- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Crime and Criminal Tracking Networks and Systems (CCTNS)
Crime and Criminal Tracking Networks and Systems (CCTNS)
29-06-2024
Ahead of the implementation of new criminal laws, the Crime and Criminal Tracking Network Systems (CCTNS) has undergone significant modifications.
About CCTNS:
- Conceptualization and Implementation:
- CCTNS was conceived by the Ministry of Home Affairs under the National e-governance plan of India.
- It has been operational since 2009 as a "Mission Mode Project (MMP)."
- Ambitious Goals:
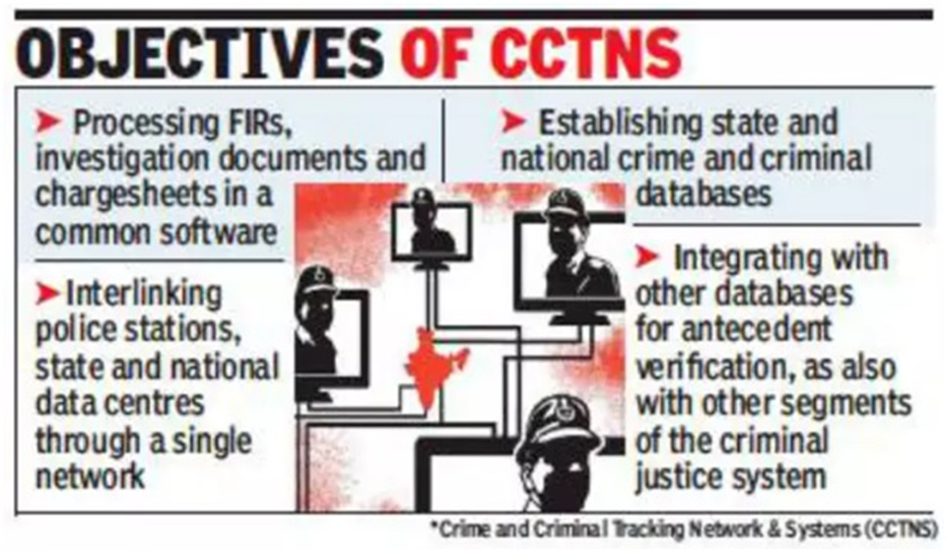
- CCTNS aims to establish a comprehensive and integrated system to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of policing at the police station level nationwide.
- Interlinking Police Stations:
- CCTNS aims to interlink all police stations under a common application software for various purposes such as investigation, data analytics, research, policymaking, and citizen-centric services.
- Accessibility of Records:
- The records of crimes and criminals available at one police station will be accessible to any other police office, facilitating information sharing and collaboration.
- Multiple Objectives:
- CCTNS aims to:
- Make police functioning citizen-friendly and transparent by automating police station operations.
- Improve citizen-centric services through effective use of ICT.
- Provide investigating officers with tools, technology, and information to facilitate crime investigation and criminal detection.
- Enhance police functioning in areas such as Law and Order and Traffic Management.
- Facilitate interaction and information sharing among police stations, districts, state/UT headquarters, and other police agencies.
- Assist senior police officers in managing the police force.
- Track the progress of cases, including in courts.
- Reduce manual and redundant record-keeping.
- CCTNS aims to:
- Collaborative Implementation:
- The CCTNS project is being implemented with close collaboration between the states and the Union Government.
National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB):
- The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) is the central nodal agency responsible for managing CCTNS.
- Established in 1986, NCRB serves as a repository of information on crime and criminals.
- It comes under the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), Government of India.
- NCRB collects and analyzes crime data, aiding investigators in tracing crimes and criminals.
- Its headquarters is in New Delhi.
- NCRB compiles and publishes national crime statistics, such as Crime in India, Accidental Deaths & Suicides, and Prison Statistics.
- NCRB assists various states in capacity building in areas related to Information Technology, CCTNS, fingerprints, network security, and digital forensics.
First Information Report (FIR):
- An FIR is information given to a police officer in writing as per the provisions of Section 154 of the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC).
- From the informant's perspective, the main purpose of an FIR is to set the criminal law in motion.
- For the police, the main purpose of an FIR is to obtain information about alleged criminal activity and take necessary steps to bring the perpetrator(s) before the court.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi



