- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
India Climbs to 3rd in Global Wind & Solar Energy Production
India Climbs to 3rd in Global Wind & Solar Energy Production

Why in News:
India has become the world's third-largest producer of electricity from wind and solar energy by overtaking Germany according to the sixth report of the global energy think tank 'Embers Global Electricity Review'. Now, only China and America are ahead of India in this sector.
Sixth Report of Embers Global Electricity Review: Key Points
- 15 percent of electricity has been produced from wind and solar energy globally, in which India's share has been 10 percent at the global level.
- Low-carbon sources, including renewables and nuclear power, together provided 40.9 per cent of the world’s electricity in 2024. This is the first time the 40 per cent mark has been crossed since the 1940s.
- In India, clean sources accounted for 22 per cent of the electricity generation. Hydropower contributed the most at 8 per cent, while wind and solar together accounted for 10 percent.
- Global solar power generation is 6.9 per cent of the electricity mix. While solar contributed 7 per cent of the India’s electricity in 2024 with addition of 24 gigawatts in the year 2024.
- India’s total electricity demand rose by 5% in 2024. However, instead of turning to coal, India is adding clean energy capacity at a record pace. In 2024, India more than doubled its new solar power capacity compared to 2023.
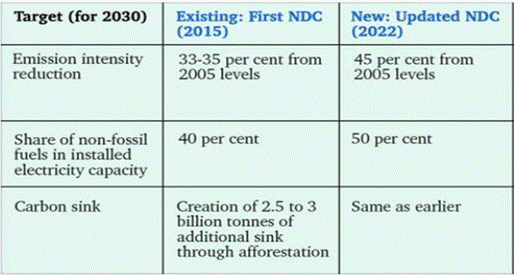
India’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs)
As part of its Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) submitted to the UNFCCC in 2022, India aims to achieve 50 per cent of its installed electric power capacity from non-fossil fuel sources by 2030.
India’s Renewable Energy Capacity [As of 31st March 2025]
- The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has reported robust progress in India’s clean energy sector for the Financial Year 2024–25.
- With a record annual capacity addition of 29.52 GW, the total installed renewable energy (RE) capacity in the country has reached 220.10 GW as of 31st March 2025.
- This reflects India's steady advancement towards the target of achieving 500 GW of non-fossil fuel-based capacity by 2030, as part of its commitments under the ‘Panchamrit’ goals.
Solar Energy Drives Growth:
- Solar energy contributed the most to the year’s capacity expansion, with 23.83 GW added in FY 2024–25
- The total installed solar capacity now stands at 105.65 GW as of 31st March 2025.
- This includes 81.01 GW from ground-mounted installations, 17.02 GW from rooftop solar, 2.87 GW from solar components of hybrid projects, and 4.74 GW from off-grid systems.
Steady Rise in Wind Installations:
- Wind energy also witnessed sustained progress during the year, with 4.15 GW of new capacity added in FY 2024-25.
- The total cumulative installed wind capacity now stands at 50.04 GW, reinforcing wind energy’s role in India’s renewable energy mix.
Bioenergy and Small Hydro Power Maintain Momentum:
- Bioenergy installations reached a total capacity of 11.58 GW, which includes 0.53 GW from off-grid and waste-to-energy projects.
- Small Hydro Power projects have achieved a total capacity of 5.10 GW.
Expanding Pipeline of Clean Energy Projects:
- In addition to the installed capacities, India has 169.40 GW of renewable energy projects under implementation.
- This includes 65.29 GW from emerging solutions such as hybrid systems, round-the-clock (RTC) power, peaking power, and thermal + RE bundling projects.
- These initiatives represent a strategic shift towards ensuring grid stability and reliable supply from renewable sources.
Government Initiatives to Promote Solar & Wind Energy
Solar Energy:
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Urja Suraksha Evam Utthaan Mahabhiyan (PM-KUSUM): Focuses on promoting solar energy in agriculture, providing financial and water security to farmers.
- PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana: Aims to install rooftop solar plants in one crore households, empowering residential households to generate their own electricity.
- Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for Solar PV Modules: Incentivizes domestic manufacturing of Solar Photo Voltaic modules, reducing dependence on imports.
- Solar Parks and Ultra Mega Solar Power: Development of large-scale solar power projects, offering a plug-and-play model for developers.
- International Solar Alliance: India plays a key role in the International Solar Alliance, which focuses on promoting solar energy globally.
- One Sun, One World, One Grid (OSOWOG): This initiative aims to create a global electricity grid, facilitating the exchange of renewable energy across borders.
Wind Energy:
- National Offshore Wind Energy Policy (2015): To develop offshore wind energy potential in India along the coastlines of Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, and other maritime regions.
- National Wind Energy Mission: Aims to expand the country's wind energy capacity, with a target of 140 GW by 2030.
- National Wind-Solar Hybrid Policy (2018): Promotion of large scale, grid connected wind-solar PV hybrid systems for optimal and efficient utilization of wind and solar resources.
- Tamil Nadu Repowering, Refurbishment, and Life Extension Policy for Wind Power Projects [2024]: Launched by Tamil Nadu government aiming to enhance wind energy output by repowering or refurbishing small wind turbines
Conclusion
MNRE has been taking various key initiatives to achieve the vision of 500 GW of renewable energy by 2030. The continued growth reflects India’s commitment to its climate goals and energy security.
The Government’s focused efforts to scale up renewable energy is important not just for its people, but also for the global fight against climate change. As the world’s most populous country India’s energy choices affect the entire planet.
|
Also Read |
|
| NCERT Books For UPSC | |
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | Best IAS Coaching in Delhi |




