- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
India’s Press Freedom Ranking in 2025
India’s Press Freedom Ranking in 2025
20-05-2025

Significance: GS II; Governance; Freedom of Speech;
Why in the News?
India ranked 151st out of 180 countries in the World Press Freedom Index 2025, moving up from 159th in 2024 and 161st in 2023.
- Despite this improvement, India remains in the “very serious” or “severe” category, indicating ongoing concerns about media autonomy and freedom.
- The World Press Freedom Index is published annually by Reporters Without Borders (RSF), a global media watchdog.
|
Key Highlights from Global Press Freedom 2025
|
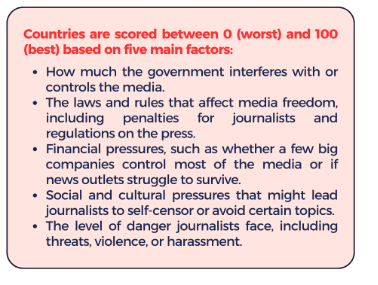
What are the key challenges before Indian and Global Media?
- Economic Survival vs. Editorial Independence: Many news organizations struggle to maintain editorial integrity while facing financial pressures, often leading to self-censorship or reliance on government/corporate funding.
- Tech Giants’ Dominance: Companies like Google, Facebook, and Amazon absorb a large share of advertising revenue, undermining the financial sustainability of traditional journalism.
- Legal and Physical Threats: Journalists face lawsuits, harassment, and violence, making it difficult to report without fear.
What are the main factors affecting India’s Press Freedom Ranking?
- Political Influence: Concentration of media ownership among political and corporate entities threatens diversity and independence.
-
- Journalists in India face threats, violence, and intimidation, which impacts their ability to report freely.
- Economic Pressures: Financial instability and dominance of tech giants in advertising revenue have weakened the media’s economic base.
- Legal Challenges: Restrictive laws, criminal defamation, and regulatory hurdles limit journalistic freedom and encourage self-censorship.
- Media Plurality: The growing monopoly of a few media houses reduces the diversity of viewpoints and increases the risk of biased reporting.
What are the potential measures to uphold Press Freedom in Indian Society?
- Ensuring Journalists’ Safety: Government needs to provide more adequate security and legal support to journalists facing threats or attacks, and hold perpetrators accountable.
- Need to provide financial assistance and regulatory support to independent media organizations to reduce their dependence on external influences.
- Promoting Principled Journalism and Media Literacy: Promote media literacy programs to educate the public on discerning credible information from propaganda and misinformation.
- Encourage media outlets to adhere to professional ethics and standards, fostering a culture of integrity and accountability.
Way Forward: India’s Ranking is up, but problems remain. In many countries, journalists are under pressure from governments, businesses, and even criminals. Many places in the world are now considered “dangerous” for journalism.
- Press freedom needs to improve, news organizations need to be financially independent, have diverse ownership, and get better legal protection.



