- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Government Notified National Geospatial Policy 2022
Government Notified National Geospatial Policy 2022
07-01-2023
Government Notified National Geospatial Policy 2022
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Science and Technology has notified a National Geospatial Policy (NGP) 2022, with the goal of making India a world leader in the Global Geospatial Sector.
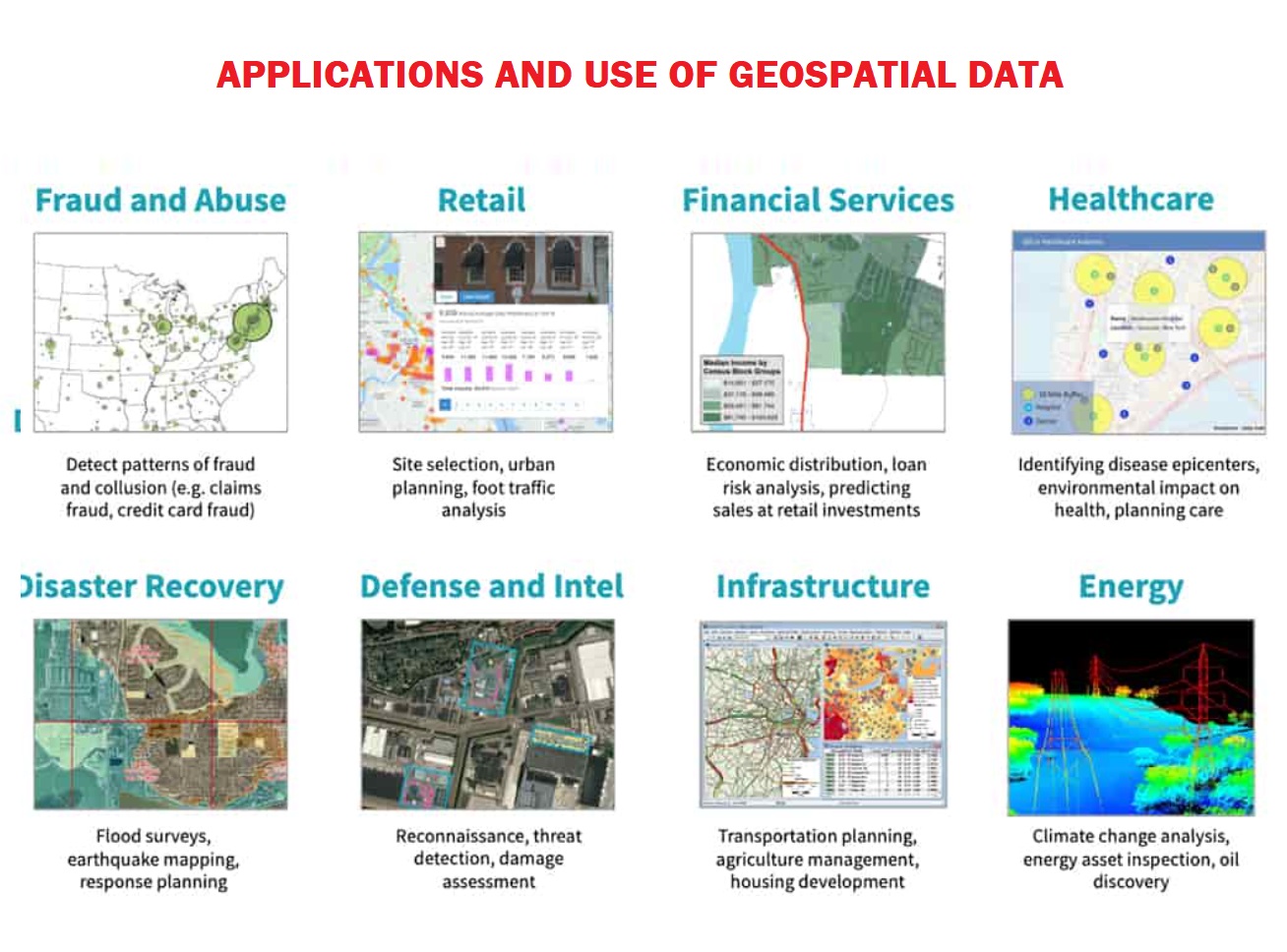
So, What is Geospatial Technology?
- Geospatial technology uses tools like GIS (Geographic Information System), GPS (Global Positioning System) and Remote Sensing for geographic mapping and analysis.
- These tools capture spatial information about objects, events and phenomena (indexed to their geographical location on earth, geotag). The location data may be Static or Dynamic.
- Static location data include position of a road, an earthquake event or malnutrition among children in a particular region while dynamic location data include data related to a moving vehicle or pedestrian, the spread of an infectious disease etc.
- The technology may be used to create intelligent maps to help identify spatial patterns in large volumes of data.
- The technology facilitates decision making based on the importance and priority of scarce resources.
- India's geospatial economy is expected to cross Rs 63,000 crore by 2025 at a growth rate of 12.8% and to provide employment to more than 10 lakh people.
About the National Geospatial Policy (NGP) 2022
- In 2021, the Ministry of Science and Technology issued “Guidelines for acquiring and producing Geospatial Data and Geospatial Data Services including Maps”.
- While the Guidelines deregulated the Geospatial sector by liberalizing Geospatial data acquisition/production/ access, the 2022 Policy takes it further by laying down framework for holistic development of the Geospatial ecosystem.
- NGP 2022 is a citizen-centric policy based on Geo-Spatial technology, which seeks to strengthen the Geospatial sector to support national development, economic prosperity and an information economy.
- The policy aimed to set up high resolution topographical survey and mapping, with a high-accuracy Digital Elevation Model (DEM) by 2030.
- A Geospatial Data Promotion and Development Committee (GDPDC) at the national level shall be the apex body for formulating and implementing strategies related to promotion of the Geospatial sector.
- GDPDC will replace and subsume the functions and powers of the National Spatial Data Committee (NSDC) constituted in 2006 and GDPDC constituted in 2021.
- Department Of Science & Technology shall continue to be the nodal Department of the Government and GDPDC shall make suitable recommendations to DST in the discharge of its functions relating to the Geospatial regime.
Vision and Goals of NGP 2022
-
- It aims to make India a World Leader in Global Geospatial space with the best in the class ecosystem for innovation.
- To develop a national framework in the country and leverage it to move towards a digital economy and improve services for the citizens.
- To develop Geospatial infrastructures, Geospatial skill and knowledge, standards, Geospatial businesses.
- To promote innovation and strengthen the national and sub-national arrangements for generation and management of Geospatial information.
Significance of NGP 2022
- Geospatial technology and data can act as agents of transformation for achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- This policy will also promote the Start-Ups.
- Geospatial data play a vital role in a wide spectrum of frequencies for critical data management applications, such as military operations, disaster and emergency management, environmental monitoring, land and city planning.
About the Related Concerns
- Geospatial data can be described as complex data objects with complex relationships among them and securing this type of data poses major challenges that are yet to be fully understood and addressed.
- Although a variety of models and techniques are available to manage access and share geospatial data, little attention has been paid to addressing the National security concerns.
- If the entire body of geospatial data will be made available by simply integrating the data from the different repositories, there is severe chances of potential data misuse and privacy violations and “also sensitive information such as building ownerships might be revealed or information about critical infrastructure could become publicly accessible and it is a major concern in context to the applications in Defence.
Way Forward
- Given the number of people and organizations involved in a disaster preparation scenario, security measures must be taken to provide users and applications only with data on a need-to-know basis.
- A clear roadmap should be drawn and Standard Operating Procedures (SOP) should be developed in National Geospatial Policy 2022 for the National Securities Issues.




