- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Coordinated Lunar Time (LTC)
Coordinated Lunar Time (LTC)
11-04-2024
Last week, the US White House officially directed the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) to create a time standard for the Moon, which different international bodies and private companies can use to coordinate their activities on the lunar surface.
About Coordinated Lunar Time (LTC)
|
Purpose:
|
|
|
Reason for LTC: |
|
Earth's Time Standard:
|
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC): |
|
|
Atomic Clocks:
|
|
|
Local Time Calculation:
|
|
FAQs:
Q: What Is Greenwich meridian?
- The Greenwich Meridian is an imaginary line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole.
- It's also known as the Prime Meridian and is the reference line for measuring longitude on Earth.
- The Greenwich Meridian is the zero reference line for astronomical observations.
- It divides the Earth into eastern and western hemispheres.
- The Prime Meridian at Greenwich has been the reference line for Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) since the late 19th century.
- The Greenwich Meridian is marked by the cross-hairs in the Airy Transit Circle eyepiece, a telescope located at the Royal Observatory Greenwich.
- It was established as the Prime Meridian in 1884 and used as the international standard for timekeeping and navigation until 1974.
Q: What is an Atomic Clock?
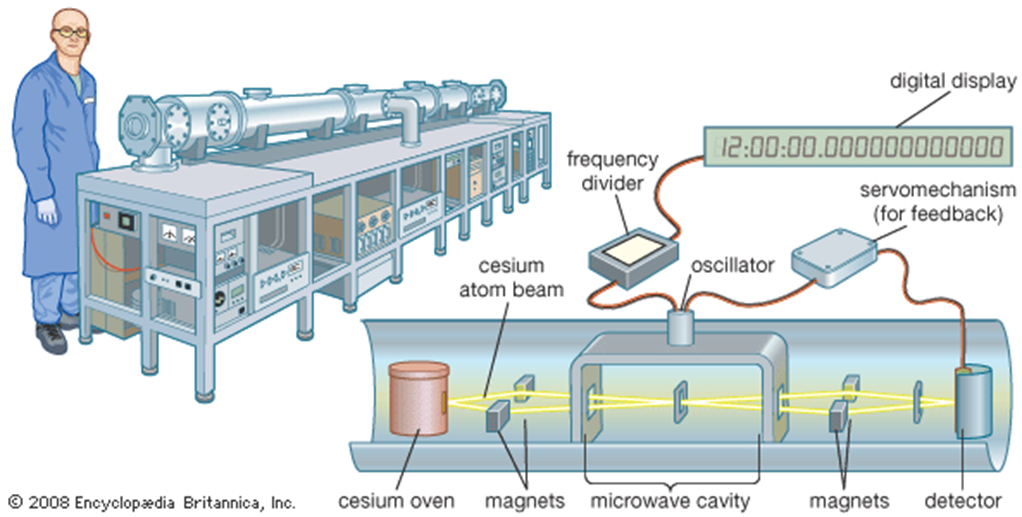
- Atomic clocks are timekeeping devices that measure time by monitoring the resonant frequency of atoms.
- They are the most accurate time and frequency standards in use, and have many applications in industry, commerce, and science
- Atomic clocks are used in many applications that require precise timing, such as GPS systems and scientific research.
For example, NASA uses atomic clocks in GPS satellites that orbit the Earth. However, these clocks must be updated twice a day to correct for their natural drift, using more stable atomic clocks



