- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
High Temperature Impacting Flight Operations
High Temperature Impacting Flight Operations
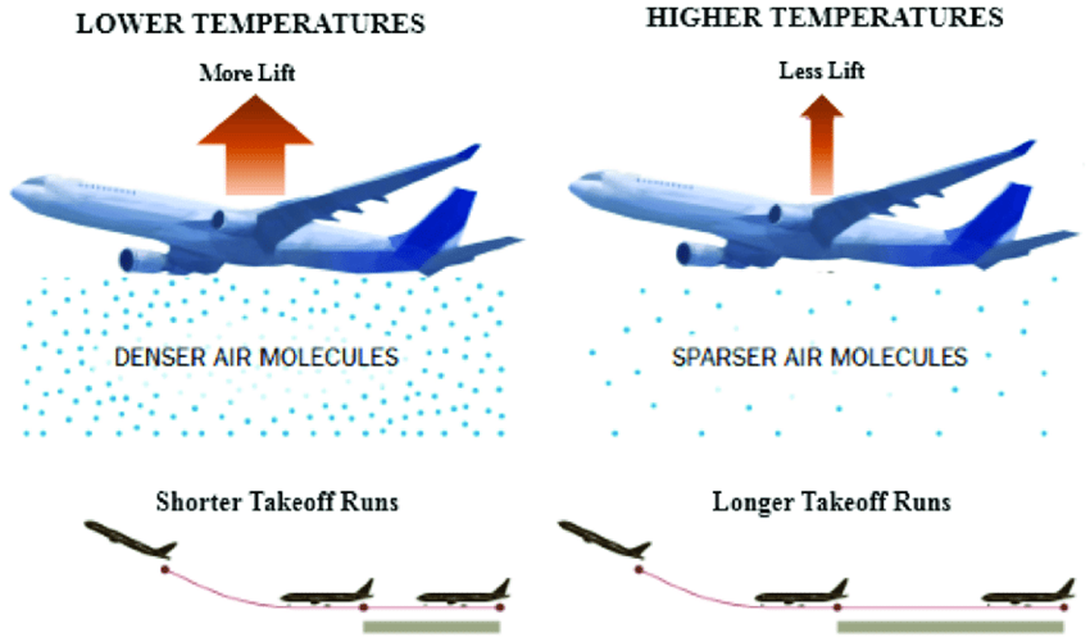
Recently, several air operators cancelled their flights to Leh due to high temperatures in the region, which led to runway restrictions. The mountainous region of Leh has experienced rising temperatures, a trend linked to climate change in India's cold desert.
Impact of High Temperatures on Aircraft Operations
-
Reduced Lift: When the air is less dense due to higher temperatures, it provides less support for an aircraft's wings. This means the aircraft needs to go faster and requires longer runways to take off. The lift-to-drag ratio suffers, affecting overall aircraft efficiency.
-
Engine Performance Deterioration: Hotter air contains less oxygen, which affects how well the engines burn fuel. This results in reduced engine thrust, making takeoff more difficult.
-
Extended Landing Distances: Less dense air also reduces the effectiveness of reverse thrust, which is used to slow down the aircraft after landing. Consequently, aircraft need longer runways to come to a stop.
-
Future Projections: A 2023 study found that due to global warming, the take-off distance for a Boeing 737-800 could increase by about 6% from 2071-2080 compared to 1991-2000. At low-altitude airports, this could mean an additional 113-222 meters needed for take-offs during future summers.
-
Operational Constraints: Airports at higher altitudes are especially affected by temperature increases. Extreme heat may lead to weight limits on takeoffs or even total suspension of flights.
Note: The global average temperature has risen by at least 1.1 degrees Celsius since 1880. India has experienced an increase of about 0.7 degrees Celsius compared to 1900 levels.
Impact of Temperature |
High Temperature |
Low Temperature |
|
Lift |
Hot air is less dense, providing less lift for the wings. This requires higher speeds and longer runways for takeoff. |
Cold air is denser, providing more lift for the wings. This allows for shorter takeoff distances. |
|
Engine Performance |
Hot air contains less oxygen, reducing engine efficiency and power output. |
Cold air contains more oxygen, improving engine efficiency and power output. |
|
Takeoff Distance |
Less lift and reduced engine power at high temperatures lead to increased takeoff distance. |
More lift and improved engine power at low temperatures lead to decreased takeoff distance. |
|
Landing Distance |
Less effective reverse thrust in hot air increases landing distance. |
More effective reverse thrust in cold air decreases landing distance. |
|
Operational Considerations |
Reduced weight limits or cancellations due to performance limitations in extreme heat. |
De-icing procedures become essential to ensure safe operation in very cold weather. |
Principle of Aircraft Flight Operation:
Aircraft need air to fly because moving air generates a lifting force. All flying objects, from kites to airplanes, rely on this principle.
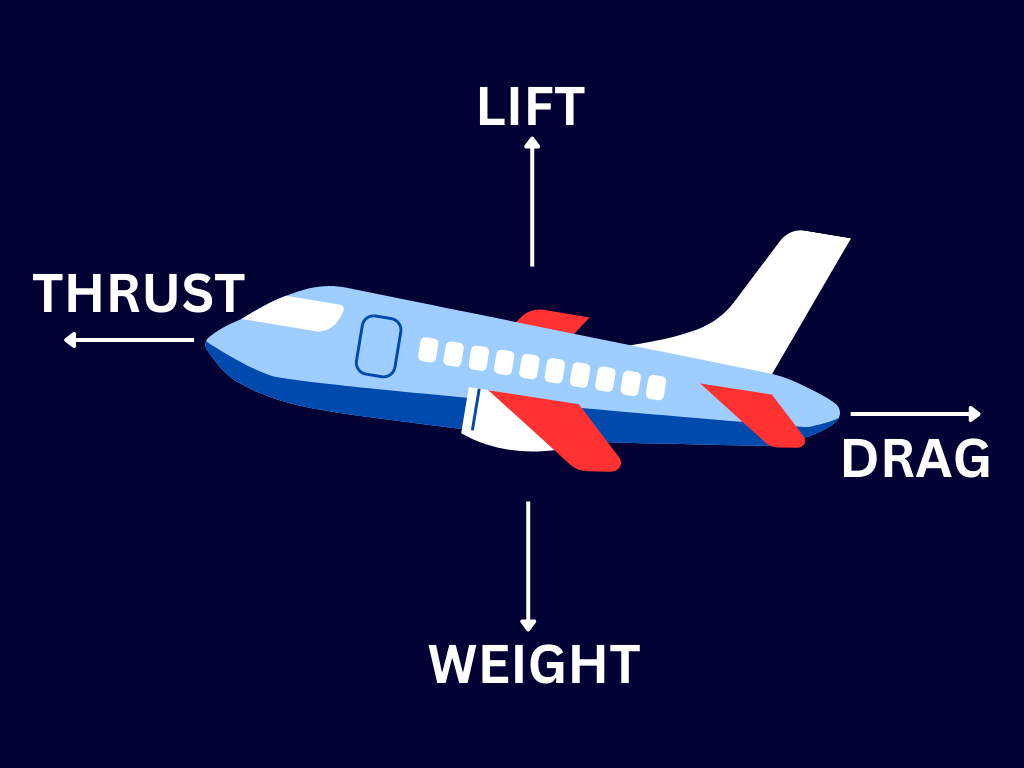
Aircraft experience four basic forces:
-
Lift: The upward force that helps the aircraft to rise.
-
Drag: The backward force caused by air resistance.
-
Thrust: The forward force produced by the aircraft’s engines.
-
Weight: The downward force due to the aircraft's mass.
An aircraft flies when the lift generated by its wings is greater than its weight. To achieve this, the aircraft must move forward at sufficient speed. The engines provide thrust, propelling the aircraft forward. The airfoil-shaped wings interact with the air to create lift.
How Lift is Generated:
- The curved upper surface of the wing accelerates air flowing over it, reducing the pressure (Bernoulli's principle).
- The air flowing underneath the wing is slightly compressed, increasing pressure.
- The difference in pressure creates an upward force, lifting the aircraft.
The angle of attack (the angle between the wing and the oncoming air) affects lift. A small increase in this angle generates more lift, but too much can cause a stall. To maintain level flight, the lift must balance the aircraft's weight. Pilots control lift by adjusting the wing’s angle of attack and shape using control surfaces.
Causes of High Temperatures in Leh-Ladakh Region
-
Altitude: Leh-Ladakh is about 3,000 meters above sea level, resulting in thinner air. The region’s clear skies and minimal cloud cover mean more solar radiation heats the area during summer.
-
Topography: The Himalayas and Zanskar ranges block moisture-laden winds, creating a rain shadow effect. This results in dry air and higher daytime temperatures.
- Rain shadow effect is a region of dry land that forms on the leeward side of a mountain range.
- As moist air is forced to rise over the mountain, it cools and releases precipitation on the windward side.
- The drier air then descends on the leeward side, warming and becoming even drier, creating a "shadow" of dryness.
-
Climate Change: Global warming has caused temperatures to rise worldwide, including in cold deserts like Leh-Ladakh. This changes local weather patterns and leads to warmer conditions.
-
Human Activities: Urbanization and infrastructure development in Leh and nearby areas contribute to local warming effects, known as the urban heat island effect. Urban areas with lots of pavement and buildings absorb and retain heat, raising local temperatures. Increased tourism and military activity also add to the rising temperatures.
Conclusion:
High temperatures in the Leh-Ladakh region, exacerbated by climate change and local factors, significantly impact flight operations by reducing lift, deteriorating engine performance, and extending landing distances. These challenges highlight the need for robust climate adaptation strategies in aviation. Looking forward, addressing the causes of high temperatures through sustainable urban planning, mitigating climate change, and enhancing aircraft technology will be crucial for maintaining safe and efficient flight operations in the region.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus