- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Global Positioning System
Global Positioning System
07-12-2023
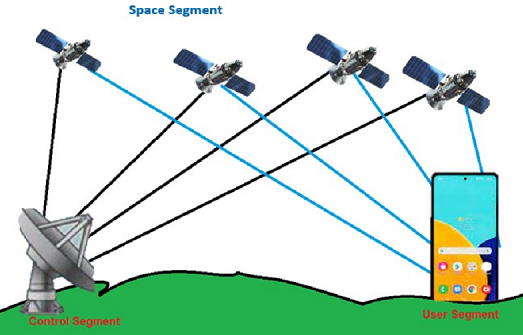
What is the Global Positioning System?
The GPS has three main segments,
- Space Segment: This segment consists of 24 satellites in six orbits (Prelims Fact) to ensure global coverage. The segment facilitates signal receivers (in hand held and other devices) to access signals from at least four satellites simultaneously for accurate positioning.
- All six orbits are positioned at an altitude of 20,200 km above the Earth, and each orbit has four satellites at all times. Each satellite completes two orbits in a single day.
- Control Segment: The Control segment is the second component of GPS, which is further divided into following sub-components.
- Monitor Station: The monitor station checks the exact latitude, Position, Speed, and overall health of the orbiting satellites. A station can track up to 11 satellites at a time. This “check-up” is performed twice a day, By each station.
- Ground Antennas: The ground Antennas monitor and track the satellites from horizon to horizon.
- User Segment: This segment includes the Receiver sets that can range from simple hand-held devices that provide only basic positioning information to complex multichannel units that perform a variety of functions.
- Most GPS receivers consist of three basic components viz. antenna, receiver-processor unit and control/ display unit.
- This segment encompasses diverse sectors from agriculture to military operations, with an estimated 6.5 billion GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) devices worldwide in 2021 underscoring its pervasive influence.

Functioning of Global Positioning System
- GPS operates through satellite-transmitted radio signals at specific frequencies (50 bits/second), received and triangulated by GPS receivers, enabling precise location determination in three dimensions of space and time.
- Satellites maintain precise time for GPS by using atomic clocks. These clocks are critical because even tiny timing differences could lead to substantial location errors.
Other Global navigation satellite system (GNSS)
- Several countries, including Australia, China, the EU, India, Japan, South Korea, Russia, and the U.K., operate their own Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) alongside GPS.
- Globally, Russia's GLONASS, the EU's Galileo, and China's BeiDou systems are among the top technologies.
- India launched its Regional Navigation Satellite System in 2006, later renamed Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC) (Prelims Fact), consisting of total seven satellites (3 in geostationary and 4 in geosynchronous orbits)
- India operates the GPS-Aided Geo Augmented Navigation (GAGAN) system, developed by ISRO and the Airports Authority of India.
- GAGAN improves the accuracy and reliability of GPS signals.
- It uses a network of ground stations to enhance standard GPS navigation.
- It supports Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) like GPS and GLONASS.
- It allows aircraft to land at small airports without costly ground equipment.
- GAGAN helps in all flight phases, from take-off to landing.
- It improves Air Traffic Management (ATM) with accurate position data.
- GAGAN also benefits maritime, road, and rail transport systems.
- It ensures better navigation accuracy, availability, and integrity across India.



