- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Discovery of Molecule That May Treat Rare Mitochondrial Diseases (2025)
Discovery of Molecule That May Treat Rare Mitochondrial Diseases (2025)
05-05-2025
- Recently, Scientists have found a molecule (a small chemical compound) that could help treat POLG-related diseases.
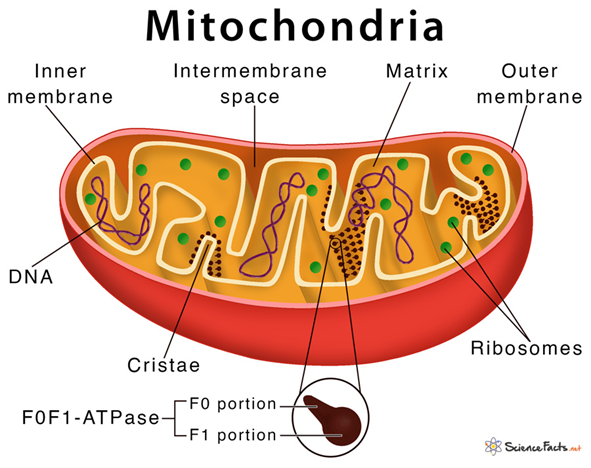
- These are rare genetic diseases that harm the mitochondria (the “powerhouses” of our cells) and make it hard for cells to get enough energy.
- This molecule appears to reverse the damage caused by mutations (changes in DNA) that affect the POLG gene (a gene responsible for a key protein in mitochondria).
What Are POLG-Related Diseases?
- POLG-related diseases are rare and caused by problems with the POLG gene.
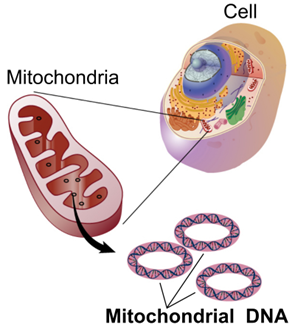
- The diseases lead to mitochondrial DNA being damaged and not being able to repair itself properly.
- This affects the body’s ability to create and use energy.
- The diseases are very variable (different people have different symptoms, and it can affect people at different ages).
- Alpers-Huttenlocher syndrome (a severe form) starts between ages 2-4 and can lead to liver failure, seizures, and death within 4 years.
- Other forms of POLG diseases may show symptoms between 12 and 40 years old, but symptoms are less severe for people who develop them later in life.
What is Mitochondrial DNA ?
|
How Does This New Molecule Work?
- The researchers wanted to find a molecule that could enhance the activity of the POLG protein (the protein made by the POLG gene).
- They screened 270,000 compounds to find one that could help the healthy POLG protein and even mutant versions of it.
- They found one promising molecule, called PZL-A, and made it more powerful by tweaking it.
- PZL-A helps stabilize the POLG protein, so it can repair DNA and work properly, even with mutations.
- This helps cells to recover from damage.
What Makes This Molecule Special?
- PZL-A works by binding to a specific part of the POLG protein that is not affected by the most common disease-causing mutations (the mutations that cause these diseases).
- The molecule stabilizes the POLG protein, allowing it to continue its work in repairing and replicating mitochondrial DNA.
- In experiments, cells with POLG mutations treated with PZL-A were able to recover their mitochondrial DNA much faster than untreated cells.
What’s Next for This Discovery?
- The team has started testing a molecule similar to PZL-A in humans.
- They’re currently testing its safety in healthy people.
- If PZL-A works well and has no harmful side effects, it could become a treatment for people with POLG diseases, which currently have no cure—only treatments for symptoms.
- The researchers are also looking into whether this molecule could help with other diseases, like those related to aging or neurodegenerative conditions (diseases like Alzheimer's that involve the breakdown of the brain).
Why Is This Important?
- This is the first drug aimed specifically at treating POLG mutations and improving mitochondrial function.
- If successful, this could change the lives of people with these devastating diseases.
- The research could also help in understanding aging diseases, since mitochondrial DNA depletion is linked to many age-related illnesses.
What Are Mitochondria?
|
|
Also Read |
|
| FREE NIOS Books | |