- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Indus Valley Civilization (IVC)/Harappan Civilization
Indus Valley Civilization (IVC)/Harappan Civilization
31-08-2024
- From referring to the Harappan civilisation as the ‘Sindhu-Sarasvati’ and ‘Indus-Sarasvati’ civilisation, to multiple mentions of the ‘Sarasvati’ river, including noting its desiccation as one of the reasons for the decline of the Harappan society, to a mention of India having had a “prime meridian of its own” called the ‘Ujjayini meridian’.
- The new NCERT Class 6 Social Science textbook incorporates new perspectives, including references to the 'Sarasvati' river and its desiccation as a contributing factor to the decline of the Harappan society.
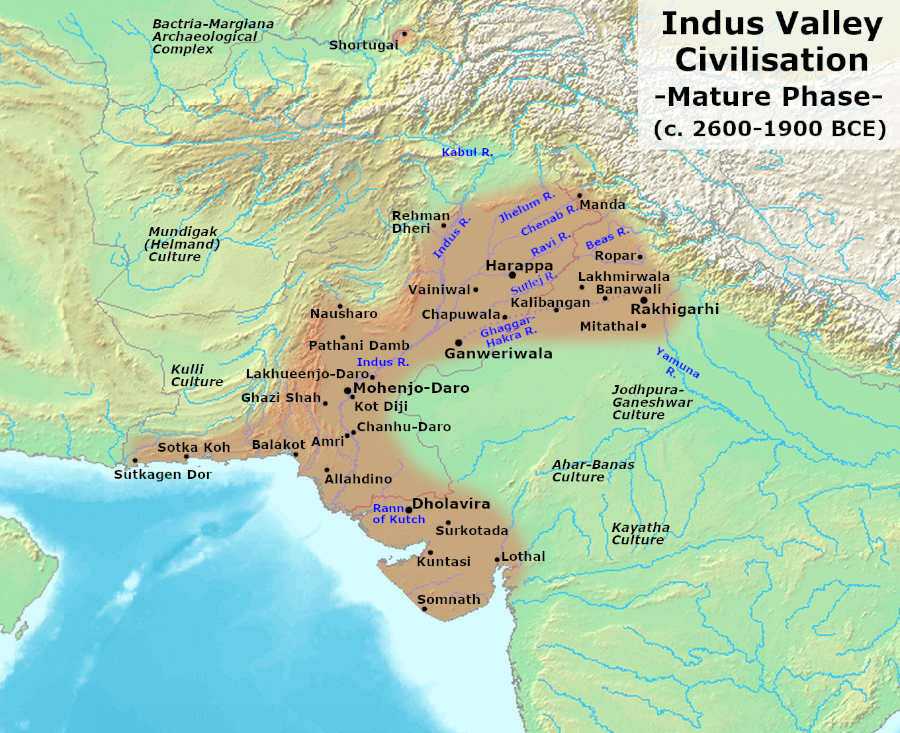
- The Indus Valley Civilization (IVC), also known as the Harappan Civilization, is one of the world's oldest urban cultures, dating back to around 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE. It was a Bronze Age civilization that flourished in the northwestern regions of South Asia, primarily in present-day Pakistan and northwest India.
Geographic Spread and Major Sites
The IVC extended over a vast area, encompassing parts of modern-day Pakistan and India. Key archaeological sites include:
- Harappa (Punjab, Pakistan): One of the first sites to be excavated, giving its name to the civilization.
- Mohenjo-daro (Sindh, Pakistan): Known for its advanced urban planning and the Great Bath.
- Dholavira (Gujarat, India): Notable for its unique water conservation system.
- Lothal (Gujarat, India): An important port city with a dockyard.
- Rakhigarhi (Haryana, India): One of the largest Harappan sites.
Urban Planning and Architecture:
The urban planning of IVC cities is a testament to their advanced engineering skills. Key features include:
- Grid Layout: Cities were laid out in a grid pattern with streets intersecting at right angles.
- Drainage System: An elaborate drainage system with covered drains and soak pits.
- Granaries: Large storage structures for surplus grain.
- Houses: Built with standardized burnt bricks, featuring multiple rooms and wells.
Economy and Trade:
The Harappan economy was primarily agrarian, supplemented by trade and commerce. Key aspects include:
- Agriculture: Wheat, barley, peas, and cotton were the main crops.
- Trade: Extensive trade networks with Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq), Afghanistan, and other regions. Evidence of trade includes seals, beads, and pottery.
- Craftsmanship: Skilled in metallurgy, bead-making, and pottery. The famous "Dancing Girl" bronze statue from Mohenjo-daro exemplifies their metallurgical prowess.
Script and Seals:
The Harappan script remains undeciphered, but numerous seals and inscriptions have been found:
- Seals: Made of steatite, featuring animal motifs and inscriptions. The "Pashupati Seal" depicting a seated figure surrounded by animals is notable.
- Script: Consists of pictographic signs, yet to be fully understood.
Social and Political Organization:
The social and political structure of the IVC is inferred from archaeological evidence:
- Society: Likely egalitarian with no clear evidence of a ruling class or centralized monarchy.
- Religion: Evidence of worship of mother goddess figures, animal worship, and possible proto-Shiva worship.
Decline of the Indus Valley Civilization:
The decline of the IVC around 1900 BCE is attributed to several factors:
- Climate Change: Shifts in the monsoon pattern leading to reduced rainfall and droughts.
- River Changes: Changes in the course of the Indus and Ghaggar-Hakra rivers affecting agriculture and settlement patterns.
- Invasion Theory: Earlier theories of Aryan invasions have been largely debunked in favor of environmental causes.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus




