- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
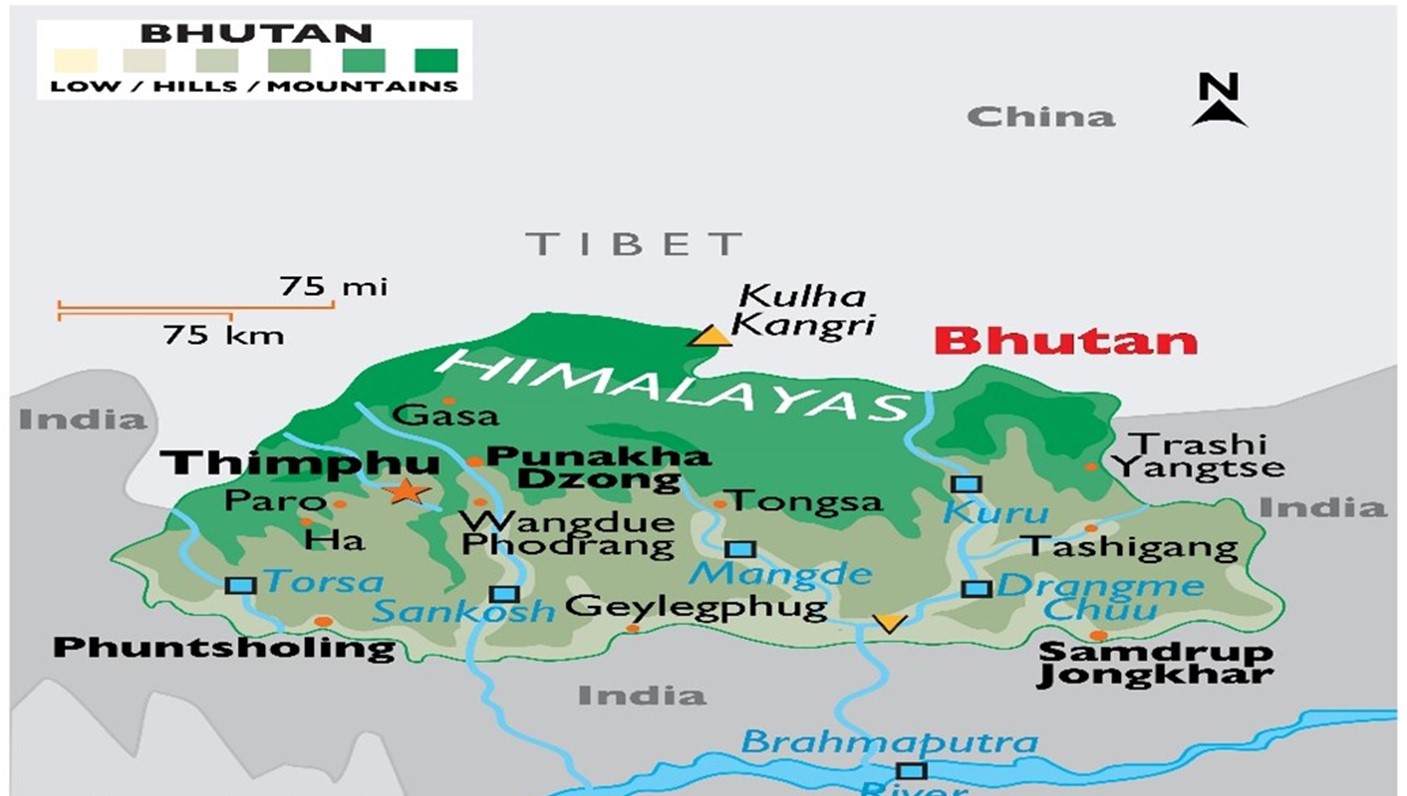
India and Bhutan
India and Bhutan
06-11-2023
Context
Recently, the King of Bhutan Jigme Khesar Namgyel Wangchuck arrived in Guwahati today on an eight-day official visit to India.
Historical Background
- 1910: Bhutan entered into a treaty with British India, granting the British guidance in its defence and foreign affairs.
- 1947: Bhutan was the first country to acknowledge India's independence.
- 1949: The India-Bhutan bilateral relations are based on the 1949 Treaty of Friendship and Cooperation.
- 1968: The diplomatic relations between India and Bhutan were established in 1968 with the establishment of a special office of India in Thimphu.
- 2007: It was revised in February 2007.
- 2018: The Golden Jubilee celebration marked the formal diplomatic relations between India and Bhutan.
Indo-Bhutan Treaty of Peace and Friendship, 1949
- Among other things, the Treaty guarantees unwavering friendship and peace, unrestricted trade and commerce, and equitable justice for the residents of both countries.
- When the treaty was renegotiated in 2007, clauses supporting Bhutan's sovereignty were included, doing away with the requirement to follow India's foreign policy directives.
- Along with close cooperation on domestic matters, the new treaty calls for further cooperation in the cultural and commercial spheres.
India-Bhutan relationship
- Trade:
- In 2021-22, Bhutan's bilateral trade reached $1.42 billion, accounting for 80% of its overall trade, with India as its top import and export destination.
- The Trade, Commerce, and Transit Agreement (2016) establishes a free trade regime between Bhutan and third countries, enabling duty-free transit of goods.
- Developmental: India offers scholarships to Bhutanese students, supports Bhutan's Gyalsung Project for skill development, and aids in sectors like health and agriculture.
- Hydropower: India has constructed four major hydroelectric projects in Bhutan and has significantly increased its revenue by purchasing the power generated there.
- Cultural: Bhutanese pilgrims visit Bodh Gaya, Rajgir, Nalanda, and other Buddhist sites in India.
- New areas: Launch of RuPay, and BHIM app in Bhutan, joint development of India-Bhutan SAT, etc.
Significance of Bhutan for India
- Because of its position between China and India, Bhutan is strategically significant to India as a buffer state that supports India's security objectives.
- India has been essential in maintaining Bhutan's territorial integrity and sovereignty.
- Bhutan's security, infrastructure, and communication capacities have all improved thanks to Indian assistance, preserving its territorial integrity.
- Bhutan's role in facilitating Indian troops' access into its territory to fight Chinese intrusions during the 2017 Doklam conflict underscores Bhutan's strategic relevance for India.
Challenges
- India has occasionally interfered in the internal affairs of Bhutan. As a result, Bhutanese people now have a negative perception of India.
- Bhutan is worried about how profitable its hydropower projects would be now that India is switching to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and other energies.
- Concerning internal security, both countries are concerned about militant groups' unauthorized camps they have set up in the deep forests of southeast Bhutan.
- China's persistent claims to significant border regions like the Chumbi Valley and Doklam, together with its persistent attempts to forge close political and economic ties with Bhutan, have consistently caused India to be concerned.
Conclusion
As the King of Bhutan sets out on an eight-day visit to India amidst changing regional dynamics, maintaining and strengthening the complex connections between the two countries becomes crucial, requiring diplomatic skill, enhanced security cooperation, and ongoing attempts to diversify the economy.