- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
India Skills Report 2025
India Skills Report 2025
12-12-2024
- In December 2024, the India Skills Report 2025 was released by Wheebox, in collaboration All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), Confederation of Indian Industry (CII), and Association of Indian Universities (AIU).
- The report highlights important data about employability across various states in India.
- The report is based on a thorough evaluation of candidates who took part in the Global Employability Test (GET) across India. It aims to compare the employability skills of candidates with global standards.
- It provides valuable insights into the preparedness of India's workforce for future job markets.
- Significance: The report evaluates candidates from various sectors, highlighting trends in skills demand, employability across industries, and regional disparities in talent.
- It serves as an essential tool for policymakers, educational institutions, and industries to understand the current state of employability in India.
Key Findings
- Global Employability Outlook: By 2025, 55% of Indian graduates are projected to be globally employable, up from 51% in 2024. This indicates a positive trend in preparing graduates for international job markets.
- Domestic Employability Growth: The employability rate of Indian graduates has increased by 7% this year, reaching 55% in 2025, compared to 51% in 2024.
- This improvement is attributed to government programs like the Skill India Mission and National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, as well as institutional efforts to better align education with industry demands.
- Most Employable Graduates
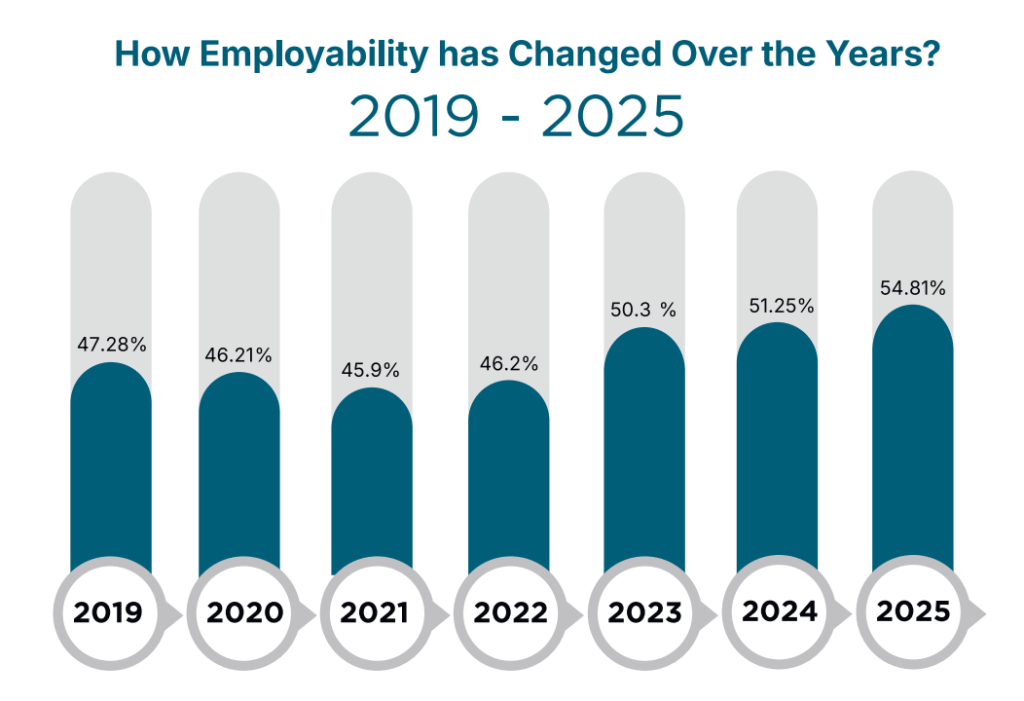
- Management Graduates: 78% employability rate, the highest among all sectors.
- Engineering Graduates: 71.5% employability rate.
- MCA Graduates: 71% employability rate.
- Science Graduates: 58% employability rate.
- Regional Trends in Employability: Maharashtra leads with the highest employability rate of 84%. Delhi follows at 78%, Karnataka at 75%, Andhra Pradesh at 72%, Kerala at 71%, and Uttar Pradesh at 70%.
- Key Hubs for Skilled Talent: Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Delhi are emerging as major centers for skilled talent. Cities like Pune, Bengaluru, and Mumbai are leading in providing a large pool of employable workers.
- States Preferred for Employment: Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, and Uttar Pradesh are among the leading states preferred for employment opportunities.
- Gender Disparity in Employability: The employability rate for men is expected to rise from 52% in 2024 to 54% in 2025. However, Women’s employability is projected to decline from 51% in 2024 to 48% in 2025, reflecting a widening gender gap.
- Top States for Male Employability: Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Maharashtra, and Uttar Pradesh.
- Top States for Female Employability: Rajasthan leads, followed by Gujarat and Kerala.
- Student Interest in Internships: 93% of students surveyed showed interest in internships, emphasizing a strong desire for practical work experience in addition to academic studies.
- Tamil Nadu shows the highest preference for internships, followed by Uttar Pradesh, Kerala, and Karnataka.
- Hiring Intent for 2025: The hiring intent for FY 2026 is projected at 9.8% across various industries. Global capability centres, heavy engineering, and the banking sector show the highest intent for hiring.
Strategic Vision for 2030: Strengthening India’s Talent Pool
The report presents strategies to enhance India's workforce:
- Vocational Training: Focus on high-demand fields like AI, cybersecurity, and green energy.
- Cross-Border Collaboration: Address skill shortages in aging populations through international partnerships.
- Technology in Education: Integrate AI and automation in education and skill assessments.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Increase female participation in the workforce.
Government Initiatives for Skill Development
- Skill India Mission (SIM): The Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) delivers skill development, re-skilling, and up-skilling training through a broad network of centers, colleges, and institutes.
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY): Focuses on providing skill development training through Short-Term Training (STT) and re-skilling/up-skilling via Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL), targeting youth, especially in rural areas.
- Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS) Scheme: Aims to train non-literates, neo-literates, school dropouts (up to 12th grade), and individuals with basic education aged 15-45.
- It offers age relaxation for "Divyangjan" and other deserving cases. Priority is given to women, SC, ST, OBC, and minorities in rural and low-income urban areas.
- Udaan Scheme: Provides skill development for youth from Jammu and Kashmir, with a focus on employability and vocational training to enhance career prospects.
- Rural Self Employment Training Institutes (RSETIs): Offer skill development and self-employment training, mainly targeting youth in rural areas to promote entrepreneurship and reduce unemployment.
- National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS): Encourages apprenticeship training by providing financial support to both apprentices and employers, helping improve industry-specific skills.




