- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
ENFORCEMENT DIRECTORATE (ED)
ENFORCEMENT DIRECTORATE (ED)
- The Directorate of Enforcement (ED) is a multi-disciplinary organization mandated with investigating economic crimes and violations of foreign exchange laws.

- The ED's origin dates back to May 1, 1956, when an 'Enforcement Unit' was formed in the Department of Economic Affairs to handle Exchange Control Laws violations under the Foreign Exchange Regulation Act, 1947 (FERA '47).
- The Unit was headquartered in Delhi and headed by a Legal Service Officer, as Director of Enforcement, assisted by an Officer drawn on deputation from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and 3 Inspectors of Special Police Establishment.
- There were 02 branches – at Bombay and Calcutta.
In the year 1957, this Unit was renamed as ‘Enforcement Directorate’, and another branch was opened at Madras.
- In 1960, the administrative control of the Directorate was transferred from the Department of Economic Affairs to the Department of Revenue.
- With the passage of time, FERA’ 47 was repealed and replaced by FERA, 1973.
- Presently, the Directorate is under the administrative control of the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance, Government of India.
- With the onset of economic liberalization, FERA, 1973 was repealed.
- A new law, the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA) came into operation on 1st June 2000.
- In tune with the International Anti Money Laundering regime, the Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA) was enacted and ED was entrusted with its enforcement on 1st July 2005.
- Recently, with the increase in the number of cases relating to economic offenders taking shelter in foreign countries, the government has passed the Fugitive Economic Offenders Act, 2018 (FEOA).
- ED is entrusted with its enforcement with effect from 21st April, 2018.
The Directorate of Enforcement investigates money laundering and foreign exchange law violations. The statutory functions of the Directorate include enforcement of following Acts:
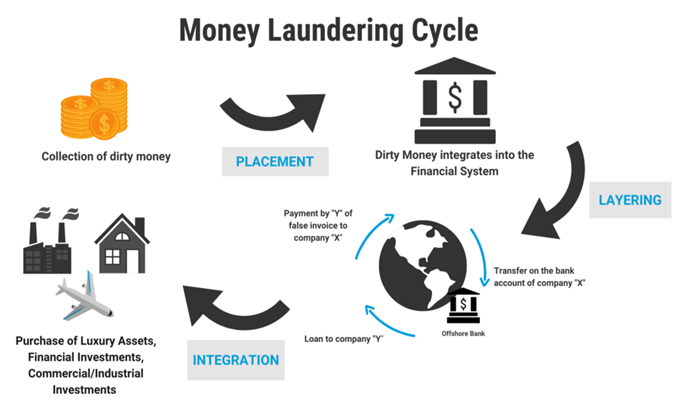
1. The Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA): This law, known as the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), was created to stop people from laundering money. It aims to take away any property that came from or was involved in money laundering. The Enforcement Directorate (ED) is tasked with enforcing the PMLA by investigating and tracking down assets that came from criminal activities. They can also temporarily seize the property and make sure those responsible are prosecuted, and the property is confiscated by a special court.
2. The Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA): The Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999, is an Act of the Parliament of India "to consolidate and amend the law relating to foreign exchange with the objective of facilitating external trade and payments and for promoting the orderly development and maintenance of foreign exchange market in India".
3. The Fugitive Economic Offenders Act, 2018 (FEOA): The Fugitive Economic Offenders Act 2018 allows any special court to confiscate the assets of economic offenders who have left India to avoid prosecution. This Act was passed to prevent economic offenders from escaping the law and to maintain the rule of law in India. The Act empowers special courts to confiscate all assets of criminals committing crimes worth more than Rs 100 crore.



