- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
EXPLAINER: WHAT IS THE SCHENGEN AREA?
EXPLAINER: WHAT IS THE SCHENGEN AREA?
09-04-2024
Bulgaria and Romania became part of the Schengen Area on March 31, 2024, which allows travelers between the two countries to travel without a passport or border checks at sea or air. This move marks a significant moment in the two countries' 13-year journey towards greater integration with the European Union.
- However, checks at land borders remain.
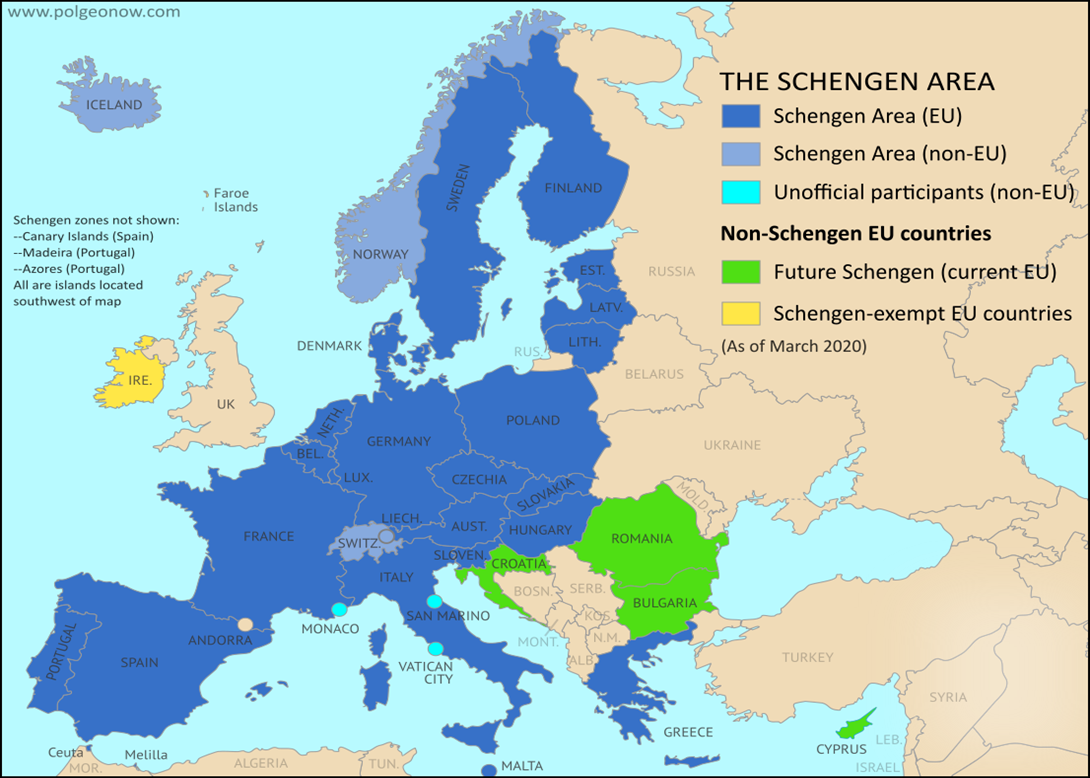
- New Additions: Bulgaria and Romania have recently joined parts of Europe's Schengen Area, facilitating air and sea travel without border checks.
- Application of Rules: Schengen regulations, including visa issuance, will now extend to these member states, with internal air and sea border controls being lifted.
- Austrian Opposition: Austria has opposed full membership, citing concerns about irregular migration and insisting on stronger measures from Bulgaria and Romania.
- Pending Decision: The European Council is expected to unanimously decide on lifting checks at internal land borders in the future.
- Expanded Membership: With Bulgaria and Romania onboard, the Schengen zone now includes 29 members, including 25 of the 27 European Union member states along with 4 non-EU countries Switzerland, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein.
- Implementation in Romania: Romania will enforce Schengen rules at 4 seaports and 17 airports, notably at the Otopeni airport near Bucharest serving as the biggest hub for Schengen flights.
Schengen Area:
- Origin: Initially aimed at facilitating the free movement of the European workforce, the Schengen concept gradually evolved into the world's largest free travel area.
- Historical Roots: Named after the Luxembourg village where key agreements were signed in 1985 and 1990, The implementation of the Schengen Agreements started in 1995, initially involving seven EU countries. Born as an intergovernmental initiative.
- Scope: The Schengen Area grants free movement to over 425 million EU citizens and legally present non-EU nationals for various purposes, without formalities.
- Benefits: This freedom enables citizens to live, work, and travel across the Schengen Area without border checks, promoting economic and cultural exchange.
- Exclusions: Cyprus and Ireland are the only EU members not part of Schengen.
- Border Control: Internal border checks within the Schengen area have been abolished, but common rules govern external borders for short-term visitors.
- Security Measures: Despite open internal borders, the Schengen countries enforce strict controls on external borders to ensure security.
- Regulation: The Schengen Borders Code regulates these rules, facilitating seamless travel while maintaining security standards.
- Impact: Schengen promotes widespread cross-border travel and residence, benefiting millions of Europeans annually and boosting tourism and the economy overall.
|
Schengen zone now includes 29 members |
||
|
EU countries issuing Schengen visas: |
EU countries not issuing Schengen visas: |
Non-EU countries issuing Schengen visas: |
(except Cyprus Ireland) |
|
|
|
||
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi



