- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Electroencephalography (EEG): Centenary year of first Human EEG
Electroencephalography (EEG): Centenary year of first Human EEG
Why in news: The year 2024 marks the centennial (100 years) of the discovery of the electroencephalogram (EEG) by German psychiatrist Hans Berger in 1924.
Relevance of Topic:
Prelims: EEG and its working
Mains: GS Paper 3 (Awareness in various Science and Technology fields).
What is Electroencephalography (EEG):
- It measures electrical activity in brain by tracking the movement of electrically charged particles using electrodes placed on scalp.
- It measures the voltage changes (in microvolts) and frequency of variations (in Hertz).
History of EEG development:
- 1875: British physician Richard Caton detected electrical activity in monkey and rabbit brains using galvanometer (instrument used to measure electrical current).
- 1890: Polish scientist Adolf Beck observed fluctuating brain activity in dogs and rabbits.
- 1912: Vladimir Pravdich-Neminsky recorded the first mammalian EEG in dog’s brain.
- 1924: Hans Berger recorded first human EEG and demonstrated its clinical use.
Working of an EEG:
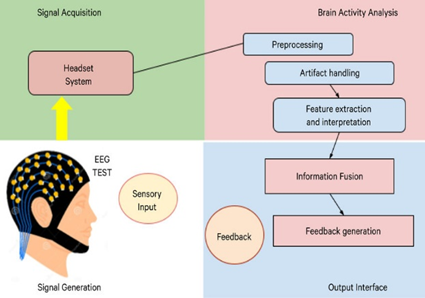
- During an EEG, electrodes are placed onto scalp. Electrodes are small metal disks with thin wires.
- Electrode detect tiny electrical charges that result from activity of brain cells. The charges are amplified and appear as graph on computer screen.
Applications of an EEG:
- Help to diagnose and monitor a number of conditions affecting brains.
- To detect and investigate epilepsy, a condition that causes repeated seizures.
- Research scientists use EEG for neuroscience, cognitive psychology, neurolinguistics and neuromarketing studies
- For diagnosis and treatment of various disorders like, Brain tumor, Brain damage from head injury, stroke, sleep disorders etc.
Advantages of an EEG:
- Non-Invasive and painless procedure: Electrodes placed on scalp to record electrical activity in brain.
- Wide range of applications: ECG used in diagnosis of various kinds of conditions including epilepsy, sleep disorders, brain tumor etc.
- Relatively simple and cost effective: EEG instrument is relatively inexpensive and doesn’t require lot of space.
- Measures rapid electrical activity: EEG is effective in tracking electrical activity in brain happening in milliseconds.
- Portable: EEG can be performed in various settings, not just in hospitals.
Disadvantages of an EEG:
Difficulty in Interpreting Data: EEG readings can be affected by volume conduction, which is a movement of electrical activity with in brain.
- Limited ability to detect deep brain activity: EEG is more sensitive to electrical signals generated by brain surface than those generated by deeper structures.
- Problem of thick hair and time consuming: Thick hair can interfere with EEG signal. The test requires applying gel and precisely placing electrodes on the scalp, which is time consuming.
|
Volume conduction: It refers to the movement of electrical activity generated by neurons through various layers of head to reach electrodes placed on scalp. |
Conclusion: EEG has revolutionized our understanding of brain activity over past century. Its ability to provide real-time insights into brain function has made it indispensable in both clinical and research settings. As we celebrate 100 years of EEG, its significance in advancing neuroscience and improving medical diagnosis is undeniable.




