- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Electrolysers: A Key Component in Green Hydrogen Production
Electrolysers: A Key Component in Green Hydrogen Production
06-05-2024
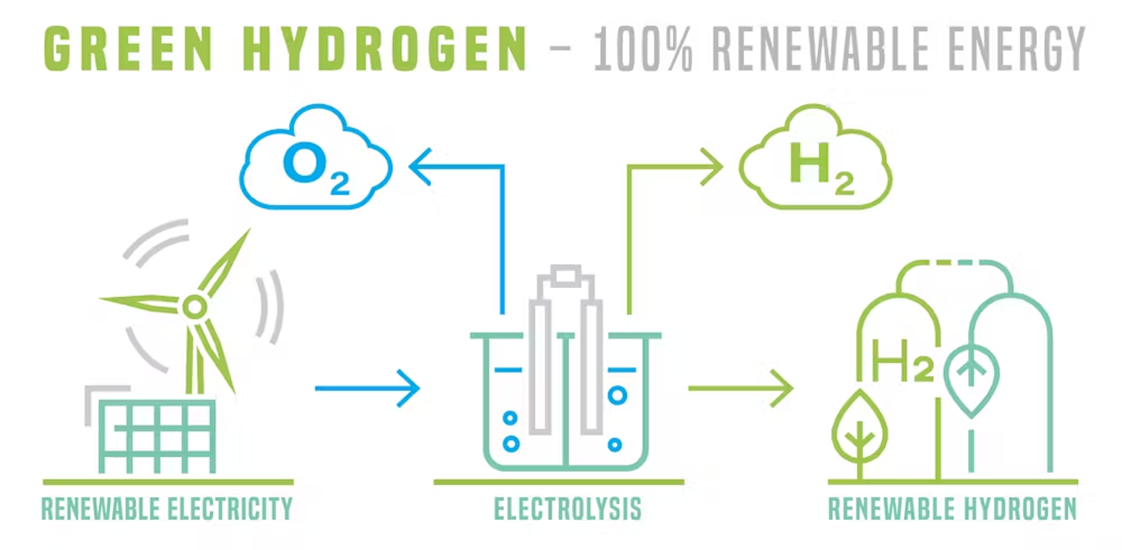
- Electrolyzers are devices that play an important role in generating green hydrogen, a clean and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
- Using electricity, electrolyzers split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen, providing a promising solution to decarbonizing various industries and sectors.
What are Electrolyzers?
- Definition: Electrolyzers are devices that use electricity to split water (H₂O) into its constituent elements: hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂). This process is called electrolysis.
- Importance: Electrolyzers are key to producing "green hydrogen." This refers to hydrogen generated using renewable energy sources like solar or wind power, making it a carbon-free fuel.
How Electrolyzers Work
- Components: An electrolyzer consists of:
- Anode: The positively charged electrode where oxygen is produced.
- Cathode: The negatively charged electrode where hydrogen is produced.
- Electrolyte: A substance (usually a liquid solution or a polymer membrane) that conducts electricity and allows ions to move between the electrodes.
- Electrolysis Process:
- Water is fed into the electrolyzer.
- Electric current is passed through an electrode immersed in the electrolyte.
- At the anode, water molecules lose electrons and split into oxygen gas and positively charged hydrogen ions (protons).
- The hydrogen ions travel through the electrolyte to the cathode.
- At the cathode, the hydrogen ions gain electrons and form hydrogen gas.
Types of Electrolyzers
- Alkaline Electrolyzers: The most mature and commercially developed technology. They use a liquid alkaline solution as the electrolyte.
- Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) Electrolyzers: Use a solid polymer membrane as the electrolyte. They are more responsive to dynamic power sources like renewables.
- Solid Oxide Electrolyser (SOECs): Operate at high temperatures and can be more efficient but are still in earlier stages of development.
Uses of Green Hydrogen (Hydrogen produced through electrolysis)
- Energy Storage: Green hydrogen can store excess renewable energy for later use.
- Decarbonizing Industry: Green hydrogen can replace fossil fuels in hard-to-decarbonize industries like steel, cement, and chemical production.
- Transportation Fuel: Used in fuel cell vehicles for zero-emission transportation.
Benefits of Electrolysers:
- Production of green hydrogen, a clean and sustainable fuel.
- Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels.
- Potential for widespread adoption across various industries, including transportation, energy storage, and industrial processes.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Scaling up electrolyser manufacturing to meet increasing global demand.
- Reducing the cost of electrolysers to make green hydrogen more competitive.
- Developing efficient and environmentally sustainable methods for hydrogen storage and transportation.
The Future of Electrolysers:
Electrolyzers hold immense potential as a key technology in the future transition to clean energy. By using electrical power to produce green hydrogen, electrolyzers contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally conscious world.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi



