- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
INDIA'S FIRST X-RAY POLARIMETRY MISSION:XPOSAT
INDIA'S FIRST X-RAY POLARIMETRY MISSION:XPOSAT
02-01-2024
Context
- ISRO's PSLV-C58 launched XPOSAT Satellite into an Eastward low inclination orbit on January 2024.
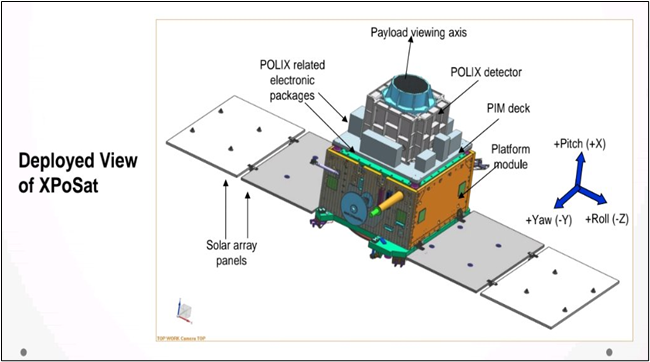
About X-Ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat)
- XPoSat is India's inaugural polarimetry mission for studying cosmic X-ray polarization and dynamics of X-ray sources.
- The spacecraft operates in Low Earth Orbit (~650 km altitude, ~6-degree inclination).
- It is the world's second X-ray polarimetry mission after NASA's Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) Mission.
- The mission's lifespan is 5 years.
- Two scientific payloads: X-Ray Polarimeter (POLIX) and X-ray SPECtroscopy and Timing (XSPECT).
POLIX |
XSPECT |
|
|
|
|
|
Objectives of the Mission
- Measure X-ray polarisation (8-30 keV) from 50 cosmic sources via Thomson Scattering using POLIX payload.
- Conduct long-term spectral and temporal studies (0.8-15 keV) of cosmic X-ray sources with XSPECT payload.
- Perform polarisation and spectroscopic measurements of X-ray emissions in a common energy band using POLIX and XSPECT payloads.
Polarisation of Light
- Light travels as transverse electromagnetic waves.
- Unpolarised light from sources like the sun vibrates in multiple planes.
- Polarisation restricts light waves' vibration to a specific direction/plane.
- Polarimetry measures polarisation characteristics, aiding astronomers in observing and measuring various object properties.
Why X-rays?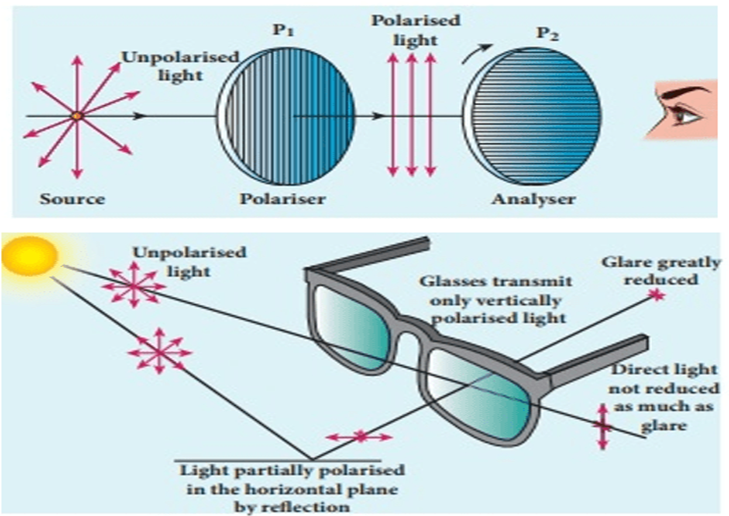
- X-rays, high-frequency and high-energy electromagnetic radiation, have short wavelengths (0.01 to 10 nanometres).
- X-rays emanate from extremely hot objects, such as pulsars and black hole accretion disks.
- Short X-ray wavelengths and high energy allow penetration of most materials, aiding in data collection from celestial sources.
- X-ray telescopes in orbit collect photons from specific sky regions, providing insights into distant celestial environments' composition, temperature, and density.
Significance of the Mission
- X-ray polarisation measurement aids in understanding X-ray emission in various astrophysical sources.
- Black holes, neutron stars, active galactic nuclei, and pulsar wind nebulae emit X-rays with complex mechanisms.
- Combining polarimetric, spectroscopic, and timing measurements overcomes limitations in understanding astronomical emission processes.
- Measuring X-ray polarisation deduces magnetic field orientation and strength in celestial objects.
- Magnetic fields play a crucial role in astrophysical processes, including particle generation, acceleration, and jet formation.
- X-ray polarisation helps understand high-energy particle behaviour in extreme environments.
- X-rays in extreme conditions come from supernova remnants, active galactic nuclei, and gamma-ray bursts.
Techniques and Challenges
- Developing precise X-ray polarimeters is challenging due to faint and complex X-ray signals.
- Analysing polarised X-ray data requires sophisticated algorithms to interpret measurements.
- Obtaining high-quality polarimetric data involves dealing with background noise and calibration issues.
Applications and Impact
- Black Hole and Neutron Star Studies: Polarimetry aids in understanding extreme conditions near black holes and neutron stars.
- Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN): Investigating X-ray polarisation helps unravel mechanisms behind AGN radiation and jet formations.
- Cosmological Insights: Polarimetry of cosmic X-ray background radiation offers insights into the universe's early stages and evolution.
Conclusion
- The XPoSat launch demonstrates India's commitment to advancing space science, specifically in X-ray astronomy.
- This mission contributes significantly to understanding high-energy astrophysical phenomena, marking a crucial step in India's space research and exploration.



