- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Emergency Alert System
Emergency Alert System
15-11-2023

Why in News?
A 6.4 magnitude earthquake and an aftershock in Nepal on November 3rd, 2023, have highlighted significant deficiencies in emergency alert systems in and around Delhi.
- Despite the region experiencing tremors, both government and private alert mechanisms failed to reach a significant number of people who experienced palpable shaking.
Emergency Alert Systems in India
-
Google’s Android Earthquake Early Warning System:
- The feature utilizes Android smartphones' sensors to detect seismic activity and alert users about potential earthquakes.
- The organization also collaborates with seismological agencies to enhance earthquake detection and analysis through data collection and sharing.
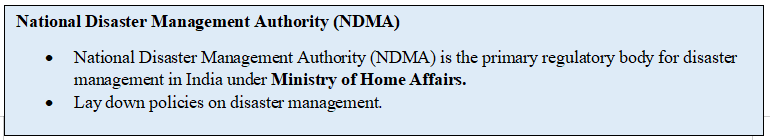
- Google introduced a new feature in India in September 2023, in collaboration with the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) and the National Centre for Seismology.
- Google's alerts are triggered using the Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI) Scale, an alternative to the Richter scale.
- The MMI scale quantifies the impact of an earthquake on a specific location, encompassing the observed effects on people, buildings, and objects.
-
Cell Broadcast Alert System (CBAS):
- The CBAS technology enables the timely and critical dissemination of disaster management messages to all mobile devices within specific geographical areas, regardless of resident or visitor status.
- Cell Broadcast is utilized for delivering emergency alerts, public safety messages, evacuation notices, and other critical information, such as severe weather warnings and earthquakes.
- The alerts are generated and disseminated in collaboration with various agencies, including the Department of Telecommunications (DOT), NDMA, and other relevant departments.
-
Ministry of Earth Science’s National Centre for Seismology (NCS):
- The agency is responsible for monitoring and reporting seismic activity in India and its surrounding areas.
- The organization operates a nationwide network of seismological observatories, providing real-time data and information on earthquakes and tsunamis.
- BhooKamp, a website and mobile app, is used to provide earthquake alerts and updates to the public.
Challenges in the Emergency Alert Systems
-
Lack of Coordination and Integration:
- India's absence of a standardized emergency alert system leads to inconsistent and unreliable information for the public and authorities.
- Multiple agencies and platforms operate independently, leading to confusion, duplication, and delays in alert generation and dissemination.
- The NCS website and app experienced a sudden crash during recent tremors in Delhi, causing a surge in traffic and requiring real-time information.
-
Lack of Accuracy and Timeliness:
- India's emergency alert systems are unable to provide precise and timely information on the location, magnitude, intensity, and impact of disasters.
- The issue is attributed to limitations in data collection, analysis, and transmission.
-
Lack of Awareness and Preparedness:
- India's emergency alert systems struggle to effectively communicate with the masses due to a lack of public awareness and preparedness among authorities.
- Many individuals lack the knowledge to access, interpret, and respond to alerts, often dismissing them as false alarms.
Way Forward
- Create a comprehensive emergency alert system that integrates various channels such as SMS, voice calls, social media, and traditional methods.
- The goal is to establish effective coordination and integration with key agencies such as MoES, DoT, NDMA, IMD, and NCS.
- Utilize advanced technologies like satellites and Artificial Intelligence to improve data collection, analysis, and transmission.
- Enhance infrastructure by expanding seismological observatories, deploying more sensors, and upgrading computing capabilities.
- The goal is to issue immediate alerts with detailed information on the location, magnitude, and impact of a disaster.
- The purpose is to educate and inform the public about disaster risks, mitigation strategies, and the functionality of emergency alert systems.
- The plan involves conducting regular drills with stakeholders and communities to test and improve alert systems and response mechanisms.