- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
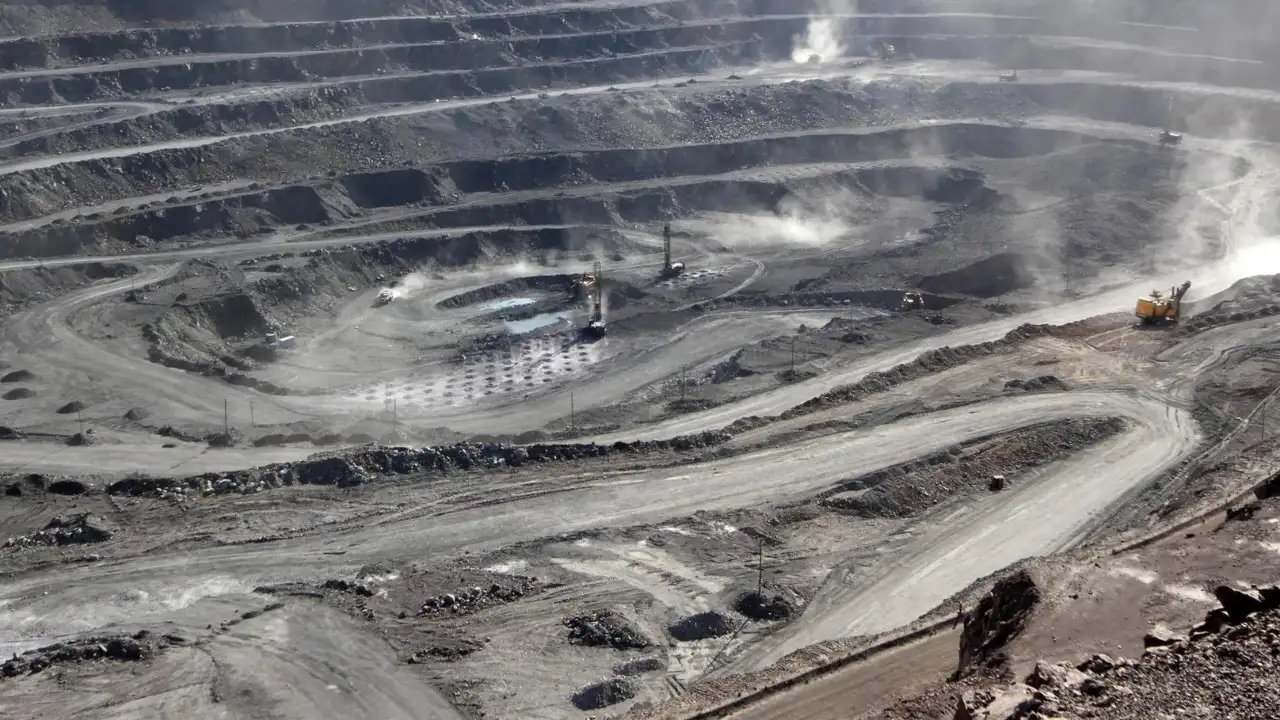
INDIAN LANDFILLS — A SOURCE OF MICROPLASTICS
INDIAN LANDFILLS — A SOURCE OF MICROPLASTICS
Context
Two research studies provide proof of tiny bits of plastic, called microplastics, in garbage sites in India. This could have a significant impact on the nearby environment.
|
What are Microplastics? |
More about Microplastics in Landfills:
1. Research has discovered tiny pieces of plastic, known as microplastics, in the liquid that comes from landfills. This liquid is called leachate and is created when rainwater passes through the waste in a landfill.
2. Landfills provide conditions that encourage the breakdown of plastic into microplastics. This happens due to various biochemical reactions, resulting in changes in temperature, high salt levels, low acidity, and the production of gasses.
Why are microplastic landfills dangerous?
A. Environmental Hazards:
- Soil and Water Contamination: Microplastics can seep into the soil and water, harming ecosystems.
- Pollution of Aquatic Life: Microplastics entering water bodies can affect aquatic organisms and disrupt the food chain.
- Airborne Spread: Tiny particles of microplastics can become airborne, potentially affecting air quality.
- Health Hazards:
1. Toxic Leaching: Microplastics can release harmful chemicals, like phthalates and Bisphenol A, into the surrounding environment.
- Bioaccumulation: Pollutants from microplastics can accumulate in organisms, posing risks to human health through the consumption of contaminated food.
- Health Impact on Humans and Animals: health issues in both humans and animals, including endocrine disruption, DNA damage, reproductive problems, and potential cancer risks.
Worldwide Efforts |
Efforts in India |
|
1. UNEP's Clean Seas Campaign |
1. Ban on single-use plastics |
|
2. Global Partnership on Plastic Pollution and Marine Litter. |
2. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) under Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules, 2022 where plastic producers are now responsible for plastic waste. |
|
3. Talks on making a worldwide rule on plastic (Global Plastics Treaty) |
3. Solid Waste Management Rules (2016), Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules, 2022. |
How to ensure Rules Enforcement?
1. Making sure landfills are set up properly and fixing open dumpsites is very important.
2. Watching to make sure rules are followed, and giving penalties if they aren't.
3. Doing research, coming up with new ideas, and using a circular economy approach.
Research Studies on Microplastics:
- Microplastics Study (NIT Andhra Pradesh)
-
- Microplastics concentrations found in landfill leachate in Hyderabad.
- Fiber was the most common microplastic shape.
- Various colors and polymer types detected.
- Groundwater Contamination Study (Anna University)
-
- Microplastics identified in groundwater samples around waste dumpsites in South India.
- Nylon, pellets, and foam were prevalent polymer types.