress.
Additional Information
About the Law Commission of India (LCI)
- It’s a non-statutory body constituted by the Government of India from time to time, with definite terms of reference to carry out research in the field of law.
- LCI works as an advisory body to the Ministry of Law and Justice.
- 1st Law Commission of independent India was established in 1955 for a 3-year term.
- The Law Commission of India has submitted almost 280 reports so far on various topics ranging from civil law, criminal law, constitutional law, family law, personal law, environmental law, human rights law, etc.
Present Law Commission is 22nd one and its chairman is Justice Rituraj Awasthi (Former Chief Justice of Karnataka HC).



