- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
DEMAND FOR GREATER TIPRALAND
DEMAND FOR GREATER TIPRALAND
A 3-party agreement has been signed between the Central government, the State government of Tripura and the TIPRA Motha.
What is the TIPRA Motha?
- The Tipra Motha, also called the Tipraha Indigenous Progressive Regional Alliance, is a regional political party in Tripura.
- It used to be a social organisation led by Pradyot Bikram Manikya Deb Barma.
- A social organization helps people and communities with social issues, like education or healthcare, without directly involving politics.
- A political party aims to win elections and influence government decisions by promoting specific policies and ideas.
- Currently, it is the 2nd-largest party in the Tripura Legislative Assembly.
What are the demands of the TIPRA Motha?
- Demand for a separate state of Greater Tipraland:
- Earlier the demand for a separate state named Tipraland existed for Tiprasa. "Tiprasa" is a term that refers to the indigenous tribal communities of Tripura.
- It included the Tripura Tribal Areas Autonomous District Council (TTAADC) and some surrounding areas to be made into a separate state from Tripura. An Autonomous District Council (ADC) is a local self-government body established under the provisions of the 6th Schedule of the Constitution of India.
- It was supposed to cover 68% of the total geographical area of Tripura.
- But later on, a new demand for Greater Tipraland emerged, which is an expanded version of Tipraland. It includes additional; regions from Assam, Mizoram and Bangladesh where Tripuri people live.
- More autonomy for TTAADC including
- Direct funding from the Central government
- Own Police force
- Share of revenue from gas exploration taking place in Tripura
- Declaration of the Roman script as the official script for the Kokborok language in the state. (Kokborok is a Tibeto-Burman language spoken in Tripura and neighbouring areas of Bangladesh)
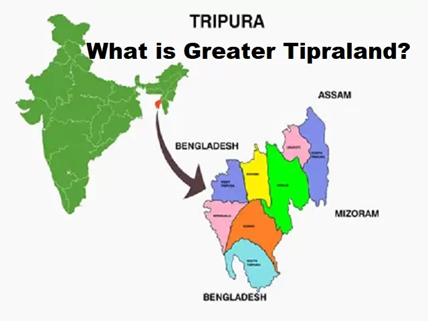
What are the reasons behind such demands?
- Demographic Change: Historically, indigenous tribal communities comprised a significant majority of Tripura's population. However, there has been a significant change in the tribal population due to the displacement of Bengalis from the erstwhile East Pakistan between 1947 and 1971 (as given below):
|
Year |
1881 |
2011 |
|
Tribal Population in Tripura |
63.8% |
32% |
- Ethnic Conflicts: There have been fights between tribal and non-tribal people, leading to serious problems, including armed conflicts in the past. As a result, the demand for Greater Tipraland grew from earlier requests for autonomy to later demands for complete sovereignty and independence.
- Alleged Discrimination: TTAADC alleged that discrimination takes place when resources are allocated in the state.
|
Population Share of TTAADC in Tripura |
40% |
|
Geographical Coverage |
66% |
|
Funds Allocation |
Only 2% of the state’s funds |
Does Parliament have the authority to create a new state (under the Constitution)?
|
Article 2 |
Parliament has the authority to make laws allowing new states to join the country or to create entirely new states. |
|
Article 3 |
Parliament can adjust state borders, form new states, expand or shrink existing states, and rename states by law. |
What does the 3-Party Agreement say?
- It seeks to peacefully settle all problems faced by the indigenous people of Tripura.
- To make this happen, a joint working group (a team from all sides) will be established to facilitate dialogue and cooperation between the concerned parties.
- The agreement stresses the importance of peace, asking everyone involved to avoid protests or activities that could disrupt the peace process.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
Watch Detailed Video Of This Topic