- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC): A Modern Silk Route
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC): A Modern Silk Route
18-04-2025
- Union Commerce and Industry Minister recently described IMEC as more than a trade route — calling it a modern-day Silk Route that connects civilizations through commerce and infrastructure.
- He emphasized that IMEC will significantly improve trade efficiency and reduce costs across continents.
Key Economic Benefits of IMEC
- Up to 30% reduction in logistics costs, making trade more affordable and competitive.
- Around 40% reduction in transportation time, ensuring faster movement of goods.
- Seamless connectivity between Asia, the Middle East, and Europe through integrated infrastructure.
Implementation Strategy Proposed by the Minister
- Stakeholder Engagement: Collaboration among industry players, think tanks, and academia is essential for effective planning and execution.
- Innovative Financing Models: Use of instruments like long-term IMEC Bonds to attract private and institutional investment for large-scale projects.
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC)
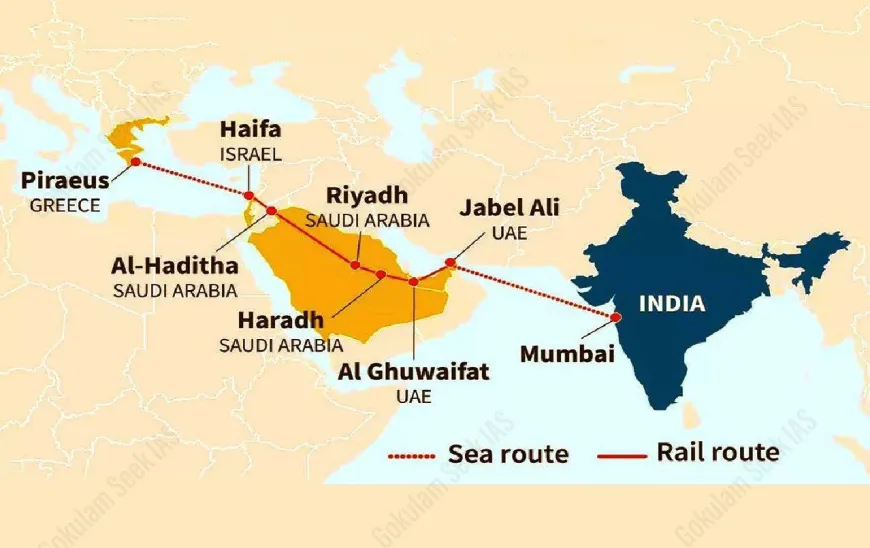
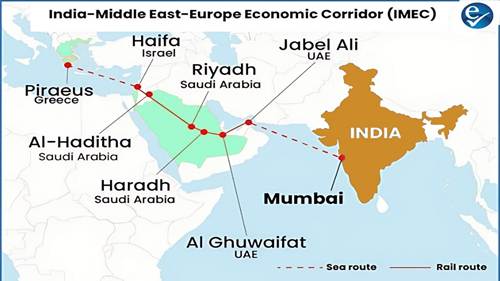
About IMEC
- Type: A multi-modal connectivity project aimed at establishing integrated trade and infrastructure corridors.
- Formalization: Signed through a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) during the G20 Summit 2023 held in New Delhi.
- Participants: India, European Union, France, Germany, Italy, Saudi Arabia, UAE, and the United States.
- Core Objective: To develop a network of ports, railways, roads, pipelines, and sea routes to enhance regional and intercontinental trade.
Strategic Significance of IMEC
- Geostrategic Relevance:
- Reduces reliance on traditional maritime routes such as the Suez Canal.
- Increases resilience against global disruptions and bottlenecks in sea trade.
- Geoeconomic Impact:
- Enables deeper economic integration between India, the Middle East, and Europe.
- Facilitates smoother movement of energy, goods, and digital connectivity.
- Alternative to China’s BRI:
- Presents a democratic, transparent, and rules-based counter-model to the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- Promotes a more inclusive global infrastructure development framework.
Historical Parallel: Silk Route
- The Silk Route was a major trade network operational from the 2nd century B.C. to the 15th century A.D..
- It connected Asia to Europe, enabling the exchange of goods, cultures, and ideas across continents.
- IMEC echoes this legacy by building a modern, strategic trade corridor in a digitally connected global economy.




