- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- NCERT Medieval History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
India's Employment Growth: A Robust Journey
India's Employment Growth: A Robust Journey

India has experienced significant employment growth, adding approximately 17 million jobs (a 36% increase) between 2016-17 and 2022-23. This growth reflects a robust economic trajectory, challenging the narrative of "jobless growth" often associated with rising GDP figures.
A Shift Away from "Jobless Growth"

Recent analyses, notably the Observer Research Foundation's report titled Busting the Myth of Jobless Growth, present data countering the concept that GDP growth does not correlate with employment increases.
Key Highlights from the Report:
- Employment Growth: Employment rose by 36%, with 17 million jobs created alongside an average GDP growth of over 6.5%.
- KLEMS Database: Employment data from the Reserve Bank of India’s KLEMS database indicates a consistent rise in employment since the 1980s.
- Worker Population Ratio (WPR): From 2017 to 2023, WPR increased by 9 percentage points (about 26%).
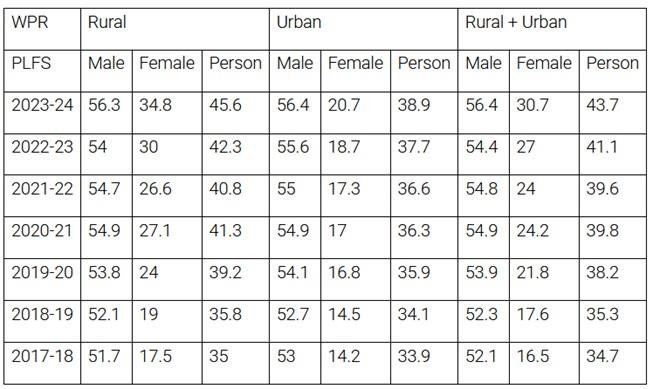
- Consumption-Driven Growth: Rising consumption is directly linked to employment generation, challenging claims of joblessness.
- Employment Elasticity: For 2017-2023, a 1.11% increase in jobs was observed for each 1% increase in value added.
- Sectoral Observations: The overall labor-capital ratio stands at 1.11, and for the services sector, it is 1.17, indicating that services contribute to job creation contrary to previous assumptions.
Economic Survey of India:

The Economic Survey of India aligns with these findings, highlighting significant improvements in employment and skill development:
Key Trends:
- Labor Market Improvement: Unemployment rate decreased to 3.2% in 2022-23.
- Sectoral Employment: Agriculture still employs over 45% of the workforce, but there's a gradual shift to manufacturing and services.
- Youth Employment: Youth unemployment dropped from 17.8% in 2017-18 to 10% in 2022-23.
- Female Workforce Participation: Increasing due to supportive government policies.
- Manufacturing Recovery: Factories with over 100 workers saw an 11.8% growth from FY18 to FY22.
- Wage Growth: Rural wages grew at 6.9% CAGR from FY15 to FY22, compared to 6.1% in urban areas.
- EPFO Payroll Growth: Net payroll additions to the EPFO more than doubled, rising from 61.1 lakh in FY19 to 131.5 lakh in FY24.
- Gig Economy Expansion: Workforce in the gig economy projected to grow to 2.35 crore by 2029-30.
- Manufacturing and AI: The manufacturing sector remains resilient against automation, indicating ongoing job opportunities.
Understanding India’s Economic Profile:
India's economic performance for FY 2023-24 indicates robust growth:
- Real GDP Growth: Estimated at 8.2% for FY 2023-24, up from 7.0% in FY 2022-23.
- Nominal GDP Growth: Increased by 9.6% in FY 2023-24, compared to 14.2% in FY 2022-23.
- Real GVA Growth: Projected at 7.2% in 2023-24, primarily driven by a 9.9% growth in manufacturing.
Conclusion:
India's employment landscape has shown remarkable improvement, driven by effective government policies, skill development programs, and robust economic growth. As India continues to harness its demographic dividend, further investments in education and skills will be essential to sustain this positive employment trajectory, positioning India as a rising global economic powerhouse.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus




