- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
India’s Fisheries and Aquaculture Sectors Critical for Nutrition Security: FAO
India’s Fisheries and Aquaculture Sectors Critical for Nutrition Security: FAO
- The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) has emphasized the critical role of India’s fisheries and aquaculture sectors for ensuring nutrition security.
- At a session organized by the FAO in New Delhi on 20 November 2024, Assistant Director-General and Director of FAO’s Fisheries and Aquaculture Division, highlighted both the opportunities and challenges facing these sectors in India.
- World Fisheries Day Event: The Indian Department of Fisheries, under the Government of India (GoI), hosted an event on 21 November 2024, to mark World Fisheries Day.
- This event provided a platform for discussions on India’s fisheries and aquaculture sectors, with a focus on climate change, food security, and nutrition security.
What is Aquaculture and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)?
|
Aquaculture |
The cultivation of aquatic plants, animals, and organisms for various purposes, including commercial, recreational, and scientific. |
|
Types of Aquaculture |
1. Marine Aquaculture: Farming oceanic species. 2. Freshwater Aquaculture: Farming species in inland waters like ponds and rivers. |
|
Purpose |
- Commercial Production: Food, industrial products, ornamental. - Stocking: Sport fisheries, bait, fee-fishing operations. - Feedstocks: For pharmaceutical and chemical industries. |
|
Historical Background |
Aquaculture dates back to 500 BC; it gained commercial importance in the mid-20th century. |
|
Global Reach |
Aquaculture happens in coastal waters, freshwater ponds, rivers, and even land-based tanks. |
|
Growth |
Fastest-growing form of food production. 50% of all seafood consumed by humans comes from aquaculture. |
|
Common Species Farmed |
- Fish: Carp, catfish, salmon, tilapia. - Shellfish: Shrimp, oysters, clams, mussels, scallops. - Seaweed: Gaining popularity. |
|
Major Global Producers |
- China: Nearly 60% of global farmed seafood. - Other leading countries: Indonesia, India, Vietnam. |
About Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) |
|
|
Overview |
A UN specialized agency established in October 1945; the oldest permanent UN agency. |
|
Mandate |
- Defeat hunger and improve global food security. - Increase agricultural productivity. - Raise rural living standards. |
|
Functions |
Coordinates efforts in agriculture, forestry, fisheries, and land and water resources. Collaborates with governments and agencies globally. |
2. The Importance of Fisheries and Aquaculture for India’s Nutrition Security:
- Critical Role in Nutrition Security: FAO stresses that India’s fisheries and aquaculture sectors are pivotal for ensuring nutrition security in the country.
- The sectors are major sources of protein and essential nutrients for millions of Indians, particularly in coastal and inland areas.
- Global Significance: Globally, approximately 600 million people rely on fisheries and aquaculture for their livelihoods, making it one of the most important sectors for food security worldwide.
- India, being the world’s second-largest producer of aquaculture, is in a prime position to leverage this sector for both national nutrition security and economic growth.
3. Climate Change: The Biggest Disruptor for India’s Aquaculture:
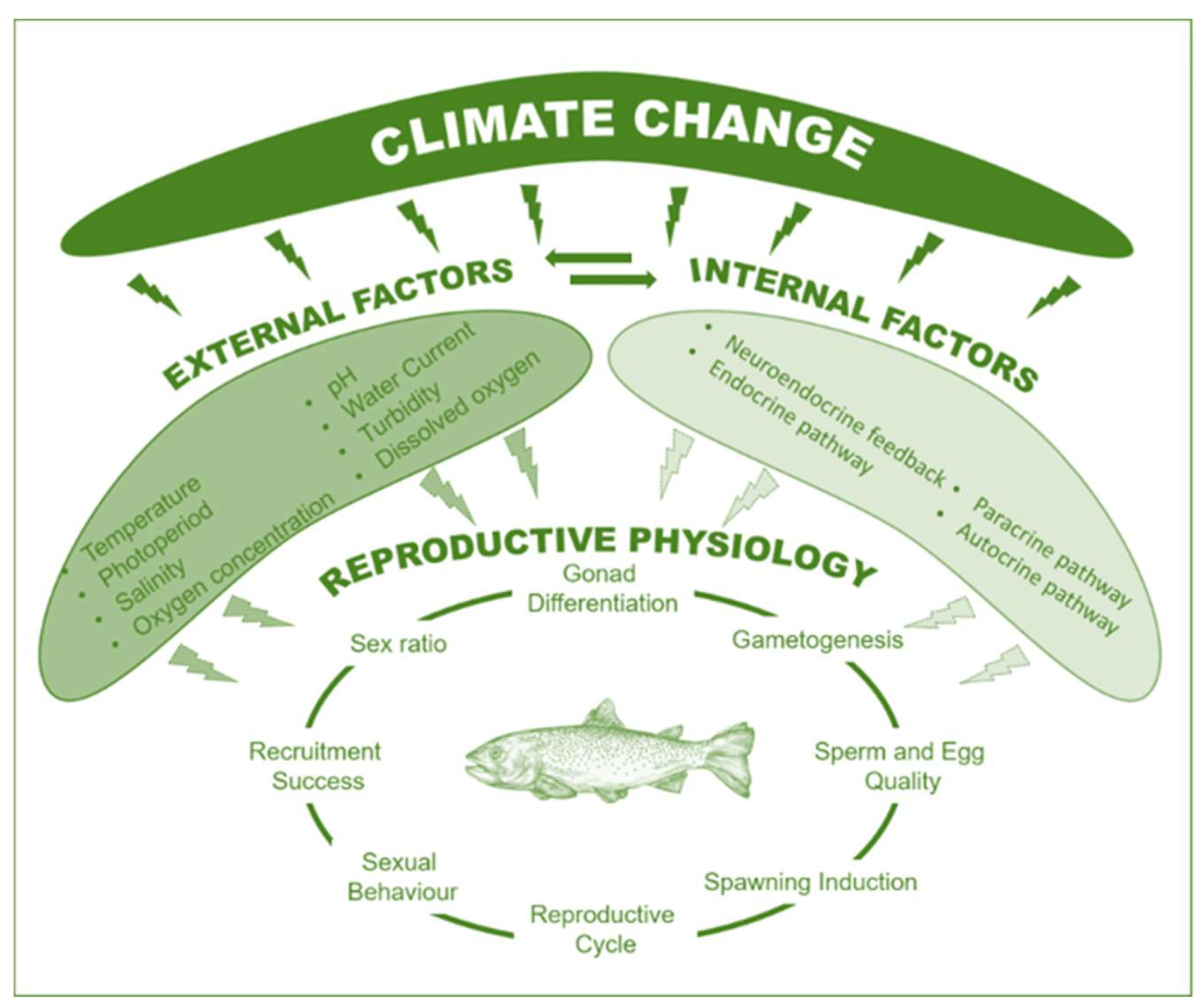
- Impact of Climate Change: During the discussions, it was highlighted that climate change is the biggest disruptor for aquaculture in India.
- Changing climate conditions, including rising temperatures, ocean acidification, and shifting fish migration patterns, are challenging the sector’s stability and productivity.
- Adaptation and Mitigation: Addressing the impact of climate change on India’s fisheries and aquaculture sectors requires adaptive measures such as sustainable fishing techniques, diversification of species, and improved management practices to ensure the sector’s resilience against climate-related disruptions.
4. India's Fisheries and Aquaculture Potential:
- India's Ranking in Global Aquaculture: India is the 2nd-largest producer of aquaculture in the world and leads in inland fisheries.
- It ranks 6th globally in marine fisheries.
- The country has immense potential to further enhance its fisheries and aquaculture output by implementing better management strategies and leveraging technological innovations.
- To realize its full potential, effective and sustainable management of both marine and inland fisheries is essential.
- The focus should be on increasing productivity, ensuring equitable distribution of benefits, and improving the livelihoods of the fishing communities involved.
5. FAO’s "Blue Transformation" and Alignment with India’s Policies:
- Blue Transformation Vision: The FAO’s Blue Transformation initiative aims to create more sustainable, productive, equitable, and impactful fisheries and aquaculture sectors.
- The vision focuses on increasing the contribution of aquatic foods to addressing hunger and poverty while integrating these foods more effectively into agrifood systems.
- India’s Alignment with Blue Transformation: India’s Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY), a flagship scheme, aligns with the FAO’s Blue Transformation vision.
- PMMSY aims to bring about a Blue Revolution through the sustainable and responsible development of India’s fisheries sector, including enhancing fish production, strengthening the value chain, and improving post-harvest management.
6. Key Objectives of India’s Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY):
- Sustainability and Inclusivity: The PMMSY focuses on the sustainable and inclusive growth of the fisheries sector, ensuring that all stakeholders, particularly small-scale fishers and fish farmers, benefit from its development.
- Improving Fish Productivity and Value Chain: The scheme aims to double the income of fishers and fish farmers, enhance fish production and productivity, and modernize the post-harvest value chain.
- This includes improving the quality and marketing of fish, strengthening the fisheries management framework, and expanding export opportunities.
7. Fisheries and Aquaculture’s Role in Employment and Income Generation:
- Livelihoods for Millions: The fisheries and aquaculture sectors are major sources of livelihood in India, employing over 20 million people at the primary level.
- The number of people employed along the value chain (processing, packaging, distribution) is even higher, indicating the sector’s vast economic impact.
- Fastest-Growing Sector: With its rapid growth, the fisheries and aquaculture sector in India is committed to become one of the fastest-growing sectors in the country, offering significant employment and income opportunities, especially in coastal regions and rural areas.
8. FAO’s Support for Strengthening India’s Fisheries and Aquaculture:
- Technical Expertise and Knowledge: The FAO continues to offer technical expertise and knowledge transfer to strengthen India’s fisheries and aquaculture sectors.
- This includes sustainable practices, climate change adaptation, and strategies for improving nutrition security.
- Collaboration Across Sectors: The FAO stresses the need for collaboration across sectors to fully tap the potential of India’s fisheries and aquaculture.
- This involves coordination between government bodies, private enterprises, research institutions, and international organizations to ensure the sector’s growth is sustainable, inclusive, and resilient.
Conclusion:
The fisheries and aquaculture sectors hold immense potential to contribute to India’s nutrition security and economic growth. However, to fully harness this potential, the sectors must adapt to climate change, implement sustainable practices, and promote inclusive growth that benefits fishing communities and aquaculture farmers across the country. The FAO will continue to offer technical expertise, policy recommendations, and capacity-building initiatives to support India in achieving a sustainable, equitable, and productive fisheries and aquaculture sector, which can contribute significantly to national food security and global nutrition goals.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus




