- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Converting Plastic Waste into Fuel
Converting Plastic Waste into Fuel
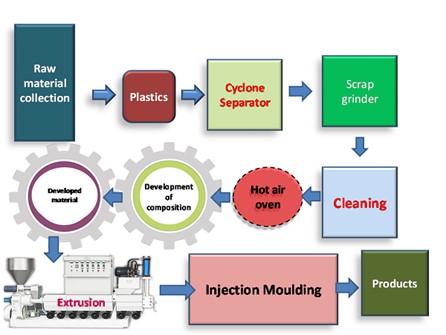

Latest Context
On the eve of World Environment Day which is observed on 5 June 2023, the Department of Science and Technology is planning to control plastic pollution with the help of advanced technologies. These technologies are being used at a pilot scale to cope with the growing challenge posed by the increasing use of plastic.
Plastic
- Introduction: The term plastic originated from the Greek word Plastikos. It refers to - “capable of being shaped or moulded.” It consists of a wide range of Synthetic or semi-synthetic materials. Their origin lies in polymers and their main feature is their plasticity and ability to undergo deformation.
- The origination of modern plastics lies in fossil fuel-based chemicals such as natural gas or petroleum. In addition, it can also be generated from renewable materials like corn or cotton derivatives. Approximately 70% of global plastic production comes from six major polymer types which are collectively referred to as commodity plastics.
Six Types of Plastics:
- Polyethylene terephthalate or PET,
- High-density polyethylene or HDPE,
- Polyvinyl chloride or PVC,
- Low-density polyethylene or LDPE,
- Polypropylene or PP,
- Polystyrene or PS,
- Other Plastics.
Key Information: Every type is identified by its Resin Identification Code (RIC) represented by symbols found on plastic products.
Resin Identification Code: The Society of the Plastics Industry (SPI) developed it in 1988. It was developed for facilitating efficient sorting and recycling of plastics. Each RIC corresponds to a specific type of resin used in a plastic product. According to RIC, proper recycling preserves the value of the product. The RIC is governed by The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) which is an international organization. It applies to different substances such as plastic, not glass, paper, or other recyclable materials.
Microplastics: They are plastic particles having a diameter of less than five millimeters.
- As far as primary microplastics is concerned, they are very tiny particles meant for commercial use in many sectors such as cosmetics, and textiles. On the other hand, secondary microplastics result from the breakdown of larger plastic items. It is found in the environment, contaminating the food chain, water sources, and air, and that poses health risks due to the toxic chemicals they contain.
- Decomposition Rate and Impact: Its decomposition rate is very slow which leads their accumulation in natural ecosystems. Instead of breaking down into harmless substances, plastics fragment into smaller particles which could lead to the presence of microplastics. As per recent global estimates, at least 50,000 microplastic particles are consumed on an average basis by humans annually due to contamination of the food chain, potable water, and air.
- Microplastics consist of toxic chemicals BPA (Bisphenol A) used to harden the plastic. BPA poses the biggest health risk. It contaminates food and drinks leading to liver damage function, insulin resistance, adverse effects on foetal development, reproductive system issues, and brain function.
Note: Trash vortex which is also known as The Great Pacific Garbage Patch (GPGP) located in the North Pacific Ocean between California and Japan, is the largest accumulation of plastic waste, formed by converging ocean currents.
Methods to Convert Plastics in Fuel
- ICT-Poly Urja Process: It starts by collecting and sorting the various types of plastic waste such as bottles or packaging materials. Cu@TiO2 catalyst which is a special substance is added to the plastic waste. The addition of this catalyst helps in breaking down the plastic into smaller molecules. After then, the whole mixture of plastic waste and catalyst is heated up under moderate conditions at high temperatures (not extremely high).
- On heating, it undergoes a chemical transformation called Catalytic Thermo Liquefaction (CTL). It transformed the plastic waste into a substance called Hydrocarbon Oil (HC-Oil). The HC-Oil which is a particular type of fuel can be used for various purposes. It has a high energy content that can be burned to generate heat, steam, or even electricity.
- Pilot Scale Mobile Plant: It is an indigenously designed process. It has led to the development of a vehicle-mounted mobile plant. It transforms various types of plastic waste into carbon-densified HC-Oil (Hydrocarbon Oil) by using a low-stringent process named ICT-Poly Urja. Institute of Chemical Technology (ICT) Mumbai developed ICT Poly Urja. It enables the low-cost conversion of plastic waste into fuel.
- Efficient and Mobile: The Catalytic Thermo Liquefaction (CTL) process requires less energy compared to traditional methods such as pyrolysis and gasification. The operating conditions which are moderate by nature contribute to energy efficiency. Its use on a vehicle offers operational benefits.
Measures of India to handle Plastic Waste Management
- India Plastics Pact
- National Dashboard on Elimination of Single-Use Plastic and Plastic Waste Management.
- Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules, 2022.
- Project REPLAN.

Q. Why is there a great concern about the ‘microbeads’ that are released into environment? (2019)
(a) They are considered harmful to marine ecosystems.
(b) They are considered to cause skin cancer in children.
(c) They are small enough to be absorbed by crop plants in irrigated fields.
(d) They are often found to be used as food adulterants.
Ans: (a)



