- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
India's elite counter-terrorism force : National Security Guard (NSG)
India's elite counter-terrorism force : National Security Guard (NSG)
22-04-2024
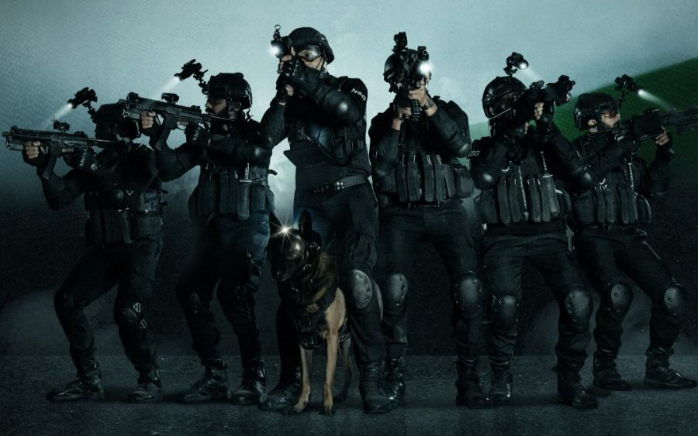

Senior IPS officer Nalin Prabhat has been appointed as the Director-General of National Security Guard (NSG), the country’s counter-terrorism force, according to a Personnel Ministry order.
- Prabhat, a 1992 batch IPS officer of Andhra Pradesh cadre, is presently working as Additional Director General in CRPF.
- “The Appointments Committee of the Cabinet (ACC) has approved his appointment as the Director General, NSG for a period up to August 31, 2028.
- Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB) chief Daljit Singh Chawdhary was holding the additional charge of the NSG.
About the National Security Guard (NSG):
- Special Force Mandate: The NSG is a specialized force primarily dedicated to counter-terrorism activities, serving as the nation's second line of defense.
- Black Cats: NSG members are commonly known as "Black Cats" due to their distinctive black drill cotton coveralls and balaclavas or helmets.
-
Establishment:
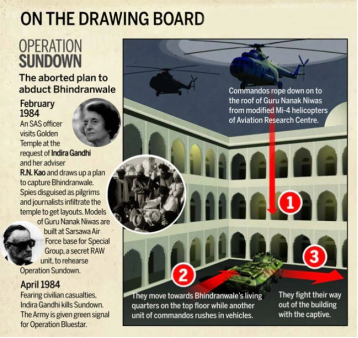
- It was raised in 1984,following Operation Blue Star and the assassination of Indira Gandhi.
- It was created by the Cabinet Secretariat under the National Security Guard Act of the Indian Parliament in 1986.
-
Inspiration: Modeled after the Special Air Service (SAS) of the UK and the GSG-9 of Germany.
-
Administrative Control: The NSG is under the administrative and operational control of the Union Ministry for Home Affairs.
-
Motto: "Sarvatra Sarvottama Suraksa" (Safety above All, Supreme Safety)
-
Headquarters: New Delhi
-
Director General (DG):
- Selection Process: The DG, who heads the NSG, is selected by the Home Ministry.
- IPS Officers: All DGs have been officers from the Indian Police Service (IPS).
-
Specific Goals:
- Neutralizing terrorist threats
- Handling hijacking situations
- Bomb disposal and IED management
- Post-blast investigations (PBI)
- Hostage rescue
- VIP security
-
Exceptional Deployment: The NSG is designed for exceptional situations, not intended to replace the functions of State Police Forces or other paramilitary forces.
-
Operational Philosophy: Swift and speedy strikes followed by immediate withdrawal from the theater of action.
-
Two Main Elements:
- Special Action Group (SAG): Comprises Army personnel.
- Special Ranger Group (SRG): Comprises personnel drawn from the Central Armed Police Forces and State Police Forces.
-
National Bomb Data Centre (NBDC):
- Centralized Database: Maintains a centralized database of bombing activities in India and abroad.
- Intelligence Gathering: Collects, collates, analyzes, and evaluates terrorist bombing activities, disseminating relevant information to law enforcement agencies.
 FAQs:
FAQs:
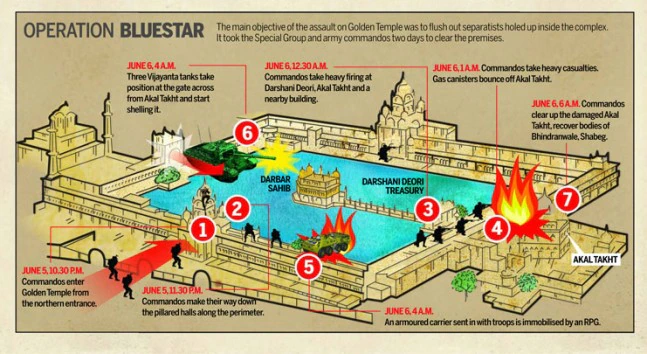
Q: What is Operation Blue Star?
- Operation Blue Star was a military operation conducted by the Indian Army in June 1984 to remove militants from the Golden Temple in Amritsar, Punjab.
- The operation was ordered by the Indian government to remove the militants, led by Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale, a former head of the Sikh seminary Damdami Taksal, and other Sikh separatists. Bhindranwale died in the operation on June 6, 1984.
- The operation resulted in a violent confrontation between the Indian Army and the militants, and the Golden Temple, a sacred Sikh shrine, was significantly damaged.
- The operation also had severe ramifications for many, including the assassination of Indian Prime Minister Indira Gandhi by her Sikh bodyguards, Satwant Singh and Beant Singh, on October 31, 1984.