- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Free Grains
Free Grains
04-01-2023
Free Grains
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution issued a notification to provide free foodgrains (rice, wheat and coarse grains) to all eligible households under the National Food Security Act, 2013, for one year from January 1, 2023.
- The government, however, discontinued the Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana.
What is Food Security?
- The Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) states that food security emerges when all people at all times have physical and economic access to sufficient, safe and nutritious food to meet their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life.
- Food security has 3 important components:
- Availability
- Accessibility
- Affordability
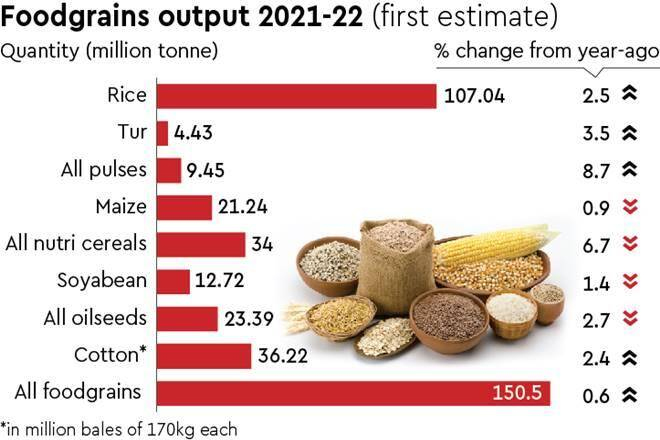
What are Coarse Cereals?
- Coarse cereals are traditionally grown in resource-poor agro-climatic regions of the country.
- Agro-climatic zone is a land unit in terms of major climates suitable for a certain range of crops.
- Sorghum, pearl millet, maize, barley, finger millet and several small millets such as kodo millet, little millet, foxtail millet, proso millet and barnyard millet together called coarse cereals.
- Sorghum, pearl millet, finger millet, maize and small millet (barnyard millet, proso millet, kodo millet and foxtail millet) are also called nutri-cereals.
- Coarse cereals are known for their nutri-rich content and having characteristics like drought tolerance, photo-insensitivity and resilient to climate change etc.
National Food Security (NFS) Act
- The NFS Act, 2013 aims to provide subsidized food grains to approximately two-thirds of India’s 1.2 billion people.
- It was signed into law on 12 September 2013, retroactive to 5 July 2013.
- It includes the Midday Meal Scheme, Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) scheme and the Public Distribution System (PDS).
- The NFSA 2013 also recognizes maternity entitlements.
- The Midday Meal Scheme and the ICDS are universal in nature whereas the PDS will reach about two-thirds of the population (75% in rural areas and 50% in urban areas).
- Pregnant women, lactating mothers, and certain categories of children are eligible for daily free cereals.
Key provisions of NFSA
- The NFSA gives a legal right to a person belonging to “eligible households” to receive foodgrains at a subsidised price.
- 2 categories of beneficiary – Antyoday Anna Yojana (35kg/family/month) and the Priority Households (5kg/person/month).
- It includes rice at Rs 3/kg, wheat at Rs 2/kg and coarse grain at Rs 1/kg under the Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS).
- These are called central issue prices (CIPs).
- Covers 67% of the total population (75% of the rural and 50% of the urban population).
- Meals to pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- Maternity benefits of not less than Rs. 6,000 to such women.
- Children up to 14 years of age will be entitled to nutritious meals.
- In case of non-supply of entitled food grains or meals, the beneficiaries will receive food security allowance.
- Grievance redressal mechanism at the District and State levels.
New changes in NFSA:
- Beneficiaries will now get 35kg of foodgrains free for the next year and others will get 5kg for free in a month till December 2023.
- The Union government has estimated an additional amount of ?2 lakh crore for the scheme. Entire expenses for the scheme would be borne by the Union Government.
What are Government Initiatives in this Regard?
- National Food Security Mission
- Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY)
- Integrated Schemes on Oilseeds, Pulses, Palm oil and Maize (ISOPOM)
- eNAM Portal
Additional Information:
About PMGKAY:
- PMGKAY is a food security welfare scheme announced by the GoI in March 2020, during the COVID-19 pandemic in India.
- The program is operated by the Department of Food and Public Distribution under the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution.
- It is the largest food security program in the world.
- The scheme targets to feed the poorest citizens of India by providing grain through the Public Distribution System to all the priority households. (Ration card holders and those identified by the Antyodaya Anna Yojana scheme).
- PMGKAY provides 5 kg of rice or wheat (according to regional dietary preferences) per person/month and 1 kg of dal to each family holding a ration card.
Must Check: Top IAS Coaching Centre in Delhi



