- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
India, UK secure ‘historic’ Free Trade Agreement
India, UK secure ‘historic’ Free Trade Agreement


- India and the United Kingdom have concluded a mutually beneficial Free Trade Agreement (FTA).
- on May 6, 2025,Iit was Announced by PM Narendra Modi and UK PM Keir Starmer
- The agreement includes a Double Contribution Convention on social security.
- FTA is a historic milestone that:
- Enhances trade, investment, and innovation.
- Deepens India–UK Comprehensive Strategic Partnership.
Aims to double bilateral trade (currently ~USD 60 billion) by 2030
What is a Free Trade Agreement (FTA)?
- An FTA is a bilateral or multilateral agreement between countries to reduce or eliminate customs duties and non-tariff barriers on goods and services traded between them.
- Objective of FTAs
- Promote trade by reducing costs and simplifying procedures for importers and exporters.
- Enhance market access for domestic producers.
- Encourage cross-border investments and ease mobility of professionals.
- Strengthen strategic and economic ties among partner nations.
- Scope of FTAs
- Trade in goods: Lower customs duties and quotas.
- Trade in services: Easier access and licensing.
- Investment protection: Stable and transparent frameworks.
- Intellectual Property Rights (IPR): Harmonized standards and enforcement mechanisms.
- Benefits of FTAs
- Wider choice and lower prices for consumers.
- Boost to exports and domestic production.
- Creation of jobs and support to MSMEs.
- Promote technology transfer and industrial upgrading.
- Facilitate integration into global value chains (GVCs).
Timeline of Negotiations between India and UK
|
Year |
Event |
|
Jan 2022 |
Official talks began post-Brexit Progress hampered by:
|
|
Nov 2024 |
Renewed push after meeting at G-20 Summit, Rio de Janeiro (Nov 2024). |
|
Feb 2025 |
Final rounds of negotiations resumed |
|
May 6, 2025 |
FTA officially concluded |
Trade in Goods: Tariff Outcomes
For India:
- 99% of Indian exports to the UK will face zero duty.
- Covers nearly 100% of bilateral trade value.
- Boosts labour-intensive exports, including:
- Textiles & garments
- Marine products
- Leather and footwear
- Gems and jewellery
- Toys, sports goods
- Engineering goods, auto components, engines
- Organic and specialty chemicals
For the UK:
- India to reduce tariffs on 90% of tariff lines.
- 85% of these become fully duty-free within 10 years.
- Notable reductions:
- Whisky & Gin: Current 150% → 75% (initial), then 40% by Year 10.
- Automotive imports: Tariffs drop from 100%+ to 10%, under quota.
- Medical devices, cosmetics, aerospace parts, electrical machinery, soft drinks, chocolates and biscuits, salmon, and lamb — significant duty cuts.
Who Benefits:
- British shoppers: Cheaper clothes, seafood (e.g., frozen prawns), footwear, and Indian food products.
- Indian consumers: Lower prices on high-end UK imports like whisky, cosmetics, and medical devices.
Services, Investments & Mobility
- Services & Investment Liberalisation
- FTA includes provisions to ease norms for:
- Cross-border services
- Digital trade
- Financial services
- Educational exchanges
- Promotes greater UK investment in Indian sectors like fintech, aerospace, healthtech, and education.
- FTA includes provisions to ease norms for:
- Professional Mobility
- It supports:
- Contractual service suppliers
- Business visitors
- Intra-corporate transferees (ICTs) and their families (with right to work)
- Independent professionals (e.g. chefs, yoga instructors)
- It supports:
What Is Double Contribution Convention (DCC) ?
- A bilateral social security agreement to avoid double social security payments by workers.
- Benefits for Indian Workers:
- 3-year exemption from paying UK social security taxes.
- Prevents double taxation—contributions in India recognized in the UK.
- Ensures retirement benefits eligibility without financial loss.
- Lowers employment costs for Indian IT and services companies in the UK
India’s FTA Landscape (as of May 2025) :
India has signed FTAs with 16 countries or regional groupings, including:
|
Country/Bloc |
Key Notes |
|
Sri Lanka, Bhutan |
Early bilateral FTAs in South Asia |
|
Thailand, Singapore, Malaysia |
Part of India–ASEAN engagements |
|
South Korea, Japan |
Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreements (CEPAs) |
|
Australia, UAE, Mauritius |
Recently concluded, covering goods and services |
|
ASEAN (10 nations) |
Multilateral framework for regional cooperation |
|
EFTA (Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, Switzerland) |
Signed in 2024–25; includes investment chapters |
India-UK Economic Relations:
Historical Perspective
|
Era |
Key Developments |
|
Colonial Rule |
1858–1947: British Crown governed India; Queen Victoria became Empress of India. |
|
Post-Independence |
1950: India remained in the Commonwealth after becoming a Republic. |
|
Cold War Period |
Strained ties due to India's non-alignment vs. UK's NATO alliance. |
|
1990s Reforms |
Economic liberalisation improved trade, investment, and political engagement. |
|
2004 Onward |
Strategic Partnership established; regular high-level visits and enhanced cooperation. |
- India and the UK share a strong bilateral economic relationship , with growing trade in goods and services, investment flows, and strategic cooperation.
- The Indian diaspora in the UK (over 1.8 million people ) plays a crucial role in enhancing ties.
Bilateral Trade : (As of August, 2024)
- India’s Rank for UK: 12th Largest Trading Partner
- Contribution to UK Total Trade: 2.1%
- India enjoys a services surplus with the UK.
Total Trade (Goods + Services)
|
Year |
Total Trade (£ billion) |
|
2021–22 |
£27.1 |
|
2022–23 |
£36.3 ↑ 34.2% (£9.2 bn increase) |
Investment Flows
Indian Investment in UK
- 108 Projects (2023–24), 7,533 New Jobs
- Ranked 2nd largest FDI source after the US.
- 971 Indian Companies in UK:
-
- Combined Revenue: £68.09 billion
- Corporate Tax Paid: £1.17 billion
- Employees: 118,430
- Over 65,000 Indian-owned companies in UK:
-
- Revenue: £36.84 billion
- Tax Paid: £1 billion+
- Jobs Created: 174,000+
UK Investment in India
- 6th Largest FDI Source (after Mauritius, Singapore, USA, Netherlands, Japan)
- Cumulative Equity Inflows: $35 billion (April 2000 – March 2024)
- Accounts for ~5.17% of total FDI inflows into India
- 635 British Companies in India:
-
- Turnover: INR 4,888.4 billion
- Employees: 666,992
Masala Bonds
- First issued by HDFC in London (2016)
-
- Masala bonds are rupee-denominated bonds issued by Indian entities in international markets.
- They are a type of debt instrument that allows Indian companies to raise funds from foreign investors in Indian rupees (INR) rather than the investor's local currency.
- The name "masala" is a reference to the Indian origin of these bonds, similar to how masala is a blend of spices used in Indian cuisine.
- Listed on London Stock Exchange
- Indian firms have raised over £13.41 billion via masala, dollar, and green bonds
- Notable issuers: NTPC, IREDA, IRFC
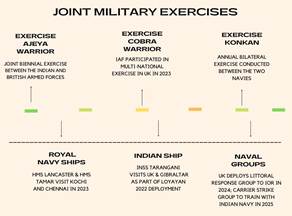
Key India-UK Joint Military Exercises :
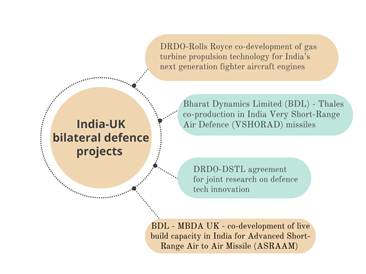
Key India-UK Bilateral Defence Projects
Significance of Bilateral Relations
- UK is part of India’s Indo-Pacific vision.
- “China Plus One” strategy aligns UK with India as a reliable partner.
- Support on UNSC reforms and Indo-Pacific stability.
- Cooperation in AUKUS, Commonwealth, G20, and Afghanistan
- Focus on renewables, net-zero targets, and energy access.
- Collaborations: Glasgow Pact, OSOWOG (One Sun One World One Grid).
5. Challenges in Bilateral Relations
|
Issue |
Details |
|
Russia-Ukraine War |
UK criticizes Russia; India remains neutral → policy divergence. |
|
Pakistan/China Ties |
UK’s balancing act complicates India’s security engagement. |
|
Khalistan Issue |
Allegations of UK harbouring Sikh separatist elements → diplomatic strain. |
|
Defence Procurement |
UK slow to align with India’s G2G (Government-to-Government) model. |
|
Extradition Issues |
Delays in high-profile cases like Vijay Mallya, Nirav Modi. |
|
Illegal Migration |
1 lakh+ undocumented Indians in UK; no migration pact yet. |
|
Colonial Legacy |
Historical grievances remain sensitive (Partition, cultural restitution, etc.). |
|
Also Read |
|
UPSC Foundation Course |
|
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | CSAT Foundation Course |




